Babesiosis is considered one of the main vector-borne diseases caused by intraerythrocytic parasites, just behind malaria disease whose etiological agent is transmitted by mosquitoes.
- Babesia spp.
- ticks
- detection
- babesiosis
1. Introduction
Ticks and tick-borne diseases are one of the main medical, veterinary and economic problems worldwide. Ticks are ectoparasites with blood-sucking habits and high vector capacity, and parasitize amphibians, birds, mammals and reptiles. In addition to the damage caused per se due to blood intake, injection of toxins and skin damage due to the bite, ticks can transmit several pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa and rickettsiae [1,2][1][2]. Currently, more than 900 species of ticks have been described worldwide, divided into four families: Argasidae, Ixodidae, Nuttalliellidae and Deinocrotonidae. The Ixodidae family represents around 700 tick species, several members of these family belonging to the genera Dermacentor, Haemaphysalis, Hyalomma, Ixodes and Rhipicephalus, and can transmit the pathogens causative of babesiosis disease [3,4,5][3][4][5].
Babesiosis is considered one of the main vector-borne diseases caused by intraerythrocytic parasites, just behind malaria disease whose etiological agent is transmitted by mosquitoes [6]. The vast distribution of Babesia parasites that affect domestic animals, in addition to the great economic losses due to the presence of babesiosis in tropical and subtropical regions of the world and joined to the zoonotic capacity of some Babesia spp., have made babesiosis a disease of public health and veterinary importance [7,8,9][7][8][9]. Babesiosis disease is caused by an intraerythrocytic protozoan parasite of the genus Babesia, belonging to the order Piroplasmidae and the phylum Apicomplexa. Babesia parasites infect red blood cells of humans, domestic and wildlife animals, and recently, have been reported in birds [6,8,10][6][8][10]. The first report about Babesia spp. was made by Victor Babes in 1888, when he discovered the parasite in the red blood cells of cattle and associated it as the cause of hemoglobinuria or red water fever in Romanian cattle [11], he also found this microorganism in erythrocytes of sheep affected by a disease called Carceag [12]. Later, Smith and Kilborne in the USA demonstrated for the first time that Boophilus annulatus ticks (now reclassified as Rhipicephalus annulatus) were the vectors responsible for transmitting “Texas Fever” disease (bovine babesiosis) [13]. Skrabalo and Deanovic [14] [14] reported the first case of human babesiosis in a splenectomized young man in Yugoslavia; while in 1970, in the United States, a middle-aged woman with intact spleen and previously reported as healthy, presented B. microti-like parasites in the erythrocytes [15]. Since then, several cases in humans have been reported in Asia, Africa, Australia, Europe, and mainly, in the USA [16]. At present, more than 100 different Babesia species have been recognized around the world, parasitizing various mammals and birds, nevertheless this number is increasing due to new research in other possible vertebrate hosts. Previously, Babesia parasites had been taxonomically classified according to their phenotypic and lifecycle characteristics, but recently, molecular phylogeny studies using the 18S rRNA gene have helped to reclassify Babesia species in a more comprehensive way, including the Babesia parasites in two large groups: Babesia sensu stricto and Babesia sensu lato [6,17,18][6][17][18].
The lifecycle of Babesia spp. (Figure 1) takes place in ticks and vertebrates, where it reproduces sexually and asexually respectively, and includes a merogony, gamogony and sporogony phase [19]. The cycle begins when the infected tick feeds on the vertebrate host and at the same time, inoculates saliva infected with sporozoites, the infective phase of Babesia. Sporozoites travel through the bloodstream and penetrate the red blood cells. Later, the hemoparasite becomes a trophozoite, taking a ring shape: trophozoites divide by binary fission (merogony phase) in two or more merozoites (it depends on Babesia species), while merozoites lyse the erythrocyte and again invade a new erythrocyte. Gamogony begins in the vertebrate host where mature merozoites turn into pre-gametocytes. When ticks suck blood, healthy and parasitized (with the different stages of Babesia) erythrocytes are ingested equally, but only pre-gametocytes survive and develop into gametocytes (beginning the sexual phase) [20,21,22][20][21][22]. In the tick gut lumen, gametocytes become gametes, also known as Strahlenkörper or spiky-rayed bodies. The gametes fuse to form an ookinete (motile zygote), the ookinete arrowhead helps them to penetrate tick gut cells, where a meiotic division occurs giving rise to a new cell, the kinete. Kinetes travel through hemolymph and invade tick tissues, including the ovaries in adult female ticks and tick embryos (transovarial transmission); at the same time, kinetes disseminate to the salivary gland, where they develop into sporoblasts [17,20,22][17][20][22]. These new cells remain inactive in the cytoplasm of the salivary gland cells until the next tick generation or the next tick stage (after molting) attaches on a mammalian host, allowing transstadial transmission. Sporoblasts present in salivary glands produce 5000–10,000 infective sporozoites by a single alveolus during the sporogony phase and are finally released to the mammalian bloodstream [19], repeating the cycle. It is important to note that transovarial transmission does not occur in Babesia sensu lato species, while transstadial transmission occurs in Babesia sensu lato and Babesia sensu stricto. In addition, not all the tick stages can transmit the parasites, each Babesia species needs a specific time for sporoblast maturation [21]. On the other hand, the tick life stage while feeding on the mammal is not an impediment for it to acquire the parasite and, in some cases, the parasite multiplication can occur [22].
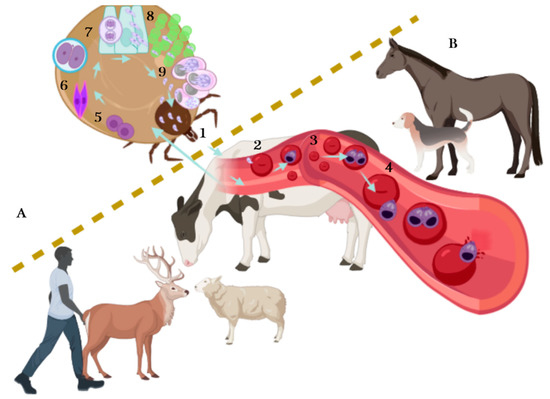
Figure 1. The lifecycle of Babesia spp. The lifecycle takes place in ticks (A) and vertebrates (B). Asexual reproduction is carried out in vertebrates: it begins when the infected tick feeds on the host and inoculates the infective phase of Babesia, the sporozoites (1). Sporozoites travel through bloodstream and invade red blood cells (RBCs) (2); once inside the RBCs, sporozoites become a trophozoite (3). Later, the merogony phase occurs, resulting in two or more merozoites (4), merozoites lyse the infected RCBs and continue invading new RBCs—some merozoites mature and turn into pre-gametocytes (beginning the gamogony phase). When ticks suck blood, healthy and parasitized RBCs are ingested, the pre-gametocytes present in RBCs develop into extracellular gametocytes (5), there is a fusion of male and female gametocytes and the ookinete is formed (6). The ookinete, also known as motile zygote, invades the intestinal cells of the tick helped by its arrowhead (7), and a meiotic division occurs giving rise to the kinetes. Kinetes travel through hemolymph and invade other tick tissues including ovaries and embryos in adult female ticks (8) and disseminate to salivary glands, where they develop into sporoblasts. The sporoblast remains inactive in salivary glands until it transforms into sporozoites (sporogony phase) (9), repeating the cycle when sporozoites are newly released to the mammalian bloodstream.
Different tests have been designed for the detection of Babesia spp. in its invertebrate and vertebrate host, based on microscopy, molecular and serological techniques, either for direct or indirect detection of the parasite. Babesia parasites can be detected by microscopy visualization in samples such as tick tissues (hemolymph, salivary gland, midgut, etc.) and host blood smears, although its use for clinical diagnosis is only suitable in symptomatic cases during the acute phases of the disease. The main drawback of this technique is the need for a qualified operator to find Babesia parasites due low levels of parasites present in the sample and, besides, who can discern between species. Molecular tools have shown high values of specificity and sensitivity, mainly PCR assays in its different formats such as conventional, hemi-nested and nested PCR. These assays are commonly followed by sequencing of PCR products obtained by sequence analysis, and most recently, by phylogenetic analysis. Other variants frequently used for this assay are PCR-RFLP, qPCR and RT-PCR. The LAMP and RAP assays are detection methods also based on the molecular identification and have been implemented to Babesia detection, but mostly in its invertebrate host. Whereas, the serological methods implemented in vertebrate hosts include: Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Test (IFAT), Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), Complement Fixation Test (CFT) and Immunochromatography Test (ICT) [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30].
The identification of Babesia in its vector tick is necessary to acquire more knowledge on the host–Babesia–vector interactions. Additionally, the detection of Babesia parasites is required to determine the prevalence of these protozoa in the different tick species and tick stages, helping to know the transmission capacity of Babesia parasites, either during the transstadial or the transovarial transmission development. Likewise, planning and development of epidemiological surveys that allow to identify the probability of babesiosis outbreaks will in turn serve to perform successful strategies to prevent and control the pathogens and the diseases they cause. Recently, some Babesia species have been identified in ticks other than those commonly known as being its main vector; furthermore, recent climate change is a new factor to be considered for monitoring ticks, due to the presence of ticks in regions previously reported as tick-free, increasing the possibility for tick-borne disease outbreaks, including babesiosis.
2. Detection Methods for Babesia Identification
Several detection methods are used for Babesia spp. identification in ticks, these include mainly molecular and microscopical tools. For the detection of Babesia parasites DNA in the various tick species and different tick stages, several authors have decided to pool various amounts of eggs, larvae or nymphs, and even adult ticks (male or female), and then take the pools as a single sample. In general, pooled ticks either belong to the progeny of the same adult female or are collected from the same animal during sampling. Pooling is recommended to obtain a greater quantity of DNA that would allow the identification of Babesia DNA. Whereas, for the microscopic detection with the hemolymph test, only the hemolymph present in one of the tick legs is utilized to search for kinetes, although the presence of kinetes can also be determined in tick egg masses. The Babesia parasites considered in this review will be approached based on the host mammal they infect and according to the detection methods used. In Table 1, the different Babesia species are tabulated according to their principal tick-vectors, regarding their geographical distribution and the detection methods utilized for its identification in tick samples. Additionally, the primers sequences used in the cited studies are summarized in Table 2, along with the identification of the target genes and the expected amplicon lengths.
Table 1. Overview of Babesia species detected in Ixodidae ticks referenced in this study and the detection methods used.
| Babesia | Species | Main Tick Vectors | Mammal Host | Geographical Distribution | Detection Methods | Tick Stage Evaluated | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. bigemina | Rhipicephalus microplus | , |
ND: tick stage was not defined.
Table 2. PCR oligonucleotide sequences used for detection of various Babesia species in the tick-vector reported in different studies. The identity of Babesia parasites amplified with non-specific primers was confirmed through sequence analysis.
| Babesia | Species Detected | PCR Format | Target Gene or Region | Primers Name | Product Size | Primer Sequence | References | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh. decoloratus | , | Rh. annulatus | , | Rh. geigyi, | Rh. evertsi | Cattle, Water buffalo | Africa, America, Australia | Microscopy, nPCR, PCR, PCR-RFLP, qPCR | Adult, nymphs, larvae, eggs. Hemolymph and eggs | ||||||||||
| B. bigemina | and | B. bovis | nPCR | SpeI | - | AvaI | rap-1 | BiIA/BiIB BiIAN/BiIBN BoF/BoR BoFN/BoRN |
278 bp 170 bp 356 bp 291 bp |
5′-CATCTAATTTCTCTCCATACCCCTCC-3′ 5′-CCTCGGCTTCAACTCTGATGCCAAAG-3′ 5′-CGCAAGCCCAGCACGCCCCGGTGC-3′ 5′-CCGACCTGGATAGGCTGTGTGATG-3′ 5′-CACGAGGAAGGAACTACCGATGTTGA-3′ 5′ CCAAGGAGCTTCAACGTACGAGGTCA 3′ 5′-TCAACAAGGTACTCTATATGGCTACC-3′ 5′-CTACCGAGCAGAACCTTCTTCACCAT-3′ | [34,37,40,41,42,43,45,47,48,49,50,51,52] | ||||||||
| [ | 38 | , | 40 | , | 41 | , | 42 | , | 43 | ] | B. bovis | Rhipicephalus microplus | , | Rh. decoloratus | , | ||||
| B. bovis | Rh. annulatus | , | Rh. geigyi | Cattle, Water buffalo | nPCRAfrica, America, Australia | msa-1 | external forward external reverse internal forwardMicroscopy, nPCR, PCR, PCR-RFLP, qPCR |
Adult, nymphs, larvae, eggs. Hemolymph and eggs |
internal reverse | [34,35 | ND 212 bp | ,36,37,40,41,43,45,47,48,49,50,53] | |||||||
| B. divergens | Ixodes ricinus, I. persulcatus | Cattle | North West Europe, Great Britain, Ireland, and Spain | PCR, PCR-RLB hybridization | Adult, nymphs, (Salivary glands) larvae, eggs. | [55,113] | |||||||||||||
| B. occultans | Hyalomma marginatum | Cattle | Africa | RLB hybridization | B. occultans- | specific probe | Adult | [60] | |||||||||||
| 5′-TTCGACCAGACCAAATTGT-3′ | B. ovata | Haemaphysalis longicornis, Ixodes ovatus | Cattle | China, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, Thailand | PCR | ND | [61] | ||||||||||||
| 5′-CGCATCAAAAGA CTCAACA-3′ | 5′-GCCCTGATCTATTTAATGCA-3′ | 5′-CCCCGTATAAACATGCTTC-3′ | [ | 35 | , | 36 | ] | ||||||||||||
| B. bovis | qRT-PCR | msa-1 | Forward/reverse Probe |
150 bp | 5′-GATGCGTTTGCACATGCTAAG-3′ 5′-TGAGAGCACCGAAGTACCCG-3′ 5′-CACGCTCAAGTAGGAAATTTTGTTAAACCTGGA-3′ |
[ | 35 | , | 36 | ] | nPCR | rap-1 | BoF/BoR BoFN/BoRN |
354 bp 291 bp |
5′-CACGAGGAAGGAACTACCGATGTTGA-3′ 5′ CCAAGGAGCTTCAACGTACGAGGTCA 3′ 5′-TCAACAAGGTACTCTATATGGCTACC-3′ 5′-CTACCGAGCAGAACCTTCTTCACCAT-3′ |
[ | 53 | ] | |
| B. bigemina | and | B. bovis | nPCR | 18S rRNA | KB-16/KB-17 KB-18/KB-19 KB-24/KB-25 |
ND 262 bp 217 bp |
5′-CATCAGCTTGACGGTAGGG-3′ 5′-GTCCTTGGCAAATGCTTTC-3′ 5′-GATGTACAACCTCACCAGAGTACC-3′ 5′-CAACAAAATAGAACCAAGGTCCTAC-3′ 5′-GGGGGCGACCTTCAC-3′ 5′-CTCAATTATACAGGCGAAAC-3′ |
[ | 44 | ] | B. canis | Dermacentor reticulatus | Dogs | Asia and Europe | PCR, real-time PCR-based assay, qPCR, PCR-RLB hybridization, | B. canis | -specific probe | Adult | [69 |
| B. bigemina | and | B. bovis | , | 75 | , | 85,86,87,88,89, | PCR | 90 | ssrDNA | A/B C/B | , | 118 bp 225 bp | 91,93] | ||||||
| 5′-TGTCCTCGTTTGCTTCTTAGAGGGACTCCT-3′ | 5′-CCGACACGATGCACACTAAACATTACCCAA-3′ | 5′-TTGGCATGGGGGCGACCTTCACCCTCGCCC-3′ | 5′-CCAAAGTCAACCAACGGTACGACAGGGTCA-3′ |
[ | 45 | ] | B. vogeli | Haemaphysalis | spp., | Rhipicephalus sanguineus, | Rh. turanicus, Rh. haemaphysaloides | Dogs | Africa, Asia, Australia, North and South America, Europe | PCR-RFLP, semi-nested PCR, PCR, nPCR, PCR-RLB hybridization, real-time PCR-based assay, Multiplex PCR | Adult, nymphs, larvae, males, and unfed females | [70,71,73,74,78,79,81,82, | |||
| B. bigemina | 83 | , | 84 | , | 91 | ] | |||||||||||||
| qPCR | 18S rDNA | RTBbF/RTBbR | ND | 5′- AGCTTGCTTTCACAACTCGCC -3′ | 5′- TTGGTGCTTTGACCGACGACAT -3′ |
[ | 51 | ] | B. gibsoni | Haemaphysalis | spp., | Rh. sanguineus, Rh. turanicus, Ixodes ricinus | Dogs | Africa, America, Asia, Australia, Europe | PCR, nPCR, PCR-RLB hybridization, Multiplex PCR | Adult, nymphs, larvae | |||
| B. bigemina | qPCR | 18S rDNA | [ | Forward/reverse | 73 | , | ND | 74 | 5′- AATAACAATACAGGGCTTTCGTCT -3′ 5′- AACGCGAGGCTGAAATACAACT -3′ | ,77,78,84] | |||||||||
| [ | 52 | ] | B. venatorum | Ixodes ricinus, I. persulcatus | Adult, larvae | ||||||||||||||
| B. bovis | , and | B. bigemina | PCR-RFLPDogs, Roe deer, Red deer, Fallow deer, Moose, White-tailed deer, European reindeer | Canada, China, Europe, Mongolia and USA | PCR, microfluidic real-time PCR, PCR-RLB hybridization | 18S rDNA | PiroA/Piro B RE: | Msp | I | Box | I | 400 bp | [77, | ||||||
| B. bovis | 250, 150 bp 290, 110 bp | 93 | , | 98 | , | 99,101,113] | |||||||||||||
| 5′-AATACCCAATCCTGACACAGGG-3′ | 5′-TTAAATACGAATGCCCCCAAC-3′ | [ | 47 | ] | B. odocoilei | ||||||||||||||
| B. bigemina | Ixodes scapularis | and | B. bovis | White-tailed deer | Canada, USA | qPCR | mitochondrialcytochrome b | Cbisg 1 and 2semi-nested PCR | Adult, Larvae |
Cbosg 1 and 2 | 88 bp 88 bp |
5′-TGTTCCAGGAGATGTTGATTC-3′ 5′-AGCATGGAAATAACGAAGTGC-3 5′-TGTTCCTGGAAGCGTTGATTC-3′ 5′-AGCGTGAAAATAACGCATTGC-3′ | [100] | ||||||
| [ | 49 | , | 50 | ] | B. caballi | Dermacentor | spp., | D. nuttalli, D. nitens, Hyalomma marginatus | , | H. truncatum | , | Otobius megnini | Horses, Donkeys, Mules and Zebras | Africa, America, Asia, Europe | |||||
| B. divergens | nPCR | Adult | [ | 105 | , | PCR | 106] | ||||||||||||
| 18S rRNA | BAB GF2/GR2 | 559 bp | 5′-GYYTTGTAATTGGAATGATGG-3′ | 5′-CCAAAGACTTTGATTTCTCTC-3′ | [ | 55 | ] | B. microti | Ixodes scapularis, I. ricinus | White-footed mouse, Humans | United States, Europe | PCR-RLB hybridization, nPCR, RT-PCR, in vitro culture-PCR |
Adult females, Nymphs | [ | |||||
| Bovine Babesia | spp. | PCR | 18S rRNA | ND | 422–440 bp | 5′-GTTTCTGMCCCATCAGCTTGAC-3′ 5′-CAAGACAAAAGTCTGCTTGAAAC-3′ | 113,114,115,118] | ||||||||||||
| [ | 56 | ] | B. motasi | Rhipicephalus bursa, Haemaphysalis longicornis, H. punctata | , | Goats, Sheep | Korea | Microscopy, PCR | |||||||||||
| B. divergens | ND | PCR | 18S rRNA | ND | 353 bp | [114 | 5′-GTTTCTGMCCCATCAGCTTGAC-3′ | ,129] | |||||||||||
| 5′-CAATATTAACACCACGCAAAAATTC-3′ | [ | 56 | ] | B. duncani | Dermacentor albipictus | Mule deer | United States | ||||||||||||
| Babesia | sp. | genotype EU1 | nPCR, PCR | Adult, larvae | [ | 116] | |||||||||||||
| PCR | 18S rRNA | ND | 362 bp | 5′-GTTTCTGMCCCATCAGCTTGAC-3′ | 5′-AGACAAGAGTCAATAACTCGATAAC-3′ |
[ | 56 | ] | B. ovis | Rhipicephalus bursa | Goats, Sheep | Iran | Microscopy, PCR-RLB, qPCR, PCR | Adult, eggs, larvae | [124,125,128,129,131,133,134] |
| B. orientalis | ||||||||||||||||
| Semi-nested PCR | ||||||||||||||||
| 18S rRNA | ||||||||||||||||
| P1/B-R2 | ||||||||||||||||
| B-P2/B-R2 | ||||||||||||||||
| ND | ||||||||||||||||
| 257 bp | ||||||||||||||||
| 5′-AACCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGTAGT-3′ | 5′-CACACGCACAACGCTGAA-3′ | 5′-TGAGAAACGGCTACCACA-3′ | 5′-CACACGCACAACGCTGAA-3′ |
[ | 57 | ] | ||||||||||
| B. occultans | PCR/RLB hybridization | 18S rRNA (V4 variable region) |
RLB-F2/RLB-R2 Probe |
460 bp | 5′-GACACAGGGAGGTAGTGACAAG-3′ 5′-biotin-CTAAGAATTTCACCTCTGACAGT-3′ 5′-GTGTGCCTCTTTTGGCCCATC-3′ Species-specific containing a C12 amino linker in 5′ |
[ | 60 | ] | ||||||||
| B. ovata | PCR | β-tubulin | ND | ND | 5′-ACACTGTGCATCCTCACCGTCATAT-3′ 5′-CTCGCGGATCTTGCTGATCAGCAGA-3′ |
[ | 61 | ] | ||||||||
| B. vogeli | PCR-RFLP | 18S rRNA | PiroA/PiroB RE: | TaqI | 400 bp 203, 171, 26 bp |
5′-AATACCCAATCCTGACACAGGG-3′ 5′-TTAAATACGAATGCCCCCACC-3′ |
[ | 46 | , | 70 | , | 83 | ] | |||
| B. vogeli | Semi-nested PCR | 18S rRNA | 455-459/793-772 BCV/793-772 |
339 bp 192 bp |
5′-GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATGGTGAC-3′ 5′-ATGCCCCCAACCGTTCCTATTA-3 5′-GTTCGAGTTTGCCATTCGTT-3′ 5′- ATGCCCCCAACCGTTCCTATTA-3′ |
[ | 68 | , | 70 | ] | ||||||
| B. vogeli | PCR | 18S rRNA | BCV-F/Ba721R | 422 bp | 5′- GTGTTCGAGTTTGCCATTCG-3′ 5′-CCCAGAACCCAAAGACTTTGATTTCTCTCAAG-3′ |
[ | 79 | ] | ||||||||
| B. vogeli | PCR-RFLP | 18S rRNA | BJ1/BN2 RE: | ApoI | 489 bp 367, 122 bp |
5′-GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATGG-3′ 5′-TAGTTTATGGTTAGGACTACG-3′ |
[ | 71 | ] | |||||||
| B. vogeli and B. canis | PCR | cox | 1 | BFor/BvRev/BcRev | 450 bp 750 bp |
5′-GCATCTGGAATAGCTAGTGC-3′ 5′-CTGCTTCTAAACCAGAAGTG-3′ 5′-TGGAAATGACCTACAACATAC-3′ |
[ | 75 | ] | |||||||
| B. gibsoni | PCR | 18S rRNA | PiroA/PiroB | 408 bp | 5′-AATACCCAATCCTGACACAGGG-3′ 5′-TTAAATACGAATGCCCCCACC-3′ |
[ | 77 | ] | ||||||||
| B. gibsoni | and | B. vogeli | nPCR (non-specific) |
18S ssrRNA | 5-22F/1661R 455-479F/793-722R (generic primers) |
293–338 bp | 5′-GTTGATCCTGCCAGTAGT-3′ 5′-AACCTTGTTACGACTTCTC-3′ 5′-GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATGGTGAC-3′ 5′-ATGCCCCCAACCGTTCCTATTA-3′ |
[ | 78 | ] | ||||||
| B. gibsoni | , | B. vogeli, B. canis | PCR/RLB hybridization | 18S rRNA (V4 variable region) |
RLB-F2/RLB-R2 Probes |
460 bp | 5′-GACACAGGGAGGTAGTGACAAG-3′ 5′-biotin-CTAAGAATTTCACCTCTGACAGT-3′ Oligonucleotides probes (species-specific) linked to N-terminal N-(trifluoracetamidohexyl-cyanoethyl, N, N-diisopropyl phosphoramidite [TFA])-C6 amino |
[ | 81 | , | 82 | , | 84 | , | 86 | ] |
| B. gibsoni | and | B. vogeli | Multiplex PCR | 18S rRNA | BAGI F/BAGI R BAB1 F/BAB4 R |
590 bp 488 bp |
5′- TTGGCGGCGTTTATTAGTTC-3′ 5′- AAAGGGGAAAACCCCAAAAG-3′ 5′- GTGAACCTTATCACTTAAAGG-3′ 5′- CAACTCCTCCAC GCAATCG-3′ |
[ | 73 | , | 74 | ] | ||||
| B. canis | PCR | 18S rRNA | BcW-A/BcW-B | 500 bp | 5′-CATCTAAGGAAGGCAGCAGG-3′ 5′- TTAATGGAAACGTCCTTGGC-3′ |
[ | 87 | ] | ||||||||
| B. canis | PCR | 18S rRNA | PiroA/PiroB | 408 bp | 5′-AATACCCAATCCTGACACAGGG-3′ 5′-TTAAATACGAATGCCCCCACC-3′ |
[ | 69 | ] | ||||||||
| B. canis | PCR (non-specific) |
18S rRNA | BJ1/BN2 (generic primers) |
ND | 5′-GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATGG-3′ 5′-TAGTTTATGGTTAGGACTACG-3′ |
[ | 72 | , | 88 | , | 89 | , | 90 | ] | ||
| B. canis | PCR nPCR |
18S rRNA | BS1/PiroC PiroA/PiroC |
ND | 5′-GACGGTAGGGTATTGGCCT-3′ 5′-CCAACAAAATAGAACCAAAGTCCTAC-3′ 5′-ATTACCCAATCCTGACACAGGG- 3′ 5′-CCAACAAAATAGAACCAAAGTCCTAC-3′ |
[ | 92 | , | 93 | ] | ||||||
| B. venatorum | PCR (non-specific) |
18S rRNA | BJ1/BN2 (generic primers) |
411–452 bp | 5′-GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATGG-3′ 5′-TAGTTTATGGTTAGGACTACG-3′ |
[ | 72 | , | 98 | , | 99 | ] | ||||
| B. odocoilei | Semi-nested PCR | 18S rDNA | Piro_18S_300F/Piro_18S_1688R Cocci_18S_595F/Piro_18S_1688R |
1393 bp 1147 bp |
5′-GACGGTAGGGTATTGGCCTA-3′ 5′-CGACTTCTCCTTCCTTTAAGTGATAAG-3′ 5′-CCGCGGTAATTCCAGCTCCAAT-3′ 5′-CGACTTCTCCTTCCTTTAAGTGATAAG-3′ |
[ | 100 | ] | ||||||||
| B. caballi | nPCR | BC48 | BC48F1/BC48R3 BC48F11/BC48R31 |
530 bp 430 bp |
5′-ACGAATTCCCACAACAGCCGTGTT-3′ 5′-ACGATTTCGTAAAGCGTGGCCATG-3′ 5′-GGGCGACGTGACTAAGACATG-3′ 5′-GTTCTCAATGTCAGTGACATCCGC-3′ |
[ | 105 | , | 106 | ] | ||||||
| B. caballi | PCR/RLB hybridization | 18S rRNA (hypervariable V4 region) | RLB-F2/RLB-R2 Genotypes A Genotypes B |
ND | 5′-GACACAGGGAGGTAGTGACAAG-3′ biotin-5′-CTAAGAATTTCACCTCTGACAGT-3′ 5′-GTTGCGTTGTTCTTGCTTTTTGCTT-3′ 5′-CGGGTTATTGACTTCGCTTTTTCTT-3′ |
[ | 109 | ] | ||||||||
| B. divergens/B. venatorum/B. microti | PCR/RLB hybridization | 18S rRNA | Bath-F/Bath-R (generic primers) |
ND | 5′-TAAGAATTTCACCTCTGACAGTTA-3′ 5′-ACACAGGGAGGTAGTGACAAG-3′ |
[ | 113 | ] | ||||||||
| B. motasi | PCR (non-specific) |
18S rRNA | BTH 1F/BTH 1R GF2F/GR2R (generic primers) |
561 bp | 5′-CCTGAGAAACGGCTACCACATCT-3′ 5′-TTGCGACCATACTCCCCCCA-3′ 5′-GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATG-3′ 5′-CCAAAGACTTTGATTTCTCTC-3′ |
[ | 114 | ] | ||||||||
| B. motasi | PCR (non-specific) |
Cytochrome b ( | COB | ) | COB F/COB R (generic primers) | 550 bp | 5′-CCATAGCAATTAATCCAGCTA-3′ 5′-ACCTTGGTCATGGTATTCTGG-3′ |
[ | 114 | ] | ||||||
| B. motasi | PCR (non-specific) |
Cytochrome c ( | COX-3 | ) | COX3 F/COX3 R (generic primers) | 552 bp | 5′-TCAACAAAATGCCAATATGT-3′ 5′-AAGTGCATCTTTGGGAGAAG-3′ |
[ | 114 | ] | ||||||
| B. microti | nPCR | β | -tubulin | Tubu93 F/Tubu897 R Tubu192 F/Tubu782 R |
551 bp | 5′-GAYAGYCCCTTRCAACTAGAAAGAGC-3′ 5′-CGRTCGAACGAACATTTGTTGHGTCARTTC-3′ 5′-ACHATGGATTCTGTTAGATCYGGC-3′ 5′-GGGAADGGDATRAGATTCACAGC-3′ |
[ | 114 | ] | |||||||
| B. microti | RT-PCR | 18S rRNA | ND Probe |
ND | 5′-AACAGGCATTCGCCTTGAAT-3′ 5′-CCAACTGCTCCTATTAACCATTACTCT-3′ 6FAM-CTACAGCATGGAATAATGA-MGBNFQ |
[ | 115 | ] | ||||||||
| B. duncani | nPCR | β-tubulin | F34/R323 BtubFn/BtubRn |
ND 175–181 bp |
5′-TGTGGTAACCAGATYGGWGCCAA-3′ 5′-TCNGTRTARTGNCCYTTRGCCCA-3′ 5′-TCWGACGAGCACGGCATYGA-3′ 5′-CCAGGCTCCAARTCCATYAA-3′ |
[ | 116 | ] | ||||||||
| B. ovis | PCR | ssrRNA | Bbo-F/Bbo-R | 549 bp | 5′-TGGGCAGGACCTTGGTTGTTCT-3′ 5′-CCGCGTAGCGCCGGCTAAATA-3′ |
[ | 124 | , | 130 | ] | ||||||
| B. ovis | qPCR (non-specific) | 18S | Bab_18s_F/Bab_18s_R Bab_18s_P |
ND | 5′-TTGGGGGCATTCGTANTNRAC-3′ 5′-TTCTTGATTAATGAAAACGTCTTG-3′ 6FAM-AAGACGAACTACTGCGAAAGCATTTGC-TAMRA |
[ | 131 | ] | ||||||||
| B. ovis | PCR (non-specific) | 18S rRNA | CRYPTOF/CRYPTOR | ND | 5′-AACCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGT-3′ 5′-GCTTGATCCTTCTGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3′ |
[ | 131 | , | 132 | ] | ||||||
| B. ovis | PCR qPCR |
BoSPD BoSPD |
SDP forward/SDP reverse SDP forward/SDP reverse |
486 bp 141 bp |
5′-ATGTTGGCCAAGTATCTTGCC-3′ 5′-CTACGTCAATTTGGCCTTGAACTC-3′ 5′-TAATGACGCAGACCTGATGG-3′ 5′-GTTTGATCACCCTCGGAAAC-3′ |
[ | 125 | , | 133 | , | 134 | ] |
ND: data not defined; RE: Restriction enzyme.
2.1. Bovine Babesiosis
The main Babesia species that have been reported as the causative agents of bovine babesiosis are Babesia bovis, B. bigemina and B. divergens (Table 1), these species elicit several important clinical signs and, in some cases, can cause death in cattle because of an inadequate diagnosis and timely treatment. Also, B. divergens is a hemoparasite of zoonotic importance. In addition to parasitizing cattle, Babesia bovis and B. bigemina can also be found in water buffalo, serving these as a reservoir, but they do not develop the clinical disease [7]. Other Babesia species with lower pathogenicity have been identified in cattle, such as B. ovata found in Asian cattle populations, which can cause severe anemia in immunosuppressed animals, hence the importance of its detection, as well as B. major, B. orientalis and B. occultans that can infect cattle [31] [31] (Table 1). Bovine babesiosis is widely distributed in the world with a global prevalence of 29%, with the highest prevalence present in South America, where Babesia bigemina is the most commonly found parasite [32,33][32][33]. Overview of Babesia species detected in Ixodidae ticks referenced in this study and the detection methods used is shown in Table 1 [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134].
2.1.1. Microscopy Tools
The detection of Babesia parasites can be accomplished by microscopical examination of hemolymph and eggs squashes obtained from engorged adult female ticks collected from infected animals [23,33][23][33]. In a study conducted in calves and cows in an endemic zone of Rh. microplus in Brazil, it was possible to correlate the quantity of kinetes present in hemolymph smears from adult engorged female ticks with the progeny larval hatching rate. After the female ticks laid their eggs on the 15th day, a leg of each adult female tick was sectioned and a hemolymph smear was made. The egg smears were made by crushing 100 eggs derived from a single female tick, while another 100 eggs were incubated to determinate the hatching rate. Results showed that for each kinete found in the hemolymph smear, the hatching rate decrease by 0.57%. Also, authors found that the Babesia frequency in hemolymph and eggs was higher in ticks collected from calves than in ticks collected from cows [34]. The efficiency of tick acquisition and transovarial transmission of B. bovis was assessed by light microscopy examination of hemolymph samples [35,36][35][36]. It was found that bovine blood with high parasite levels in acutely infected animals is directly related to high kinete levels found in replete females following acquisition feeding. There was a positive correlation between the highest parasite levels in the blood and the percentage of engorged females containing high levels of kinetes in hemolymph samples [35]. However, female ticks that fed to repletion on persistently infected calves did not show detectable kinetes by light microscopy. Even though there were no parasites detected by light microscopy in tail capillary smears from persistently infected calves during female tick acquisition, female ticks can acquire the parasite and pass it trans-ovarially to larval offspring [36][35].
In another study conducted on B. bigemina infecting various genetic groups of cattle, Babesia spp. kinetes were found in the hemolymph obtained from Rh. microplus female ticks that engorged on calves. Regardless of the genetic group of the tick-infested cattle, a range of 0.13–3.2 kinetes per microscopic field was observed [37]. It is important to point out that in the studies conducted by Oliveira et al., the identification of Babesia species (either B. bigemina or B. bovis) was not achieved, due to the difficulty represented by the microscopic identification of Babesia kinetes. It has been established that the usefulness of assessing the gross morphological features to differentiate Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina kinetes in a hemolymph sample from engorged female ticks is dubious [33]. In addition, it was demonstrated that tick hemolymph infection is sometimes undetectable by light microscopy examination, but transmission to larval progeny occurs as demonstrated in a tick larvae-infested bovine [36]. The difficulty to define Babesia species based on kinete morphology determined in hemolymph samples from engorged female R. microplus ticks infected with B. bovis or B. bigemina can be better exemplified in Figure 2. Therefore, nowadays, it is imperative to apply the overly sensitive molecular tools currently available in these types of studies to determine, besides the species, the vector competence for single or dual Babesia infection in ticks.
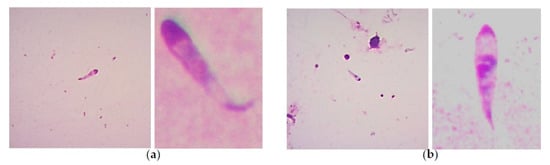
Figure 2. Giemsa-stained smears showing examples of bovine Babesia spp. kinetes found in tick hemolymph samples of Rh. microplus engorged females: (a) B. bovis kinetes can present a curved or semi-curved tail, but this is not always the case, with an anterior position nucleus (that generally could be found at the middle of the cells) that can have a mean length of 14.30 ± 0.922 μm and a mean width of 3.33 ± 0.315 μm. (b) B. bigemina kinetes show a straight tail and a median nucleus position, and present a smaller size to B. bovis kinetes (mean length of 11.27 ± 0.900 and width of 2.24 ± 0.287 μm). Kinetes size of both species can have variations depending on the strains examined and the geographic origin, added to the fact that B. bovis curved tail it is not always present, that makes the standardizations of the criteria difficult to be followed for microscopic identification.
2.1.2. Molecular Tools
The molecular identification of B. bovis and B. bigemina through nested-PCR is one of the main utilized techniques, due to the high sensibility and specificity achieved. In several studies, the primers designed for the amplification of the SpeI-AvaI restriction fragment for B. bigemina (BiIA/BiIB and BiIAN/BiIBN) and for the amplification of a B. bovis gene encoding a 60 kDa merozoite surface protein (BoF/BoR and BoFN/BoRN) have been successfully used in the past for detection of both parasite species in tick samples (Table 2). These nPCR assays were originally designed to identify Babesia parasites in red blood cells, however, several studies have found their utility for B. bovis and B. bigemina detection on samples derived from adult, eggs and larvae tick stages [38,39][38][39]. The first study carried out to detect B. bigemina and B. bovis in adult ticks by PCR using the primers described above was published in the year 2000 [40]. The authors found relatively high infection rates in collected ticks: the 5% B. bigemina infection rate in B. decoloratus allowed to oviposit before PCR analysis, whereas 60% were positive with primers for B. bovis. Similarly, in B. microplus allowed to oviposit, 69% were positive for B. bovis DNA and 12% were positive for B. bigemina [40]. Next, a molecular epidemiological study evaluating the nPCR assays mentioned previously was conducted in Brazil, where the authors identified higher Babesia positivity in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks collected from calves than in ticks removed from cows, as well as a higher percentage of B. bigemina-infected ticks as compared to the B. bovis-infected ticks. In addition, the eggs oviposited by the collected ticks were also evaluated, and similarly, B. bigemina showed a higher presence in eggs derived from the ticks present in calves, whereas the infection rate was low for both parasites in ticks derived from cows. Of note is that DNA extraction was made from 20 mg of eggs out of every single tick collected. Despite the high sensitivity shown by nPCR, the authors reported a false-negative host vertebrate sample, since they found ticks positive for B. bovis or B. bigemina but derived from nPCR-negative animals to the corresponding species [41]. In another study, PCR based on primers BiIA/BiIB and BiIAN/BiIBN has been used in India to determine the B. bigemina molecular prevalence in egg masses and unfed larvae from Rh. microplus ticks (Table 2). For both types of samples, a pull of 100 eggs/larvae derived from the same progeny were used for DNA extraction. In that study, nPCR was compared to conventional PCR and microscopy detection from hemolymph and squashed egg samples. Results showed a higher number of positive samples when nPCR was used, proving the suitability of nPCR to identify B. bigemina-infected ticks [42]. The same four pairs of primers were used in malaria-endemic regions of Colombia to detect babesiosis prevalence in humans, cattle and ticks that parasitized them, finding 18.5% of Babesia-infected ticks, out of which 73.3% were infected with B. bigemina and 16.7% with B. bovis [43]. The 18S ribosomal RNA gene has also been utilized as a target sequence to detect Babesia bigemina and B. bovis presences in the vector tick (Table 2). Guerrero et al. [44] used a PCR assay to detect the causal agent of bovine babesiosis outbreaks in Texas. To accomplish this, several tick strains taken from sick cattle were evaluated, along with Mexican and Brazilian tick strains. The assay sensitivity achieved with the PCR assay allowed detection of the equivalent of a single infected larva with both Babesia species, but only B. bigemina-positive R. microplus ticks were found.
A nPCR assay with primers specific to msa-1 gene (Table 2) was developed to detect B. bovis DNA in R. microplus hemolymph samples with no kinetes detectable by light microscopy [35]. With the high analytical sensitivity reported for the nPCR (from 1 to 10 parasites), hemolymph samples collected from female ticks between 7- and 10-days post-repletion were analyzed. Out of a total of 62 females with no kinetes detectable by light microscopy, 32 were determined positive by nPCR with primers amplifying msa-1. Most importantly, it was found that larvae derived from replete females with exceptionally low levels of kinete infection, as demonstrated by light microscopy and nPCR, had infection rates from 22% up to 40% and transmitted B. bovis during transmission feeding experiments [35]. Thus, the differences in analytical sensitivity and specificity of the nPCR assay may account for the higher tick infection rates determined in that study. In addition, a real-time PCR assay performed on individual larvae from females having hemolymph samples with >10 kinetes per microscopic field showed levels ranging from 4.8 × 101 to 1.2 × 105 parasites per tick on day 3 of feeding in a recipient susceptible calf (Table 2).
A second study carried out utilizing spleen-intact, persistently infected calves with B. bovis, having lower parasite levels in peripheral blood, resulted in lower kinete levels in replete females and subsequently lower larval infection rates (0% to 20%), as estimated by using the nPCR assay [36]. Larvae tested by real-time PCR after 3 days of transmission feeding had parasite levels ranging from 2.4 × 102 to 1.9 × 105, values comparable to those found in the previous study, in which groups of larvae were derived from females harboring elevated levels of kinetes in their hemolymph [35]. The results showed that females fed on persistent carriers, despite low blood parasite levels, can acquire the parasite and pass it transovarially to larval offspring, which in turn are capable of transmitting B. bovis to a susceptible host [36].
In Egypt, prevalence determination of B. bigemina and B. bovis in Rhipicephalus annulatus (adult and nymph) ticks was achieved using a PCR assay [45]. To amplify the small subunit rDNA genes of each Babesia species, previously reported primers were implemented (Table 2). DNA samples used were obtained by pooling 2 to 4 nymphs, while adult ticks were utilized individually. Results showed 55% of B. bovis-infected ticks, 66% infected with B. bigemina and 12% infected with both parasite species. To confirm the authentication of the amplified PCR products, the amplicons were sequenced, and derived DNA sequences were submitted to a BLASTN homology search. B. bovis samples showed a high similarity with rDNA sequences of several Mexican isolates and one isolate from Israel, while B. bigemina samples had 100% sequence identity with the Spain isolate [45].
A different format of the PCR assay based in enzymatic digestion of PCR products to detect Babesia bovis and B. bigemina in its vector, the Rh. microplus tick, was carried out in Mexico [46]. The PCR-RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism) can identify both parasites at the same time, due to the amplification of a variable portion of the 18S rDNA gene, by using the Piro A/Piro B oligonucleotides designed to amplify different Babesia species [46]. After amplification, PCR products (400 bp) were digested with the restriction enzymes Box I and Msp I, that only recognize and cleave a specific site of B. bigemina and B. bovis sequences, with the recognition sequences 5′-GACNN↓NNGTC-3′ (Box I) and 5′-C↓CGG-3′ (Msp I), respectively (Table 2). With the PCR-RFLP assay, fragments of different size are produced after enzymatic digestion: two fragments of 250 and 150 bp are obtained for B. bovis, while two fragments of 290 and 110 bp are produced in B. bigemina samples. The PCR-RFLP assay is a precise and reliable technique, which can also be used for cattle monitoring during the acute phase of bovine babesiosis [47]. Disadvantages of the PCR-RFLP method include the requirement for specific endonucleases, the high purity and the amount of material collected to perform the reaction. Moreover, since PCR-RFLP consists of several steps, including an electrophoretic separation step, it is relatively time-consuming, and therefore the technique is not suitable for high-throughput analysis.
Another variant of the PCR assay is the quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) technique, which was recently used in Brazil to study the host–Babesia–tick interaction. Through amplification of the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene of B. bovis and B. bigemina [48] [48] (Table 2), the number of copies of each Babesia species present in larvae tick and blood samples was achieved, and although the number of base pairs expected for both species is the same (88 bp), the melting curves differ, which allowed the species differentiation. The qPCR assay had a high level of sensitivity; according to the Poisson distribution, at least three copies of the DNA fragment can be detected in the assay. Results obtained in this study displayed 100% of positive samples in either larvae or bovine blood, without significant differences between the number of copies found among Babesia species. Likely, in the case of tick samples, the results can also be a consequence of the larvae handling, because processed larvae (a pool of 100) were obtained from a pool of eggs oviposited by 10 adult engorged female ticks, thus increasing the chance of finding the minimum number of copies needed for amplification [49]. The same qPCR test was used for the detection of B. bigemina and B. bovis in Rh. microplus ticks fed on water buffalo and cattle. Tick samples were collected from calves and adult animals. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the capability for transmission between water buffalo–Babesia–ticks and prove the ability of buffalo to act as reservoir hosts. Despite ticks being found only in calves (80%) and adult buffalo not showing tick infestation, the reproductive performance of female ticks was similar in those obtained from water buffalo calves than those from cattle calves. Additionally, a similar Babesia positivity was found in the progeny of female ticks fed in cattle calves and water buffalo calves, with a higher presence of B. bovis in ticks as compared to B. bigemina [50].
Studies conducted on subolesin vaccination and release of tick larvae after subolesin knockdown by RNA interference (RNAi) have demonstrated to be effective for control of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infestations in cattle [51]. By applying a qRT-PCR assay using primers that target the rDNA genes of B. bigemina (Table 2), the results showed that parasite infection levels were over 87% lower in ticks fed on subolesin-vaccinated cattle and after gene knockdown by RNAi when compared to control ticks [51]. Similarly, as determined by quantitative PCR (qPCR) of the 18S rDNA gene of B. bigemina, RNA interference studies in R. annulatus leading to knockdown of the Tick Receptor for Outer Surface Protein A (TROSPA) and serum amyloid A significantly reduced B. bigemina infection levels by 83% and 66% respectively, in R. annulatus when compared to control ticks. In R. microplus, knockdown of TROSPA and serum amyloid A also reduced pathogen infection levels by 70% and 86% respectively, while calreticulin knockdown resulted in 73% lower infection levels as compared with controls. However, subolesin knockdown did not affect B. bigemina infection levels in R. annulatus ticks [52].
Nested primer sets used to amplify a fragment of the B. bovis rap1 gene [38] [38] (Table 2) have also been utilized to determine tick infection rates in a parasite transmission experiment. Adult female ticks whose vitellogenin receptor gene had been RNA interference-silenced for expression in the ovary during tick feeding on B. bovis-infected cattle had reduced tick reproductive fitness [53]. An overall female infection rate of around 70% demonstrated that silencing the vitellogenin receptor did not affect B. bovis acquisition during tick feeding. However, B. bovis tick infection rates in larval progeny were 12% to 17% for non-silenced control groups, whereas there were no larvae infected with B. bovis from the vitellogenin receptor gene-silenced group, confirming that transovarial transmission of B. bovis to the offspring was diminished [53]. The Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) assay is another molecular technique that has been implemented to detect B. bigemina and B. bovis in infected cattle (Table 2). This method can amplify 109 copies from template DNA and is less expensive and time-consuming than a conventional PCR assay. A LAMP assay developed in China was 1000-fold more sensitive than PCR for B. bovis and B. bigemina detection under analytical examination, when the PCR technique is performed with the same external primers as those used in the LAMP assay. Also, when used with field samples, a greater number of LAMP-positive samples were found as compared to the PCR assay [27]. However, when the same LAMP assay was compared with nPCR (primers set BV5650), only 90% of sensitivity for specific detection of Babesia bovis was displayed [54]. Perhaps the LAMP assay could be of great help in detecting Babesia parasites in the vector tick, but so far, no study has been reported.
2.1.3. Other Babesia Species that Affect Cattle
A study was conducted to investigate the mechanisms that control B. divergens transmission in the tick vector Ixodes ricinus. By designing an artificial feeding technique that allowed infection of ticks with known numbers of parasites, the transstadial and transovarian transmission of B. divergens by I. ricinus was demonstrated [55]. Conventional PCR assays with 18S rRNA as the target gene (Table 2) performed on DNA extracted from tick salivary glands which identified the presence of B. divergens after molting of the artificially infected larvae and nymphs, as parasite DNA, could be amplified from all tested females and from all tested pools of nymphal salivary glands. In addition, PCR of the nymphs that molted from infected larvae fed on non-parasitized gerbils showed that parasite DNA was still present in salivary glands, indicating that the parasite persists from the larvae to the nymph (transstadial transmission). Similarly, positive PCR detection of parasite DNA on pools of eggs from adults infected by skin feeding demonstrated the transovarial transmission of B. divergens. PCR amplifications performed on hatched larvae 3 months later were also positive, indicating that the parasite DNA remained in the larvae. In all cases, sequencing of the PCR products showed that the recovered DNA was B. divergens [55]. In some cases, Babesia-infected ticks can be found on different invertebrate hosts other than those commonly parasitized, an important finding that was reported in Switzerland where Ixodes ricinus female ticks collected from goat, chamois and red deer were identified as B. divergens-positive. B. major was also found in I. ricinus female ticks derived from two red deer. Babesia sp. genotype EU1 was also found in Ixodes ricinus male ticks, suggesting the possibility of a transstadial transmission. Moreover, a new Babesia sp. denominated as genotype CH1, closely related to B. odocoilei, was reported in I. ricinus obtained from red deer. This finding was made possible by using a conventional PCR with generic and species-specific primers designed by the authors [56]. It was determined that better results would be found by using a more sensitive test such as the nPCR assay. This, coupled to detection of bovine Babesias in the wild ruminants sampled, could be a way forward for future research.
Babesia orientalis is another parasite commonly found in water buffalo in Asia [57], and a molecular technique designed for the detection of this parasite is the semi-nested PCR (Table 2). The assay has been successfully used in buffalo blood samples and Rhipicephalus hemaphysaloides tick samples, including the detection of the Babesia parasite in the tick progeny. The assay had an analytical sensitivity of 0.00000012% and did not show specificity when tested on other species of blood microorganisms that affect buffalo, such as bovine piroplasms, Eperythrozoon wenyonii, Anaplasma marginale and Mycobacterium bovis. The restriction endonuclease SacII was also implemented to confirm the nature of the amplicon obtained, with the production of two DNA fragments of 174 and 83 bp. In addition, PCR products were cloned and sequenced to confirm the identity with the 18S rRNA gene [57]. B. orientalis has also been identified in water buffalo by the LAMP assay, showing better results as compared to light microscopy and the semi-nested PCR assay mentioned above, though no studies were conducted in tick samples [58].
In 1981, a previously undescribed Babesia species was isolated from Hyalomma marginatum rufipes ticks collected from cattle in South Africa [59]. The piroplasms were morphologically like both B. bovis and B. bigemina but produced only mild clinical reactions even in splenectomized animals, and since the Babesia occurs at exceptionally low parasitemias, it was proposed as B. occultans [59]. Later, a study conducted in Tunisia reported the finding for the first time of B. occultans in Hyalomma marginatum ticks collected in northern Africa and described the use of the 18S rRNA gene (Table 2) as a target for the design of a species-specific probe for detecting B. occultans by Reverse Line Blot (RLB) hybridization [60].
A PCR assay was developed that allowed the identification of Babesia ovata in samples of H. longicornis and I. ovatus ticks. The assay was based on the beta-tubulin gene (β-tubulin) (Table 2), a component of microtubules in the cytoskeleton that is highly conserved among apicomplexan parasites, but with different sequence lengths. In the same study, a PCR test previously successfully used to detect B. ovata in cattle samples, based on apical membrane antigen-1 (AMA-1) as the target gene, was evaluated to detect B. ovata-positive ticks, showing inadequate results. None of the tick samples that were spiked with B. ovata DNA were amplified, probably due to non-specific binding of the primers with tick DNA. In contrast, the β-tubulin PCR assay displayed a better specificity and sensitivity to detect the protozoan parasite in tick samples [61]. Although B. ovata does not have a high economic impact in livestock, it is necessary to monitor its distribution in areas where other piroplasms are present due to the synergistic damage that they can cause.
References
- Gondard, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Charles, R.A.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Albina, E.; Moutailler, S. Ticks and tick-borne pathogens of the Caribbean: Current understanding and future directions for more comprehensive surveillance. Front. Cell. Infect. Micro-biol. 2017, 7, 1–16, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2017.00490.
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and tick-borne diseases: A one health perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446, doi:10.1016/j.pt.2012.07.003.
- Dantas-Torres, F. Species concepts: What about ticks? Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 1017–1026, doi:10.1016/j.pt.2018.09.009.
- Gray, J.S.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Zintl, A. Vectors of babesiosis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 149–165, doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-011118-111932.
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Robbins, R.G.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Petney, T.N.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Horak, I.G.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. The Argasidae, Ixodidae and Nuttalliellidae (Acari: Ixodida) of the world: A list of valid species names. Zootaxa 2010, 2528, 1–28, doi:10.5281/zenodo.196488.
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2012.07.004.
- Bock, R.; Jackson. L.; De Vos, A.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, 247–269, doi:10.1017/s0031182004005190.
- Uilenberg, G. Babesia a historical overview. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 3–10, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.01.035.
- Vannier, E.G.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A.; Ben Mamoun, C.; Krause, P.J. Babesiosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2015, 29, 357–370, doi:10.1016/j.idc.2015.02.008.
- Levine, N.D. Taxonomy of the piroplasms. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 1971, 90, 2–33, doi:10.2307/3224894.
- Babes, V. Sur l’hemoglobinurie bacterienne du boeuf (on the bacterian hemoglobinuria of cattle). Compt. Rend. Hebd. Acad. Sci. 1888, 107, 692–694. (In French)
- Babes, V. L’etiologie d'une enzootie des moutons, dénommé Carceag en Roumanie. Compt. Rend. Hebd. Acad. Sci. 1892, 105, 359–361.
- Smith, T.; Kilborne, F.L. Investigation into the nature causation and prevention of Texas or southern cattle fever. U.S. Dept. Agri. Bur. Anim. Ind. 1893, 1, 1–301.
- Skrabalo, Z.; Deanovic, Z. Piroplasmosis in man. Report of a case. Doc. Med. Geogr. Trop. 1957, 9, 11–16.
- Western, K.A.; Benson, G.D.; Gleason, N.N.; Healy, G.R.; Schultz, M.G. Babesiosis in a Massachusetts resident. N. Engl. J. Med. 1970, 283, 854–856, doi:10.1056/NEJM197010152831607.
- Vannier, E.; Gewurz, B.E.; Krause, P.J. Human babesiosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2008, 22, 469–488, doi:10.1016/j.idc.2008.03.010.
- Gray, S.J.; Weiss, M.L. Babesia microti. In Emerging Protozoan Pathogens; Khan, N.A., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2008, 303–349.
- Lack, J.B.; Reichard, M.V.; Van Den Bussche, R.A. Phylogeny and evolution of the Piroplasmida as inferred from 18S rRNA sequences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 353–363, doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2012.02.005.
- Mehlhorn, H.; Schein, E. The piroplasms: Life cycle and sexual stages. Adv. Parasitol. 1985, 23, 37–103, doi:10.1016/S0065-308X(08)60285-7.
- Chauvin, A.; Moreau, E.; Bonnet, S.; Plantard, O.; Malandrin, L. Babesia and its hosts: Adaptation to long-lasting interactions as a way to achieve efficient transmission. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 37, doi:10.1051/vetres/2009020.
- Jalovecka, M.; Hajdusek, O.; Sojka, D.; Kopacek, P.; Malandrin, L. The complexity of piroplasms life cycles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 248, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2018.00248.
- Jalovecka, M.; Sojka, D.; Ascencio, M.; Schnittger, L. Babesia life cycle—When phylogeny meets biology. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 356–368, doi:10.1016/j.pt.2019.01.007.
- Alvarez, J.A.; Rojas, C.; Figueroa, J.V. Diagnostic tools for the identification of Babesia sp. in persistently infected cattle. Pathoghens 2019, 8, 143, doi:10.3390/pathogens8030143.
- Homer, M.J.; Aguilar-Delfin, I.; Telford, S.R.; Krause, P.J.; Persing, D.H. Babesiosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 451–469, doi:10.1128/cmr.13.3.451-469.2000.
- Lei, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, N. Rapid isothermal duplex real-time recombinase polymerase amplifi-cation (RPA) assay for the diagnosis of equine piroplasmosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4096, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-60997-1.
- Lempereur, L.; Beck, R.; Fonseca, I.; Marques, C.; Duarte, A.; Santos, M.; Zúquete, S.; Gomes, J.; Walder, G.; Domingos, A.; et al. Guidelines for the detection of Babesia and Theileria parasites. Vector Borne Zoonotic. Dis. 2017, 17, 51–65, doi:10.1089/vbz.2016.1955.
- Liu, A.; Guan, G.; Du, P.; Gou, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Ma, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, Q.; et al.Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method based on two species-specific primer sets for the rapid identification of Chinese Babesia bovis and B. bigemina. Parasitol Int. 2012, 61, 658–663, doi:10.1016/j.parint.2012.07.004.
- Mosqueda, J.; Olvera-Ramirez, A.; Aguilar-Tipacamu, G.; Canto, G.J. Current advances in detection and treatment of babesi-osis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1504–1518, doi:10.2174/092986712799828355.
- Sparagano, O.A.; Allsopp, M.T.; Mank, R.A.; Rijpkema, S.G.; Figueroa, J.V.; Jongejan, F. Molecular detection of pathogen DNA in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae): A review. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1999, 23, 929–960, doi:10.1023/a:1006313803979.
- Westblade, L.F.; Simon, M.S.; Mathison, B.A.; Kirkman, L.A. Babesia microti: From mice to ticks to an increasing number of highly susceptible humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2903–2912, doi:10.1128/JCM.00504-17.
- Sivakumar, T.; Igarashi, I.; Yokoyama, N. Babesia ovata: Taxonomy, phylogeny and epidemiology. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 229, 99–106, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.10.006.
- Jacob, S.S.; Sengupta, P.P.; Paramanandham, K.; Suresh, K.P.; Chamuah, J.K.; Rudramurthy, G.R.; Roy, P. Bovine babesiosis: An insight into the global perspective on the disease distribution by systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109136, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109136.
- Guglielmone, A.A.; Gaido, A.B.; Mangold, A.J. Light microscopy diagnosis of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina kinetes in the haemolymph of artificially infected Boophilus microplus engorged female ticks. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 61, 15–20, doi:10.1016/0304-4017(95)00813-6.
- Oliveira, M.C.S.; Oliveira-Sequeira, T.C.G.; Araujo, J.P., Jr.; Amarante, A.F.T.; Oliveira, H.N. Babesia spp. infection in Boophilus microplus engorged females and eggs in Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 130, 61–67, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.03.007.
- Howell, J.M.; Ueti, M.W.; Palmer, G.H.; Scoles, G.A.; Knowles, D.P. Transovarial transmission efficiency of Babesia bovis tick stages acquired by Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus during acute infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007a, 45, 426–431, doi:10.1128/JCM.01757-06.
- Howell, J.M.; Ueti, M.W.; Palmer, G.H.; Scoles, G.A.; Knowles, D.P. Persistently infected calves as reservoirs for acquisition and transovarial transmission of Babesia bovis by Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3155–3159, doi:10.1128/JCM.00766-07.
- Oliveira, M.C.S.; Oliveira-Sequeira, T.C.G.; Regitano, L.C.A.; Alencar, M.M.; Néo, T.A.; Silva, A.M.; Oliveira, H.N. Detection of Babesia bigemina in cattle of different genetic groups and in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus tick. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 155, 281–286, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.04.022.
- Figueroa, J.V.; Chieves, L.P.; Johnson, G.S.; Buening, G.M. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction based assay for the detection of Babesia bigemina, Babesia bovis and Anaplasma marginale DNA in bovine blood. Vet. Parasitol. 1993, 50, 69–81, doi:10.1016/0304-4017(93)90008-B.
- Figueroa, J.V.; Álvarez, J.A. Investigaciones sobre la aplicación de técnicas moleculares en el diagnóstico y control de la babesiosis bovina. Cienc. Vet. 2003, 9, 75–104.
- Smeenk, I.; Kelly, P.J.; Wray, K.; Musuka, G.; Trees, A.J.; Jongejan, F. Babesia bovis and B. bigemina DNA detected in cattle and ticks from Zimbabwe by polymerase chain reaction. J. South Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2000, 71, 21–24, doi:10.4102/jsava.v71i1.671.
- Oliveira-Sequeira, T.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Araujo, J.P., Jr.; Amarante, A.F. PCR-based detection of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in their natural host Boophilus microplus and cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 105–111, doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2004.09.002.
- Bhat, S.A.; Singh, N.K.; Singh, H.; Rath, S.S. Molecular prevalence of Babesia bigemina in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks infesting cross-bred cattle of Punjab, India. Parasite Epidemiol. Control. 2017, 2, 85–90, doi:10.1016/j.parepi.2017.04.002.
- Gonzalez, J.; Echaide, I.; Pabón, A.; Gabriel Piñeros, J.J.; Blair, S.; Tobón-Castaño, A. Babesiosis prevalence in malaria-endemic regions of Colombia. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2018, 55, 222–229, doi:10.4103/0972-9062.249480.
- Guerrero, F.D.; Bendele, K.G.; Davey, R.B.; George, J.E. Detection of Babesia bigemina infection in strains of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from outbreaks in South Texas. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 156–163, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.11.014.
- Adham, F.K.; Abd-El-Samie, E.M.; Gabre, R.M.; El-Hussein, H. Detection of tick blood parasites in Egypt using PCR assay I-Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 721–730, doi:10.1007/s00436-009-1443-8.
- Carret, C.; Walas, F.; Carcy, B.; Grande, N.; Précigout, E.; Moubri, K.; Schetters, T.P.; Gorenflot, A. Babesia canis canis, Babesia canis vogeli, Babesia canis rossi: Differentiation of the three subspecies by a Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism analysis on amplified small subunit ribosomal RNA genes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 298–303, doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1999.tb05128.x.
- Figueroa-Millán, J.V.; Lira-Amaya, J.J.; Castañeda-Arriola, R.; Álvarez-Martínez, J.A.; Rojas-Martínez, C.; Bautista-Garfias, C.R. Optimización de una prueba de PCR-RFLP para detección y diferenciación de Babesia sp en garrapatas Rhipicephalus mi-croplus. Entomol. Mex. 2014, 1, 978–983.
- Giglioti, R.; Oliveira, H.N.; Santana, C.H.; Ibelli, A.M.G.; Néo, T.A.; Bilhassi, T.B.; Rabelo, M.D.; Machado, R.Z.; Brito, L.G.; Oliveira, M.C.S. Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infection levels estimated by qPCR in Angus cattle from an endemic area of São Paulo state, Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 657–662, doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2016.02.011.
- Giglioti, R.; Nunes de Oliveira, H.; Okino, C.H.; de Sena Oliveira, M.C. qPCR estimates of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina infection levels in beef cattle and Rhipicephalus microplus larvae. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 75, 235–240, doi:10.1007/s10493-018-0260-0.
- Obregón, D.; Corona-González, B.; Díaz-Sánchez, A.A.; Armas, Y.; Roque, E.; de Sena Oliveira, M.C.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. Efficient transovarial transmission of Babesia spp. in Rhipicephalus microplus ticks fed on water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Pathoghens 2020, 9, 280, doi:10.3390/pathogens9040280.
- Merino, O.; Almazán, C.; Canales, M.; Villar, M.; Moreno-Cid, J.A.; Galindo, R.C.; de la Fuente, J. Targeting the tick protec-tive antigen subolesin reduces vector infestations and pathogen infection by Anaplasma marginale and Babesia bigemina. Vac-cine 2011, 29, 8575–8579, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.09.023.
- Antunes, S.; Galindo, R.C.; Almazán, C.; Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Grubhoffer, L.; Shkap, V.; do Rosário, V.; de la Fuente, J.; Domingos, A. Functional genomics studies of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus ticks in response to infection with the cattle protozoan parasite, Babesia bigemina. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 187–195, doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2011.12.003.
- Hussein, H.E.; Johnson, W.C.; Taus, N.S.; Suarez, C.E.; Scoles, G.A.; Ueti, M.W. Silencing expression of the Rhipicephalus microplus vitellogenin receptor gene blocks Babesia bovis transmission and interferes with oocyte maturation. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 7, doi:10.1186/s13071-018-3270-1.
- AL-Hosary, A.A.T.A. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for diagnosis of bovine babesiosis (Babesia bovis infection) in Egypt. J. Adv.Vet. Res. 2017, 7, 71–74.
- Bonnet, S.; Jouglin, M.; Malandrin, L.; Becker, C.; Agoulon, A.; L’Hostis, M.; Chauvin, A. Transstadial and transovarial per-sistence of Babesia divergens DNA in Ixodes ricinus ticks fed on infected blood in a new skin-feeding technique. Parasitology 2007, 134, 197–207, doi:10.1017/S0031182006001545.
- Hilpertshauser, H.; Deplazes, P.; Schnyder, M.; Gern, L.; Mathis, A. Babesia spp. Identified by PCR in ticks collected from domestic and wild ruminants in southern Switzerland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6503–6507, doi:10.1128/AEM.00823-06.
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhou, D.N.; Liu, E.Y.; Du, K.; Chen, S.G.; Yao, B.A.; Zhao, J.L. Semi-nested PCR detection of Babesia orientalis in its natural hosts Rhipicephalus haemaphysaloides and buffalo. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 143, 260–266, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.08.016.
- He, L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Oosthuizen, M.C.; Zhao, J.L. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) detection of Babesia orientalis in water buffalo (Bubalus babalis, Linnaeus, 1758) in China. Vet Parasitol. 2009, 165, 36–40, doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.06.036.
- Gray, S.; de Vos, A. Studies on a bovine Babesia transmitted by Hyalomma marginatum rufipes Koch, 1844. OnderstepoortJ. Vet. Res. 1981, 48, 215–223.
- Ros-García, A.; M’Ghirbi, Y.; Bouattour, A.; Hurtado, A. First detection of Babesia occultans in Hyalomma ticks from Tunisia. Parasitology 2011, 138, 578–582, doi:10.1017/S0031182011000060.
- Sivakumar, T.; Tattiyapong, M.; Okubo, K.; Suganuma, K.; Hayashida, K.; Igarashi, I.; Zakimi, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Inokuma, H.; Yokoyama, N. PCR detection of Babesia ovata from questing ticks in Japan. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 305–310, doi:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.12.006.
