Human Immunodeficiency Virus type-1 (HIV-1) establishes a latent viral reservoir soon after infection, which poses a major challenge for drug treatment and curative strategies. Many efforts are therefore focused on blocking infection. To this end, both viral and host factors relevant to the onset of infection need to be considered. Given that HIV-1 is most often transmitted mucosally, strategies designed to protect against infection need to be effective at mucosal portals of entry. These strategies need to contend also with cell-free and cell-associated transmitted/founder (T/F) virus forms; both can initiate and establish infection.
- mucosal transmission
- transmitted/founder virus
- viral entry
- neutralizing antibody
- entry inhibitor
1. Introduction
Although the physiopathology of HIV-1 is now well known, a cure or a vaccine remains elusive. While combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) allows effective management of HIV infection, it does not cure infected individuals due to viral persistence in latent reservoirs [1]. Pre-exposure prophylaxis, the practice whereby uninfected persons take antiretroviral medication prior to possible exposure to HIV, is highly efficacious but faces challenges as a long-term solution [2]. There have been a few cases of HIV-1 remission following allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with HIV-resistant donor cells [3] [3] but the risks, complexity, and costs of these procedures make them non-viable options for curing HIV infection worldwide. It is therefore widely held that the key to preventing HIV infection globally is by stopping viral entry, which would then prevent viral dissemination and latent infection within the host.
As most HIV-1 infections occur upon mucosal transmission [4], understanding the social-behavioral and mucosal context (immunological, hormonal, microbial, and physiologic) favoring or limiting transmission is critical for the development of effective intervention strategies. The first lever of action to reduce HIV-1 mucosal transmission is based on social-behavioral variables that increase the risk, especially in women, of HIV exposure and acquisition. These include early age at sexual debut (defined as having first sexual intercourse at or before age 14) [5], age-disparate sexual coupling [6], multiple concurrent sexual partners [7], female disempowerment [8], failure to negotiate safe sexual practices leading to low or no use of condoms [9], and gender-based violation [10][11][10,11]. HIV risk can also be augmented by intravaginal practices, such as cleansing or the insertion of products for hygienic or sexual reasons [12][13][12,13].
Although HIV transmission rate varies at different mucosal surfaces, the risk of transmission following unprotected sexual contact is higher during anal (0.3–5%) than vaginal intercourse (0.03–0.5%) [4][14][4,14]. The lowest probability of sexual transmission is at the male genital tract (0.04–0.14%), followed by the oral mucosa, which can vary from 0.01% during oral sex to 5–20% during breastfeeding [4][14][15][4,14,15]. The efficiency of HIV transmission is influenced also by the distinct anatomy and physiology of these mucosal tissues. Stratification and keratinization of the epithelium, as well as the population of intra-epithelial immune cells, are key factors defining the robustness of these mucosal barriers [16][17][18][16,17,18].
HIV-1 transmission can occur via cell-free virus particles or cell-associated virus [14]. Cell-free transmission occurs when free-floating virions, for example, in plasma or mucosal fluids, infect a new target cell. In contrast, cell-associated virus is transmitted from one cell to another via close cell-to-cell contact. As reviewed elsewhere [15], there is increasingly strong evidence for a key role of the cell-to-cell mode of transmission on HIV pathogenesis and the generation and maintenance of the latent virus reservoir. Cell-to-cell transmission limits accessibility of virus particles by entry inhibitors, such as innate antiviral factors and neutralizing antibodies (nAbs), potentially contributing to immune evasion [16]. HIV-1 transmission by cell-to-cell contact concentrates the release of virus particles at the contact site, making this mode of transmission generally more efficient than free virions. The current model of cell-to-cell transmission resembles the immunological synapse and is also known as the infectious synapse or the virological synapse [15]. The formation of these synapses facilitates infection, as it activates cell signaling cascades and promotes cell stimulation [15][17][15,17]. Virus infection via the infectious synapse occurs when a cell (e.g., antigen-presenting cell, epithelial cell, and fibroblast) transiently captures HIV without being infected and transmits the particles to CD4+ T cells. Alternative modes of transmission have also been proposed, such as phagocytosis, syncytium formation, and tunneling nanotubes [15].
In the majority of cases following mucosal transmission, only a single viral variant, the T/F virus, initiates infection [18]. The T/F virus is at the origin of a rapid and wide evolution of the infected individual’s viral population. The factors that impact selection of the T/F virus from the myriad of transmitted variants and the subsequent evolution of HIV upon infection are not yet fully understood. It is clear however that selection can also be less stringent, resulting in multivariant transmission and more than one variant initiating infection. Multivariant transmission has been reported in 20% of heterosexual transmissions and 30–40% in men who have sex with men should not be ignored [19][20][19,20]. Nevertheless, it has become increasingly clear that understanding features that typify the T/F virus and the molecular details of the interactions mediating viral cell entry could help to inform intervention strategies targeting the onset of the infection [21].
In-depth antigenic and molecular characterization of the HIV envelope glycoprotein spike (Env) has spurred the development of novel vaccine immunogens and cell entry inhibitors. Current recombinant forms of HIV Env, such as the so-called SOSIPs [22], NFL-TDs [23], and UFOs [24] [24] largely mirror antigenicity of native Env and approximate the pre-fusion conformation. Recently, cryo-electron microscopy resolution of native Env trimer, full-length, wild-type HIV-1 Env on HIV-1 virion, as well as C-terminally truncated and stabilized versions, have revealed the (near-)native structure of the Env [25][26][25,26]. Resolution of the Env-gp120 during the different stages of interaction with the CD4 receptor and the coreceptors, C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)/C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), also allows modeling, at the molecular level, of the first step of HIV-1 cell entry, and improves development of inhibitor strategies [27].
The course of HIV infection can be divided in four phases: the eclipse phase, the acute infection phase, the chronic infection phase, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). While systemic infection is currently irreversible after the onset of the acute infection, the most promising window of opportunity for viral clearance is in the earliest step of the infection during the eclipse phase. It is at this step, normally lasting about one week [28], that mucosal transmission, viral entry into primary target cells, and T/F selection can be blocked to prevent irreversible infection.
2. Viral and Host Factors Modulating HIV-1 Entry
The identification of viral and host factors that play a role in HIV mucosal transmission and cell entry is fundamental for the development of strategies to inhibit infection.
2.1. Viral Factors Modulating HIV-1 Mucosal Transmission and Infection
Although HIV-infected individuals harbor a pool of HIV quasispecies, infection is typically initiated by only one variant, termed the T/F virus, following mucosal transmission. The selection of the T/F virus is a multifactorial process resulting from positive and negative selection pressure in the mucosa [18][29][18,29]. Below we discuss the phenotypic and antigenic characteristics of T/F viruses and how these attributes might be exploited to block infection onset [30].
2.1.1. Phenotypes of Transmitted Founder Viruses
Among the features resulting from T/F virus selection is increased binding to target cells, as Env trimers on these viruses tend to display enhanced CD4-binding site access [31], resulting in increased affinity [32]. Initial studies, using relatively small numbers of T/F and chronic control viruses, suggested that T/F viruses might display more Env per virion than viruses isolated during the chronic phase of infection [33][34][33,34]. However, a 2017 report based on investigations with a large set of HIV isolates from donor and recipient pairs suggests that mucosal transmission does not necessarily select for viruses with increased Env content [35]. However, there is consensus that some T/F viruses have enhanced infectivity [33][34][35][33,34,35]. Subtype A and C T/F viruses often have relatively shorter V1/V2 and V4 loops, likely increasing access to CD4 and co-receptor binding sites [36][37][38][39][36,37,38,39]. Similarly, glycosylation of the T/F Env also differs from chronic-phase viruses [40], with fewer potential N-glycosylation sites around the V1/V2 [41][42] [41,42] and C3/V4 region [43], which seems to provide increased transmission fitness [42][43][42,43].
HIV-1 T/F viruses normally use the CCR5 as a co-receptor, though CXCR4tropism of T/F viruses has been observed occasionally [44]. CXCR6-tropism has been reported for some T/F viruses in infected infants [45], even though CXCR6 is considered a minor contributor to HIV-1 infection in general [46].
There is mounting genotypic and phenotypic evidence suggesting that T/F viruses with a higher replicative capacity are preferentially selected [47][48][47,48]. The high level of replication in the early steps of mucosal HIV-1 infection is thought to be necessary to evade innate immune responses, facilitate exposure to target cells, and establish persistent infection [49][50][49,50]. Another feature that may provide infectious advantage to the selected T/F virus is resistance to innate antiviral type I interferon (IFN) response [35][51][35,51]. Finally, T/F viruses also show resistance to IFN-inducible transmembrane proteins, which usually restrict entry by inhibiting viral membrane fusion to the target cell [52].
2.1.2. Identification of HIV-1 Target to Inhibit Viral Cell Binding and Entry
HIV cell entry is mediated by Env, which binds first to the primary receptor CD4, followed by binding to a coreceptor, usually CCR5 or CXCR4. Although the cell type targeted by HIV-1 depends on the relative expression of the CD4 and CCR5/CXCR4 receptors, other attachment factors (glycolipids, proteoglycans, integrins, mannose receptors, and lectins) also play a role. Thus, HIV-1 can enter multiple cell types, including monocytes, T cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs), as well as non-immune cells such as epithelial cells, and fibroblasts [53][54][53,54].
Unraveling the structure of Env and its dynamic interaction with CD4 and CCR5/CXCR4 has spurred the development of various immunogens and entry inhibitors [24][55][56][24,55,56]. The Env is a trimer of a heterodimer composed of the glycoprotein subunits gp120 and gp41 (Figure 1). The gp120 subunit, responsible for enabling virus binding to CD4, comprises five conserved domains (C1–C5) and five variable loops (V1–V5). The gp41 subunit mediates fusion of viral and cellular membranes. Viral cell entry is orchestrated by a series of conformational changes of the Env trimer triggered by sequential binding of gp120 to the CD4 receptor and then coreceptor CCR5/CXC4, which "releases" gp41 and leads to the fusion of the viral with the target cell membranes and release of the viral core into the cell. For detailed descriptions of the mechanisms of the receptor-mediated entry of HIV-1 the reader is referred to several recent review articles on the subject [56][57][56,57]. Here, we will focus on viral entry targets under investigation for the development of entry inhibitors and immunogens.
The main targets of entry inhibitor-based strategies are the domains on gp120 involved in the binding interaction with the CD4 receptor and the CCR5/CXCR4 coreceptor. Prior to engaging CD4, functional Env trimers on the virus are in a closed but metastable state (dubbed state 1 [56]) that seems to be stabilized by the cholesterol-enriched viral membrane [58]. Binding of a single gp120 protomer to CD4 transitions the other protomers within a trimer to a default intermediate conformation (state 2) and partially opens the Env trimer structure with each protomer displaying asymmetric conformation [59]. In this second state, the protomers not initially bound can engage additional CD4 receptors, resulting in a further opening of the trimer. This opening leads to a positional shift or rearrangement of the V1/V2 and V3 loops to enable access to the coreceptor binding site in the CD4-bound conformation state (state 3).
An additional target for entry inhibitors is gp41. During the rearrangements in gp120 mentioned above, gp41 is triggered to mediate fusion of the viral membrane with the target cell membrane by insertion of its N-terminal hydrophobic peptide into the target cell membrane. This action allows the formation of an energetically favorable hairpin structure that drives the fusion of the two membranes [56].
In addition to Env, viral and cellular membrane lipids also play a role in HIV cell entry [60]. Recent evidence shows that the membrane-proximal external region (MPER) and the transmembrane domain sequester cholesterol to constrain the antigenic conformation of the MPER [61] [61] and facilitate membrane fusion [62]. Another mediator of HIV cell entry has been described; the phosphatidylserine exposed on the viral membrane can interact with host phosphatidylserine-binding molecules [63]. However, while membrane-active compounds could inhibit HIV-1 cell entry and display virucidal activity, they face the same challenges as all lipophilic antivirals, a lack of specificity and high cell toxicity [64].
Interactions with other cell-surface molecules is thought to facilitate Env binding by bringing the virus particle closer to CD4 and coreceptor. These attachment factors have different roles in HIV-1 transmission and infection, and are cell-type dependent. HIV Env can interact with galactosylceramide and heparan sulfate proteoglycans [65][66][67][65,66,67], mannose receptors [68][69] [68,69] on macrophages and epithelial cells, and gut-homing α4β7 integrins on T and B lymphocytes [70]. On DCs and Langerhans cells (LCs), two Ca2+-dependent C-type lectins, the langerin [71][72] [71,72] and the dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecular 3-grabbing non-integrin (DC-SIGN), can bind carbohydrate moieties on gp120 [73]. While some studies show that HIV-1 particles can in part be degraded within DCs, other studies show that DC-SIGN+ DC’s promote HIV-1 transmission to CD4+ T cells via the immunological synapse in a cell-to-cell mode of interaction [15][74][75][76] [15,74,75,76]. This mode of transmission can also be promoted through α4β7 integrins by activating lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 integrins [77]. Antibodies targeting the α4β7 and the C-type lectins were shown to reduce mucosal and plasma viral load in rhesus macaques and are associated with protection in highly HIV-1 exposed seronegative individuals (HESN) [78][79][78,79].
Another feature of HIV-1 Env that influences viral infectivity is glycosylation [80]. In some cases, single point mutations have revealed the essential role of specific glycans around the CD4-binding site [81], on variable loops [82][83][84][82,83,84], and on gp41 [73][84][85][73,84,85], for viral binding and infectivity. High-mannose glycans on gp120 can also bind langerin on LCs and DC-SIGN on DCs [86][87][86,87].
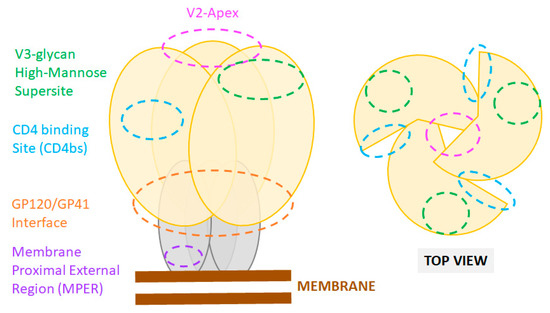
Figure 1. Sites of vulnerability on the HIV-1 Env trimer. Cartoon representation of the Env trimer composed of three gp120 (yellow) and three gp41 subunits (grey) as displayed at the viral membrane (brown). Epitope locations of common bnAbs are shown as color-coded dashed line circles. Footprints of bnAbs on an actual X-ray crystal structure of the HIV Env are also presented in recent reviews [88].
2.2. Host Factors Modulating HIV-1 Mucosal Transmission and Infection
Many host factors contribute to the bottleneck [30] [30] that typifies HIV mucosal transmission and local viral replication before systemic dissemination. As reviewed recently, these factors depend on the biophysical differences between HIV-1 exposed mucosa, female and male genital mucosa, and rectal and intestinal mucosa [4] [4]. As such, the mucus layer and the underlying epithelium are anatomical and physiological barriers limiting mucosal HIV-1 infection [49]. However, HIV can penetrate the epithelial barrier via multiple mechanisms including, epithelium micro-laceration, virus-triggered disruption of tight junctions, and transcytosis. Once this first barrier is overcome, several cell types influence the selection of the founder virus, viral spread, and disease progression (Figure 2) [18][43][18,43]. The outcome of HIV-1 mucosal transmission and infection is influenced by the broad spectrum of mucosal cells interacting with HIV-1 at the mucosal site, the multiple mechanisms of transmission, and mucosal immune activation.
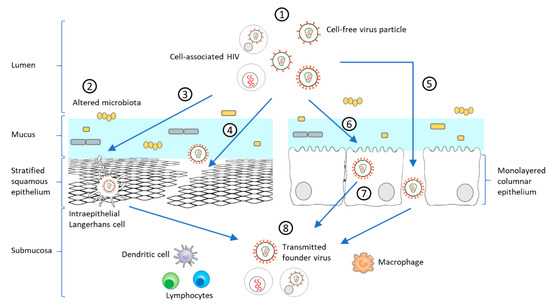
Figure 2. Model of HIV-1 mucosal transmission. (1) Most HIV-1 infections begin at the rectal or genital mucosa, where infected fluid transmits the virus as cell-free virus particles or cell-associated forms (2) Among the risk factors facilitating mucosal transmission in the female genital tract, an altered microbiota, such as during bacterial vaginosis (BV) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can increase the anaerobic bacterial population, decreasing mucus pH and viscosity, and initiating a mucosal inflammatory response leading to disruption of the epithelial barrier. HIV-1 can pass through the epithelium via different mechanisms including (3) capture of intraepithelial LCs, (4) paracellular penetration following epithelium micro-laceration or (5) tight-junction disruption. (6) HIV-1 can also enter epithelial cells by micropinocytosis or endocytosis [89][90][89,90], which can lead to prolonged sequestration of the virus or a transient passage by transcytosis to the submucosa. (8) Following these different routes, HIV-1 can be present in the submucosa and exposed to immune target cells (lymphocytes, DCs, LCs, macrophages). Inflammatory responses heighten the recruitment of innate and adaptive immune cells, which promotes viral replication and dissemination [89][91][92][93][89,91,92,93]. These varied steps of mucosal transmission shape the selection of the T/F virus.
3. Early Prevention of HIV-1 Infection: Passive and Active Immunization Targeting HIV Env-Mediated Cell Entry
The association of anti-HIV antibody responses with viral evolution and infection outcome has long supported the rationale for passive and active immunization strategies [94][136]. The past decade was marked by the discovery of a new generation of nAbs with exceptional neutralization breadth and potency. These broadly active nAbs (bnAbs) protect against infection when administered prophylactically in animal challenge studies and serve as templates for vaccine design capable of protecting from infection as prophylaxis in animal challenge studies [94][136]. Although bnAbs are mostly described as systemic circulating IgG, their protective role at the mucosal portal of entry is being evaluated with increasing interest [95][137].
3.1. Neutralizing Antibodies: Epitopes and Functions
The HIV Env is the sole antigenic target of nAbs. NAbs can target a variety of exposed epitopes on Env. However, only six major epitopes for bnAbs have been defined: (1) the CD4-binding site, (2) the high-mannose patch at the base of the V3 loop, (3) the “silent” face, (4) the V2-apex, (5) the gp120/gp41 interface including the fusion peptide, and (6) the gp41 MPER. One notable characteristic of bnAbs, extensively reviewed elsewhere [96][138], is their general ability to engage or penetrate the extensive HIV glycan shield. Indeed, most bnAb epitopes are easily accessed on gp120 or gp41 soluble monomers but are occluded in the functional conformation of the Env spike [96][97][98][99][138,139,140,141]. Binding of nAbs to Env blocks virus entry through various mechanisms, including direct competition and steric hindrance for binding to the receptor and co-receptors, trimer stabilization preventing conformational change necessary for membrane fusion initiation, and destabilization of the Env trimer rending virion non-infectious.
While nAbs have been shown to be very efficient at blocking infection of cell-free virions in vitro, their potency is significantly decreased in in vitro models of cell-to-cell transmission [100][101][102][103][142,143,144,145]. Several factors, such as high local multiplicity of infection at the viral synapse and membrane steric hindrance, might explain such differences and are thoroughly reviewed elsewhere [104][146]. However, bnAbs can still suppress post-transcytosis HIV-1 infectivity and are superior to non-neutralizing antibodies (non-nAbs) at preventing virus infection of mucosal tissues [105][147]. Indeed, one report showed that a V3/glycan-specific bnAb (10-1074) was highly effective in protecting against cell-associated transmission in macaques [105][147]. Whether the efficacy of bnAbs against cell-associated virus is virus-dependent remains to be elucidated fully.
Like all antibodies, bnAbs can mediate Fc-dependent activities which can lead to the destruction of virions and infected cells through antibody-dependent (AD) cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), phagocytosis (ADCP), and complement-mediated lysis (ADCML). In the RV144 clinical trial, which showed modest protective efficacy of a candidate vaccine formulation [106][107][108][148,149,150], Fc-mediated functions of elicited antibodies seem to be correlated with slow HIV-1 disease progression and viral escape [109][151]. An increasing body of evidence also supports a role for Fc-mediated functions in bnAb-conferred protection in vivo [110][152]. In one study, it was estimated that Fc-mediated functions contributed as much as 50% of the total antiviral antibody activity in vivo in mouse and macaque infection models [111][153].
Subclass-specific characteristics and Fc-functions are likely to also impact antibodies' protective capacity. Many bnAbs have been cloned, therefore precluding identification of the subclass from which they derive. However, for those bnAbs that have been recovered by in vitro cultures, many have been found to be IgG1. A notable exception is antibodies targeting the MPER region, which have been isolated predominantly as IgG3 [112][113][154,155]. The flexibility of the IgG3′s long hinge region has been suggested to favor access to the MPER epitope in very close proximity to the membrane. IgG3 flexibility was also proposed to increase the neutralizing capacity of bnAbs targeting the V2-apex [114][156]. Reports suggest that IgA bnAbs can emerge from IgM or IgG through direct or so-called sequential class switching [115][116][157,158], which redefines the specific contribution of antibody subclasses in mucosal humoral immunity (reviewed in [116][158]). Moreover, models evaluating protection against HIV showed differential impacts of IgG and IgA in various compartments. For example, IgG appear to take precedence over IgA in HIV bnAbs protection in ex vivo human vaginal explants and macaques intrarectal challenge models [117][159], while dimeric IgA in breast milk show a critical role at the gut mucosa and in protection against mother-to-child transmission [118][160]. Antibody Fc-functions may also play a role in antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) (reviewed in [119][161]). Although only observed in vitro, ADE was suggested to explain increased infection rates in individuals with relatively low antibody responses in vaccine trials [120][162]. ADE was also correlated with particular FcR genotypes, characterized by stronger Fc-binding affinities and higher infection risk [121][122][163,164]. Maintaining protective concentrations of bnAbs, especially at the mucosa, may thus be needed to decrease the putative risk of ADE.
3.2. Targeting the Transmitted Founder Virus
As mentioned above, several Env phenotypic and genotypic traits have been linked to viral transmission. The Env of viruses isolated during acute infection are typically CCR5-tropic and have, on average, fewer N-linked glycosylation sites [41][42][41,42], and shorter variable loops [37][38][39] [37,38,39] compared to Env from viruses isolated during the chronic phase of infection. These features, which potentially increase the exposure of nAb epitopes, have been associated with increased sensitivity to autologous nAbs in HIV-1 infected individuals [42][123][124][125][126][127][42,165,166,167,168,169]. Strikingly, these same antigenic features have also been associated with an increase in resistance to neutralization by heterologous nAbs and bnAbs at a population level over the course of the pandemic [128][129][170,171].
Although increased neutralization susceptibility of T/F viruses has been reported in some studies [39][41][130][39,41,172], the converse observation has also been made [126][131][132][168,173,174]. The discrepancies might be due to variation in subtypes, study populations, and specific methods used to assess neutralization sensitivity. Indeed, Env neutralization susceptibility signatures appear to be bnAb-specific even within an epitope class and typically correlate with bnAb-HIV subtype preferences [123][165]. Therefore, the evaluation of neutralization sensitivity to heterologous plasma from HIV-infected individuals or pooled HIV-IgGs is often confounded by the very nature of polyclonal responses, which are likely dominated by strain-specific nAb responses [131][173]. To circumvent these caveats, some studies have tracked transmission pairs showing an apparent selection of more sensitive variants at transmission in some cases [39][41] [39,41] but no differences in others [132] [174]. Co-receptor tropism was also correlated to neutralization sensitivity with CXCR4-tropic T/F viruses, reported to be more resistant to neutralization, possibly due to structural differences of the V1/V2 and V3 loops [133][175].
Overall, studies comprehensively evaluating sensitivity to bnAbs have not observed any particular neutralization susceptibility of T/F compared to chronic viruses [123][165]. Nevertheless, the bnAb and subtype-specific neutralization susceptibility signatures highlight the importance of continuous monitoring of circulating T/F viruses to ensure the adequacy of bnAbs included in passive immunization strategies in different regions of the world.
3.3. Systemic and Mucosal Antibody-Mediated Protection against HIV-1
The identification of exceptionally potent and broad HIV nAbs has reinvigorated efforts towards the development of an effective vaccine as well as increased the possibility of antibody-based immunotherapies against HIV [134][176]. Indeed, in vitro and in vivo studies [135] [177] have provided extensive evidence that passive immunization can protect against HIV acquisition, which is currently also being evaluated in human clinical trials.
Antibodies targeting the CD4-binding site have long been the primary focus of bnAb intervention strategies, due to the critical functional role of this target site. One of the first representatives clinically tested was F105 [136][178]. The antibody had a good safety profile and a blood half-life of 13 days. Among the new generation of bnAbs, VRC01-class CD4-binding site bnAbs have been highly prioritized for both vaccine and passive immunization strategies. Among this bnAb family, 3BNC117 [137] [179] showed good safety and high efficacy in a phase I/IIa study and suppressed viral rebound when ART was interrupted [138][139][180,181], despite the occurrence of breakthrough infections by resistant HIV-1-strains [139][181]. Combination therapy of bnAbs targeting different regions on gp120, more likely to be most effective, is now preferentially being evaluated. The combination of 3BNC117 and 10-1074, a bnAb to high-mannose patch at the base of the V3 loop of gp120, is well tolerated in healthy adults [140][182].
To further improve the pharmacokinetics of these antibodies, modifications have been introduced in their Fc domain [141][183]. The so-called LS mutation (M428L/N434S) increases binding affinity for neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), resulting in a 2–3-fold increase in antibody half-life. VRC01, which also has shown good tolerability and safety in a phase I clinical study [142][184], is currently being assessed in phase I/II studies in comparison to the LS-version [143][185]. Two large-scale double-blinded, multi-centered phases IIb clinical trials, HVTN 703/HPTN 081 and HVTN 704/HPTN 085, also dubbed the AMP studies, are being conducted in parallel to evaluate the safety and efficacy of VRC01 in preventing HIV-1 infection in sexually active adult women (sub-Saharan Africa) and men or transgender persons who have sex with men (USA, Brazil, and Peru), respectively. Results are expected by early 2021 and should serve as a benchmark for the field to determine protective thresholds. Determining the concentration of passively administered bnAbs at the mucosa will be of particular interest in these trials, providing clues for antibody titers required for protection. The impact of mucosal environment-specific parameters, such as pH, on antibody binding capacity, may also need to be considered. Specifically, bnAbs targeting the CD4-binding site rely on a critical salt bridge for binding, which is disrupted at vaginal pH (4.5) [144][186].
4. Treatment of HIV-1 Infection with Entry Inhibitors
In the previous section, we discussed passive and active immunization strategies to block HIV infection at entry. In this section, we review the current state of the art in terms of inhibiting cell entry with non-antibody inhibitors.
Currently, HIV-1 infection is commonly treated with highly active ART (HAART); the drugs reduce the viral load to undetectable levels and thus prevent a progression to AIDS [145][218]. This therapeutic approach consists of a mixture of at least three different viral inhibitors, targeting three different viral proteins required for replication [146][219]. Although these antagonists are generally effective, the emergence of resistant strains is a constant challenge [147][220]. New HIV-1 inhibitors are therefore being investigated. HIV-1 entry-inhibitors add an additional dimension to the broad pallet of anti-retroviral drugs and provide more flexibility for current HAART schedules. Entry inhibitors provide a significant advantage compared to other inhibitor-classes because they block the infection before the virus infects the cell. Obviously, this is a feature that reverse-transcriptase, protease, and integrase inhibitors do not possess [148][221].
Entry inhibitors encompass a large variety of compounds distinguished by their target protein and, therefore, by the stage at which they block the cell entry (Figure 3) [149][150][222,223]. The common targets are the Env gp120 [151][152] [224,225] and gp41 [153][226], the host receptor CD4 and the host coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4 [154][227].
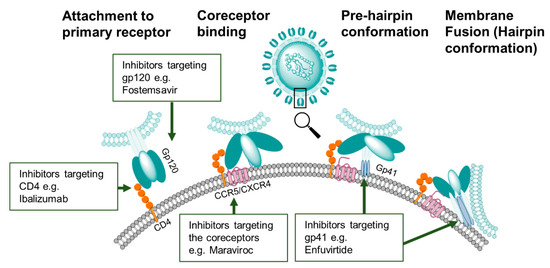
Figure 3. HIV-1 entry inhibitor targets. Compounds that inhibit the first stage of viral binding target epitopes on the primary receptor CD4 or on gp120. Other classes of entry inhibitors target subsequent conformation states of the Env trimer to block CCR5/CXCR4 co-receptor binding or gp41-mediated membrane fusion.
In addition to their mode of action, inhibitors can also be differentiated by their chemical nature (Figure 4). Numerous inhibitors are small molecules based on heteroaromatic scaffolds [151][154][224,227]. Another major group of inhibitors is amino acid-based, ranging from small peptides to proteins like lectins and antibody-like molecules [152][225]. A common strategy to create multifunctional entry inhibitors is to covalently link two or more proteins or peptides [150][223]. The resulting fusion proteins, also known as bifunctional antiviral proteins (bAVPs), then combine features of two different entities, which can lead to broader viral specificity. Other scaffolds like polyanions [155][228], and even whole cells [156] [229] have also been studied to prevent viral cell entry.
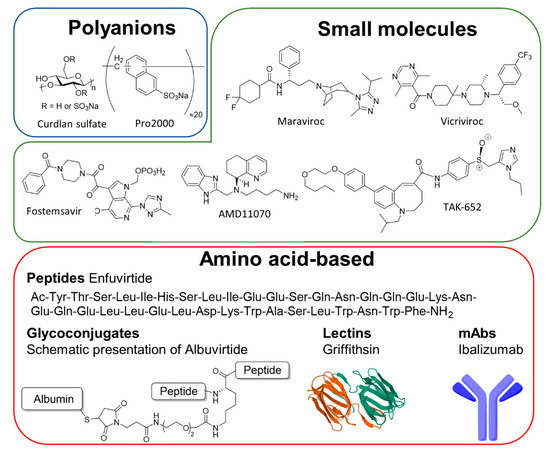
Figure 4. Entry inhibitors classified by chemical nature. Entry inhibitors can be classified chemically into three categories, the polyanions, the small molecules, and the amino acid-based inhibitors which included peptides, glycoconjugates, lectins, and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
This section will give an overview of the different concepts that have been evaluated to prevent HIV cell entry. To underline successful strategies and discuss issues that have arisen, we will focus primarily on inhibitors assessed in human clinical studies (Table 1). Additionally, we will discuss novel strategies that have been developed to improve inhibitor properties and overcome observed pitfalls.
Table 1. List of entry inhibitors tested in clinical trials to date.
Site of Interaction | Name of Inhibitor | Generic Name | Type of Molecule | Current Clinical Status | Reference | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
GP120 | Dextrane sulfate (UA001) | - | polyanion | Phase I, NCT00001009 |
[157] |
[230] |
|||||||||||
Curdlan sulfate | - | polyanion | Phase I, NCT00002100 |
[158] |
[231] |
||||||||||||
Pro2000 | - | polyanion | Phase III, NCT00262106 |
[159] |
[232] |
||||||||||||
Fostemsavir | Rukobia | small molecule | Approved |
[160] |
[233] |
||||||||||||
Griffithsin gel | - | lectin | Phase I, NCT02875119 |
[161] |
[234] |
||||||||||||
F105 | - | mAb | Phase I, NCT00001105 |
[136] |
[178] |
||||||||||||
3BNC117 | - | mAb | Phase I+II, NCT02588586 | ||||||||||||||
10-1074-LS | - | mAb | Phase I, NCT03554408 |
[140] |
[182] |
||||||||||||
VRC01 | - | mAb | Phase I+II, NCT02664415 |
[142] |
[184] |
||||||||||||
VRC01LS | - | mAb | Phase I+II, NCT02797171 |
[143] |
[185] |
||||||||||||
CD4-Ig2 (PRO 542) | - | bAVP | Phase I/II, NCT00055185 |
[162] |
[235] |
||||||||||||
CCR5 | Maraviroc | Celsentri | small molecule | Approved |
[163] |
[236] |
|||||||||||
INCB009471 | - | small molecule | Phase II, NCT00393120 |
[164] |
[237] |
||||||||||||
PF-232798 | - | small molecule | Phase II, NCT00495677 |
[165] |
[238] |
||||||||||||
TAK-652 | Cenicriviroc | small molecule | Phase II, NCT01092104 |
[166] |
[239] |
||||||||||||
MK-4176, SCH 417690 | Viciviroc | small molecule | Phase III, NCT00474370 |
[167] |
[240] |
||||||||||||
GW873140, AK602 | Aplaviroc | small molecule | Phase II+III terminated, NCT00197145 |
[168] |
[241] |
||||||||||||
HGS004 | - | mAb | Phase I, NCT00114699 |
[169] |
[242] |
||||||||||||
PRO 140 | Leronlimab | mAb | Phase II/III, NCT03902522 |
[170] |
[243] |
||||||||||||
CXCR4 | AMD11070 | - | small molecule | Phase I/II, NCT00089466 |
[171] |
[244] |
|||||||||||
GP41 | Enfuvirtide | Fuzeon | peptide | Approved |
[172] |
[245] |
|||||||||||
Albuvirtide | - | protein-conjugate | Phase II+III, NCT04560569 |
[173] |
[246] |
||||||||||||
C34-CXCR4 | - | cell | Phase I, NCT03020524 |
[174] |
[247] |
||||||||||||
2F5/4E10 | - | mAb | Phase I/II, NCT00219986 |
[175] |
[248] |
||||||||||||
10E8.4/iMab | - | bAVP | Phase I, NCT03875209 |
[176] |
[249] |
||||||||||||
CD4 | Ibalizumab (TNX-355) | Trogarzo | mAb | Approved | [177] | [250] |
4.1. Gp120 Inhibitors
The first group of inhibitors in this category is the indiscriminating polyanions [155]. These compounds, active against several different viruses, are administered orally or as a gel in the genital tract. They are based on a neutral polymer that is further functionalized by sulfate groups. The resulting highly charged polymers prevent HIV attachment to the host receptor or coreceptors by binding positively charged residues present on gp120 [178]. Dextrane sulfate (UA001) is one of the first representatives of this class [179]. The highly sulfated, α-linked glucose polymer binds to gp120 and prevents subsequent binding to the coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4. After promising results in vitro, the tolerability of oral administration of UA001 sulfate was assessed in a phase I clinical study. Although well-tolerated in most study subjects, the inhibitory effect was minimal [157]. Another gp120-binding polyanion based on glucose, the β-linked polymer curdlan sulfate (CRDS), which interacts with the V3 loop and CD4-binding site on gp120 [180], showed no major side effects in a phase I study [160]. The highly sulfated polynaphthalene PRO2000 [159], a polyanion with a different polymeric backbone, also proved to be safe and well-tolerated when administered as a vaginal gel, but did not reduce HIV-1 infection significantly in a phase III study [181].
One of the most extensively evaluated small molecule inhibitors targeting gp120 is the heterocyclic compound Fostemsavir (Formerly BMS-663068/GSK3684934), a prodrug version of the drug Temsavir [182]. In addition to a good safety profile, the antagonist reduced viral loads in patients with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 by up to 60% and was recently approved by the FDA [160]. Fostemsavir binds directly to gp120, leading to Env conformational changes that disable the virus and prevent it from subsequent CD4-receptor attachment [183]. This compound can also abolish the interaction of gp120 with CD4-negative cells, suggesting an additional mechanism that is not fully understood yet [184]. Due to the low solubility of the active drug Temsavir, meaning relatively low bioavailability, the application of Fostemsavir is recommended for the treatment of people with limited therapeutic options. One group recently reported on the synthesis of several derivatives of Temsavir, in which the central piperazine ring was replaced by other heterocyclic structures [185]. Although none of the new compounds had significantly increased solubility, two hits showed better stability, suggesting higher serum concentrations of the drug. Regrettably, this modification also reduced the binding affinity to gp120.
Another group of HIV entry inhibitors is formed by lectins. HIV gp120 is heavily glycosylated, meaning that a lectin that binds to this glycan shield could be a putative entry inhibitor. Griffithsin, isolated from the algae Griffithsia sp., was identified as such a lectin and shown to bind HIV Env with picomolar avidity [161][186]. Griffithsin binds oligomannosidic glycans on gp120 and is postulated to cluster HIV virions. However, the detailed mode of action is still unclear [161][187]. As with other inhibitors, resistance resulting from variability in gp120 glycosylation pattern have been reported [188]. The safety of Griffithsin is currently being investigated in two phase I studies (NCT04032717 and NCT02875119), where it is being administered as a gel or by an enema.
Finally, fusion proteins combining the activity of different proteins hold promise for targeting cell-to-cell transmission. An example is CD4-IgG2 (PRO542), in which a human IgG2 was grafted with the V1 and V2 domains of the human CD4-receptor [189]. This chimeric antibody bound gp120 with nanomolar affinity, blocked cell-to-cell transmission, and neutralized several HIV-1-strains. This fusion protein was well tolerated in a phase I/II study in children and reduced the viral burden [190].
4.2. Gp41-Inhibitors
One of the last steps of viral cell entry is the fusion of viral and cell membranes, initiated by conformational changes in gp41. To inhibit the fusion process, a range of antagonists based on HIV-1 peptide and protein structures are being developed [191]. The only fusion inhibitor approved so far is Enfuvirtide (T20, Fuzeon), a 36-amino acid peptide [192]. It was designed based on the second heptad repeat (HR2) of gp41, one of the helices formed during fusion. T20 binds to first heptad repeat of gp41, thereby blocking formation of a molecular hairpin and membrane fusion. After showing a good performance in clinical studies, T20 was approved for HIV-1 treatment and is now administered to treatment-experienced patients in combination with other inhibitors [172]. Major disadvantages include the need for subcutaneous injection, the short half-life, and the occurrence of resistant HIV-1-strains. A peptide-protein conjugate dubbed Albuvirtide (ABT) was developed to overcome some limits of Enfuvirtide [193]. To extend the peptide’s half-life, it was conjugated to human serum albumin [194]. ABT efficiently inhibited a large panel of HIV-1 viruses from the A, B, and C subtypes and showed a half-life of 11–12 days, thus allowing for weekly injections. Additionally, it was well-tolerated in early clinical studies and was also effective in neutralizing enfuvirtide-resistant strains [173]. ABT is currently being assessed as combination therapy in a phase II/III trial but was approved in 2018 in China. Another HR2-conjugate, produced by Hoxie and coworkers [174], entails the 34-amino acid HR2 peptide fused to the N-terminus of the coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4 to position the inhibitor at the virus binding site. These constructs are expressed by primary CD4 T cells and inhibit diverse HIV-1 isolates. Remarkably, the constructs appear not to be particularly sensitive to co-receptor tropism, as the CXCR4 constructs bound CCRR5 viruses and vice versa. Additionally, the cells inhibited viral isolates that were resistant to the soluble HR2-peptide or enfuvirtide. The tolerance of autologous C34-CXCR4 cells is currently being assessed in a phase I study.
Gp41 is also a convenient target for bnAbs. 2F5 and 4E10 are two MPER-specific bnAbs with modest potency against several viral strains alone and in combination with other antibodies [175][195][196][197]. 2F5 and 4E10, when combined with 2G12, a bnAb targeting the high mannose patch of the HIV-1 Env, were shown to be safe in a Phase I/II study [175]. The modest potency of these antibodies however prevented their clinical translation. A substantially more potent MPER-specific bnAb, called 10E8 [198], has since been reported and is currently being investigated in a bispecific format (10E8.4/iMab) with the CD4-receptor specific antibody ibalizumab (iMab) in a phase I study. Another approach consists of designing small molecules mimicking antibodies to the MPER. A high-throughput inhibition screening a 162,000 compound library with an MPER peptide and the 2F5 antibody [199] has led to the identification of a potent inhibitory small molecule that inhibits membrane fusion.
4.3. CD4-Modulators
Given that the CD4-receptor is the first attachment point of HIV-1, CD4-modulators have also been developed to inhibit cell entry. The aforementioned antibody Ibalizumab (Formerly TNX-355), a humanized monoclonal antibody, is the first and only of that kind that has been approved by the FDA so far [200]. It binds to the CD4-domains D1 and D2 but on the opposite side of gp120 binding. This interaction disables gp120 rearrangement upon HIV-1 Env binding, preventing binding to CCR5 and CXCR4 co-receptor [177]. An interesting feature of this antibody is that its epitope is on the opposite side of the MHC-II-receptor binding site, and therefore does not impair MHC-II-mediated immunity. Ibalizumab was tested as well-tolerated and effective in treatment-experienced patients after a single dose every two weeks and is currently administered in combination with other antiretroviral drugs [177][201].
4.4. Coreceptor Inhibitors
4.4.1. CCR5
The majority of HIV-1 strains transmitted via vaginal or rectal mucosa are CCR5-tropic, making the CCR5-receptor a promising target for HIV-1-drug design [202][203]. Many clinical studies are currently in progress to assess the safety and efficacy of these inhibitors. To date, only one is clinically approved, the CCR5 inhibitor Maraviroc, which is currently used in combination with other retroviral drugs [162][204]. The crystal structure of Maraviroc in complex with a human CCR5-receptor provided detailed information about the inhibitor binding pocket [205], showing that maraviroc inhibits CCR5 in an allosteric way, leading to a conformational change in the receptor that prevents HIV-1 binding. Another high affinity CCR5 antagonist is INCB9471 [164]. It is hypothesized that INCB9471 inhibits CCR5 in an allosteric and non-competitive way, but at a binding site different from Maraviroc [206]. Although a phase II study was initiated and completed in 2007, no results of that study have been reported so far. To improve on Maraviroc, a second generation of similar inhibitors, including the imidazopiperidine PF-232798, have been developed [165]. Despite the structural similarities between Maraviroc and PF-232798, a crystal structure of the latter revealed a distinct binding mode and explaining the complementary resistance profile of the two inhibitors [207]. Currently, PF-232798 is being evaluated in a phase II clinical study. A third CCR-antagonist is the anilide cenicriviroc (TBR-652 formerly TAK-652) [166]. In addition to its high affinity for CCR5, TBR-652 is a potent antagonist of CCR2 and has showed activity against protease and reverse-transcriptase inhibitor-resistant HIV-1-strains. A phase II study showed that this inhibitor was well-tolerated and highly effective at reducing viral load. Additionally, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) levels in study subjects were increased, a feature consistent with CCR2 inhibition, resulting in a beneficial anti-inflammatory effect [208]. Another allosteric inhibitor of CCR5 is the pyrimidine Viciviroc [209]. Encouraging results in phase I/II studies led to two phase III studies in which Viciviroc was administered in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Whereas individuals who obtained more than three additional drugs showed no effect, patients with ≤2 drugs showed a slight decrease in viral load compared to the placebo group [167]. However, the effect was not sufficiently substantial to pursue the approval of Viciviroc.
Although small molecules can lead to very effective inhibitors, they sometimes exhibit severe side effects. The 2,5-diketoperazine Aplaviroc, for instance, provided subnanomolar activity against several HIV-1 isolates and was well tolerated in monkeys [168]. However, during clinical studies, severe hepatotoxicity was detected, leading to its clinical termination.
In addition to small molecule inhibitors, antibodies have been evaluated for inhibition of CCR5-tropic virus. One example is the IgG4-formatted antibody HGS004, which binds to the second extracellular loop of CCR5. HGS004 has been shown to be well-tolerated in patients infected with CCR5-tropic HIV-1 and reduced viral load in more than 50% of patients after a single dose [169]. However, further clinical testing was not pursued after an initial trial. An excellent safety profile was also determined for the monoclonal antibody PRO140 (Leronlimab) [170]. Remarkably, this antibody has the potential to provide HIV-1-prophylaxis after a single subcutaneous injection a week and is currently further under investigation in a phase IIb and phase III study.
4.4.2. CXCR4-Inhibitors
The CXCR4 receptor is a very extensively studied chemokine receptor as it plays a major role in multiple diseases [210]. However, in contrast to the large number of CCR5-inhibitors that have been discovered or that are in developmentfor HIV-1-treatment, the number of CXCR4 inhibitors is more limited. The only CXCR4 inhibitor that was clinically tested in HIV-1-patients is the Benzodiazol AMD11070 [211]. A phase Ib/IIa revealed a good safety profile in a group of six HIV-1-infected participants [171]. However, the study provided discordant results regarding the efficacy and the evaluation was terminated after observation of increased toxicity in preclinical animal studies. The importance of CXCR4 in multiple processes makes it a difficult target for HIV-1-treatment since inhibitors can easily cause side-effects. The bicyclam AMD3100, for instance, was initially designed as an HIV-1 inhibitor [212] but it was shown that AMD3100 could cause leukocytosis [213]. In another study, it was shown that HIV-1-entry inhibitors possessing an agonistic rather than an antagonistic effect on CXCR4 are less disruptive, which may lead to safer HIV-1 entry inhibitors [214].
4.1. Gp120 inhibitors
The first group of inhibitors in this category is the indiscriminating polyanions [230]. These compounds, active against several different viruses, are administered orally or as a gel in the genital tract. They are based on a neutral polymer that is further functionalized by sulfate groups. The resulting highly charged polymers prevent HIV attachment to the host receptor or coreceptors by binding positively charged residues present on gp120 [253]. Dextrane sulfate (UA001) is one of the first representatives of this class [254]. The highly sulfated, α-linked glucose polymer binds to gp120 and prevents subsequent binding to the coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4. After promising results in vitro, the tolerability of oral administration of UA001 sulfate was assessed in a phase I clinical study. Although well-tolerated in most study subjects, the inhibitory effect was minimal [232]. Another gp120-binding polyanion based on glucose, the β-linked polymer curdlan sulfate (CRDS), which interacts with the V3 loop and CD4-binding site on gp120 [255], showed no major side effects in a phase I study [233]. The highly sulfated polynaphthalene PRO2000 [234], a polyanion with a different polymeric backbone, also proved to be safe and well-tolerated when administered as a vaginal gel, but did not reduce HIV-1 infection significantly in a phase III study [256].
One of the most extensively evaluated small molecule inhibitors targeting gp120 is the heterocyclic compound Fostemsavir (Formerly BMS-663068/GSK3684934), a prodrug version of the drug Temsavir [257]. In addition to a good safety profile, the antagonist reduced viral loads in patients with multidrug-resistant HIV-1 by up to 60 % and was recently approved by the FDA [235]. Fostemsavir binds directly to gp120, leading to Env conformational changes that disable the virus and prevent it from subsequent CD4-receptor attachment [258]. This compound can also abolish the interaction of gp120 with CD4-negative cells [259], suggesting an additional mechanism that is not fully understood yet [260]. Due to the low solubility of the active drug Temsavir, meaning relatively low bioavailability, the application of Fostemsavir is recommended for the treatment of people with limited therapeutic options. One group recently reported on the synthesis of several derivatives of Temsavir, in which the central piperazine ring was replaced by other heterocyclic structures [261]. Although none of the new compounds had significantly increased solubility, two hits showed better stability, suggesting higher serum concentrations of the drug. Regrettably, this modification also reduced the binding affinity to gp120.
Another group of HIV entry inhibitors is formed by lectins. HIV gp120 is heavily glycosylated, meaning that a lectin that binds to this glycan shield could be a putative entry inhibitor. Griffithsin, isolated from the algae Griffithsia sp., was identified as such a lectin and shown to bind HIV Env with picomolar avidity [236,262]. Griffithsin binds oligomannosidic glycans on gp120 and is postulated to cluster HIV virions. However, the detailed mode of action is still unclear [236,263]. As with other inhibitors, resistance resulting from variability in gp120 glycosylation pattern has been reported [264]. The safety of Griffithsin is currently being investigated in two phase I studies (NCT04032717 and NCT02875119), where it is being administered as a gel or by an enema.
Finally, fusion proteins combining the activity of different proteins hold promise for targeting cell-to-cell transmission. An example is CD4-IgG2 (PRO542), in which a human IgG2 was grafted with the V1 and V2 domains of the human CD4-receptor [265]. This chimeric antibody bound gp120 with nanomolar affinity, blocked cell-to-cell transmission, and neutralized several HIV-1-strains. This fusion protein was well tolerated in a phase I/II study in children and reduced the viral burden [266].
4.2. Gp41-inhibitors
One of the last steps of viral cell entry is the fusion of viral and cell membranes, initiated by conformational changes in gp41. To inhibit the fusion process, a range of antagonists based on HIV-1 peptide and protein structures are being developed [267]. The only fusion inhibitor approved so far is Enfuvirtide (T20, Fuzeon), a 36-amino acid peptide [268]. It was designed based on the second heptad repeat (HR2) of gp41, one of the helices formed during fusion. T20 binds first to the heptad repeat of gp41, thereby blocking the formation of the molecular hairpin and membrane fusion. After showing a good performance in clinical studies, T20 was approved for HIV-1 treatment and is now administered to treatment-experienced patients in combination with other inhibitors [247]. Major disadvantages include the need for subcutaneous injection, the short half-life, and the occurrence of resistant HIV-1-strains. A peptide-protein conjugate dubbed Albuvirtide (ABT) was developed to overcome some limits of Enfuvirtide [269]. To extend the peptide’s half-life, it was conjugated to human serum albumin [270]. ABT efficiently inhibited a large panel of HIV-1 viruses from the A, B, and C subtypes and showed a half-life of 11-12 days, thus allowing for weekly injections. Additionally, it was well-tolerated in early clinical studies and was also effective in neutralizing enfuvirtide-resistant strains [248]. ABT is currently being assessed as a combination therapy in phase II/III trial but was approved in 2018 in China. Another HR2-conjugate, produced by Hoxie and coworkers [249], entails the 34-amino acid HR2 peptide fused to the N-terminus of the coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4 to position the inhibitor at the virus binding site. These constructs are expressed by primary CD4 T cells and inhibit diverse HIV-1 isolates. Remarkably, the constructs appear not to be particularly sensitive to co-receptor tropism, as the CXCR4 constructs bound CCRR5 viruses and vice versa. Additionally, the cells inhibited viral isolates that were resistant to the soluble HR2-peptide or enfuvirtide. The tolerance of autologous C34-CXCR4 cells is currently being assessed in a phase I study.
Gp41 is also a convenient target for bnAbs. 2F5 and 4E10 are two MPER-specific bnAbs with modest potency against several viral strains alone and in combination with other antibodies [250,271–273]. 2F5 and 4E10, when combined with 2G12, a bnAb targeting the high mannose patch of the HIV-1 Env, were shown to be safe in a Phase I/II study [250]. The modest potency of these antibodies however prevented their clinical translation. A substantially more potent MPER-specific bnAb, called 10E8 [274], has since been reported and is currently being investigated in a bispecific format (10E8.4/iMab) with the CD4-receptor specific antibody ibalizumab (iMab) in a phase I study. Another approach consists of designing small molecules mimicking antibodies to the MPER. A high-throughput inhibition screening a 162.000 compound library with an MPER peptide and the 2F5 antibody [275] has led to the identification of a potent inhibitory small molecule that inhibits membrane fusion.
4.3. CD4-modulators
Given that the CD4-receptor is the first attachment point of HIV-1, CD4-modulators have also been developed to inhibit cell entry. The aforementioned antibody Ibalizumab (Formerly TNX-355), a humanized monoclonal antibody, is the first and only of that kind that has been approved by the FDA so far [276]. It binds to the CD4-domains D1 and D2 but on the opposite side of gp120 binding. This interaction disables gp120 rearrangement upon HIV-1 Env binding, preventing binding to CCR5 and CXCR4 co-receptor [252]. An interesting feature of this antibody is that its’ epitope is on the opposite side of the MHC-II-receptor binding site and therefore does not impair MHC-II-mediated immunity. Ibalizumab was tested as well-tolerated and effective in treatment-experienced patients after a single dose every two weeks and is currently administered in combination with other antiretroviral drugs [252,277].
4.4. Coreceptor inhibitors
4.4.1. CCR5
The majority of HIV-1 strains transmitted via vaginal or rectal mucosa are CCR5-tropic, making the CCR5-receptor a promising target for HIV-1-drug design [110,278]. Many clinical studies are currently in progress to assess the safety and efficacy of these inhibitors. To date, only one is clinically approved, the CCR5 inhibitor Maraviroc, which is currently used in combination with other retroviral drugs [238,279]. The crystal structure of Maraviroc in complex with a human CCR5-receptor provided detailed information about the inhibitor binding pocket [280], showing that maraviroc inhibits CCR5 in an allosteric way, leading to a conformational change in the receptor that prevents HIV-1 binding. Another high-affinity CCR5 antagonist is INCB9471 [239]. It is hypothesized that INCB9471 inhibits CCR5 in an allosteric and non-competitive way but at a binding site different from Maraviroc [281]. Although a phase II study was initiated and completed in 2007, no results of that study have been reported so far. To improve on Maraviroc, a second generation of similar inhibitors, including the imidazopiperidine PF-232798, have been developed [240]. Despite the structural similarities between Maraviroc and PF-232798, a crystal structure of the latter revealed a distinct binding mode and explaining the complementary resistance profile of the two inhibitors [282]. Currently, PF-232798 is being evaluated in a phase II clinical study. A third CCR-antagonist is the anilide cenicriviroc (TBR-652 formerly TAK-652) [241]. In addition to its high affinity for CCR5, TBR-652 is a potent antagonist of CCR2 and has shown activity against protease and reverse-transcriptase inhibitor-resistant HIV-1-strains. A phase II study showed that this inhibitor was well-tolerated and highly effective at reducing viral load. Additionally, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) levels in study subjects were increased, a feature consistent with CCR2 inhibition, resulting in a beneficial anti-inflammatory effect [283]. Another allosteric inhibitor of CCR5 is the pyrimidine Viciviroc [284]. Encouraging results in phase I/II studies led to two phase III studies in which Viciviroc was administered in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Whereas individuals who obtained more than three additional drugs showed no effect, patients with ≤2 drugs showed a slight decrease in viral load compared to the placebo group [242]. However, the effect was not sufficiently substantial to pursue the approval of Viciviroc.
Although small molecules can lead to very effective inhibitors, they sometimes exhibit severe side effects. The 2,5-diketoperazine Aplaviroc, for instance, provided subnanomolar activity against several HIV-1 isolates and was well tolerated in monkeys [243]. However, during clinical studies, severe hepatotoxicity was detected, leading to its clinical termination.
In addition to small molecule inhibitors, antibodies have been evaluated for inhibition of CCR5-tropic virus. One example is the IgG4-formatted antibody HGS004, which binds to the second extracellular loop of CCR5. HGS004 has been shown to be well-tolerated in patients infected with CCR5-tropic HIV-1 and reduced viral load in more than 50 % of patients after a single dose [244]. However, further clinical testing was not pursued after an initial trial. An excellent safety profile was also determined for the monoclonal antibody PRO140 (Leronlimab) [245]. Remarkably, this antibody has the potential to provide HIV-1-prophylaxis after a single subcutaneous injection a week and is currently further under investigation in a phase IIb and phase III study.
4.4.2. CXCR4-inhibitors
The CXCR4 receptor is a very extensively studied chemokine receptor as it plays a major role in multiple diseases [285]. However, in contrast to the large number of CCR5-inhibitors that have been discovered or that are in development for HIV-1-treatment, the number of CXCR4 inhibitors is more limited. The only CXCR4 inhibitor that was clinically tested in HIV-1-patients is the Benzodiazol AMD11070 [286]. A phase Ib/IIa revealed a good safety profile in a group of six HIV-1-infected participants [246]. However, the study provided discordant results regarding the efficacy and the evaluation was terminated after observation of increased toxicity in preclinical animal studies. The importance of CXCR4 in multiple processes makes it a difficult target for HIV-1-treatment since inhibitors can easily cause side-effects. The bicyclam AMD3100, for instance, was initially designed as an HIV-1 inhibitor [287] but it was shown that AMD3100 could cause leukocytosis [288]. In another study, it was shown that HIV-1-entry inhibitors possessing an agonistic rather than an antagonistic effect on CXCR4 are less disruptive, which may lead to safer HIV-1 entry inhibitors [289].
- Conclusion
As shown in current HIV-1 infection models, the biological context of viral cell entry challenges the development of effective entry inhibitors and vaccine candidates. A better understanding of how the mucosal environments can increase or reduce mucosal barrier function against the virus is essential to the development of an efficient strategy preventing HIV mucosal transmission. The potential to better understand the basic mechanisms of mucosal barrier function relevant to HIV transmission and entry makes a significant impact on the advancement of HIV prevention research.
As mucosal transmission mechanisms are being elucidated further along with the viral and host factors modulating infection initiation, preclinical models should also be evaluated to better represent natural infection [24,380]. For instance, it is common practice to infect the animals with cell-free virus particles to evaluate one treatment, although it is now established that infected body fluids at the origin of mucosal transmissions, such as semen, vaginal fluid, and breast milk, contain both cell-free and cell-associated HIV. As discussed above, the protective abilities of HIV-neutralizing agents (bnAbs and other molecules) are not limited to the neutralization of cell-free virus particles but also include cell-associated HIV [290]. Efforts in evaluating mucosal protection against both cell-free virus particles and cell-associated virus in preclinical studies should be encouraged to better model natural infections [291].
Similarly, evaluation of correlates of protections also demonstrates the multifactorial nature of HIV mucosal infection and spurs alternative approaches to limit HIV-1 infection. As such, some approaches investigate the reduction of HIV receptor and co-receptors expression [292] or develop new virucidal compounds [293,294]. As attempts to elicit bnAbs have encountered extreme difficulties [138], studies are increasingly oriented toward the prophylactic use of anti-HIV antibodies. Increasing efforts in antibody engineering to improve half-life and safety make passive immunization strategies exceedingly attractive. An example of advanced immunoprophylaxis is adeno-associated virus-mediated antibody gene delivery [295,296], which could be an alternative to vaccination to induce sustained expression of HIV nAbs.
5. Conclusions
As shown in current HIV-1 infection models, the biological context of viral cell entry challenges the development of effective entry inhibitors and vaccine candidates. A better understanding of how the mucosal environments can increase or reduce mucosal barrier function against the virus is essential to the development of an efficient strategy preventing HIV mucosal transmission. The potential to better understand the basic mechanisms of mucosal barrier function relevant to HIV transmission and entry make a significant impact on the advancement of HIV prevention research.
As mucosal transmission mechanisms are being elucidated further along with the viral and host factors modulating infection initiation, preclinical models should also be evaluated to better represent natural infection. For instance, it is common practice to infect the animals with cell-free virus particles to evaluate one treatment, although it is now established that infected body fluids at the origin of mucosal transmissions, such as semen, vaginal fluid, and breast milk, contain both cell-free and cell-associated HIV. As discussed above, the protective abilities of HIV-neutralizing agents (bnAbs and other molecules) are not limited to the neutralization of cell-free virus particles but also includes cell-associated HIV [215]. Efforts in evaluating mucosal protection against both cell-free virus particles and cell-associated virus in preclinical studies should be encouraged to better model natural infections [216].
Similarly, evaluation of correlates of protections also demonstrates the multifactorial nature of HIV mucosal infection and spurs alternative approaches to limit HIV-1 infection. As such, some approaches investigate the reduction of HIV receptor and co-receptors expression [217] or develop new virucidal compounds [218][219]. As attempts to elicit bnAbs have encountered extreme difficulties [94], studies are increasingly oriented toward the prophylactic use of anti-HIV antibodies. Increasing efforts in antibody engineering to improve half-life and safety make passive immunization strategies exceedingly attractive. An example of advanced immunoprophylaxis is adeno-associated virus-mediated antibody gene delivery [220][221], which could be an alternative to vaccination to induce sustained expression of HIV nAbs.
The extensive search towards antagonists that efficiently prevent viral entry enabled the approval of four different inhibitors that are now commonly used for HIV-treatment. Numerous inhibitors that are still under clinical evaluation will extend this list even further. Although no magic bullet has been identified so far, those inhibitors add to the armamentarium of existing HAART and therefore contribute to the treatment of drug-resistant viral strains. The high structural diversity among entry inhibitors demonstrates that similar effects can be achieved with small molecules or large antibodies, and concepts like bAVP have revealed the great potential of multifunctional inhibitors, which could be the appropriate answer to combat the multifactorial nature of HIV-infection [150].
The extensive search towards antagonists that efficiently prevent viral entry enabled the approval of four different inhibitors that are now commonly used for HIV-treatment. Numerous inhibitors that are still under clinical evaluation will extend this list even further. Although no magic bullet has been identified so far, those inhibitors add to the armamentarium of existing HAART and therefore contribute to the treatment of drug-resistant viral strains. The high structural diversity among entry inhibitors demonstrates that similar effects can be achieved with small molecules or large antibodies, and concepts like bAVP have revealed the great potential of multifunctional inhibitors, which could be the appropriate answer to combat the multifactorial nature of HIV-infection [225].
