Wastewater generation and treatment is an ever-increasing concern in the current century due to increased urbanization and industrialization. To tackle the situation of increasing environmental hazards, numerous wastewater treatment approaches are used—i.e., physical, chemical, and biological (primary to tertiary treatment) methods. Various treatment techniques being used have the risks of producing secondary pollutants. The most promising technique is the use of different materials as adsorbents that have a higher efficacy in treating wastewater, with a minimal production of secondary pollutants. Biosorption is a key process that is highly efficient and cost-effective. This method majorly uses the adsorption process/mechanism for toxicant removal from wastewater.
- adsorption
- agriculture waste and peels
- nanotechnology
- biosorption mechanism
- contaminant removal
1. Introduction
Water is an important natural resource; therefore, it must be preserved. As an important reserve for prevailing flora and fauna, it is necessary to prevent contamination via organic and inorganic pollutants. However, some technologies used for this purpose release secondary contaminants or byproducts which further pollute the environment [1,2]. Therefore, cost-effective and efficient wastewater treatment technologies are urgently needed [3,4]. Severe water scarcity is experienced throughout the world, highlighting the dire need for adequate food production throughout the year to fight hunger, deprivation, and malnutrition, requiring wastewater reuse for irrigation purposes [
Water is an important natural resource; therefore, it must be preserved. As an important reserve for prevailing flora and fauna, it is necessary to prevent contamination via organic and inorganic pollutants. However, some technologies used for this purpose release secondary contaminants or byproducts which further pollute the environment [1][2]. Therefore, cost-effective and efficient wastewater treatment technologies are urgently needed [3][4]. Severe water scarcity is experienced throughout the world, highlighting the dire need for adequate food production throughout the year to fight hunger, deprivation, and malnutrition, requiring wastewater reuse for irrigation purposes [5]. Water reuse through industrial wastewater recycling has gained the scientific community’s interest in the last few decades. Wastewater recycling is of great advantage in farming activities because it contains an ample amount of nutrients [6], so its treatment followed by agricultural application should be conducted with great prudence to ensure it is environmentally friendly, economical, and increases agricultural output [
5]. Water reuse through industrial wastewater recycling has gained the scientific community’s interest in the last few decades. Wastewater recycling is of great advantage in farming activities because it contains an ample amount of nutrients [6], so its treatment followed by agricultural application should be conducted with great prudence to ensure it is environmentally friendly, economical, and increases agricultural output [5].
].
The challenge in treating wastewater is much greater than it seems. There are two primary sources of contaminants in wastewater: (i) natural, including but not limited to volcanic activity, soil erosion, and the weathering of rocks, and (ii) mineral contaminant dispersion through anthropogenic activities, waste disposal sites, urban runoff, mining, the manufacture of printed circuit boards, agricultural activities, the treatment and electroplating of metal surfaces, fuel burning, textile dyes, the manufacture of semiconductors, etc., [7,8]. Wastewater generated from agriculture, industries, and the household sector contains a varying amount of noxious inorganic (heavy metals and excessive nutrients) and organic (pigments, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, etc.) contaminants that pose serious environmental and health risks [9,10,11,12]. Among the heavy metals (potentially toxic elements or PTEs) and metalloids, PTEs belong to the group of trace elements with a density > 4 ± 1 g cm
The challenge in treating wastewater is much greater than it seems. There are two primary sources of contaminants in wastewater: (i) natural, including but not limited to volcanic activity, soil erosion, and the weathering of rocks, and (ii) mineral contaminant dispersion through anthropogenic activities, waste disposal sites, urban runoff, mining, the manufacture of printed circuit boards, agricultural activities, the treatment and electroplating of metal surfaces, fuel burning, textile dyes, the manufacture of semiconductors, etc., [7][8]. Wastewater generated from agriculture, industries, and the household sector contains a varying amount of noxious inorganic (heavy metals and excessive nutrients) and organic (pigments, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, etc.) contaminants that pose serious environmental and health risks [9][10][11][12]. Among the heavy metals (potentially toxic elements or PTEs) and metalloids, PTEs belong to the group of trace elements with a density > 4 ± 1 g cm
−3. These include copper (Cu), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), zinc (Zn), tin (Sn), iron (Fe), lead (Pb), silver (Ag), manganese (Mn), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), arsenic (As), aluminum (Al), and nickel (Ni) [13,14] (
. These include copper (Cu), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), zinc (Zn), tin (Sn), iron (Fe), lead (Pb), silver (Ag), manganese (Mn), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), arsenic (As), aluminum (Al), and nickel (Ni) [13][14] (
Supplementary Information Table S1). Due to their persistence, higher mobility, and solubility, wastewater containing these PTEs is not properly treated and discharged into freshwater resources with various environmental and health effects. Additionally, these PTEs are taken up by aquatic organisms, crops, and other plant species and make their way to the human food chain, thereby exerting negative impacts on human health [15,16,17].
). Due to their persistence, higher mobility, and solubility, wastewater containing these PTEs is not properly treated and discharged into freshwater resources with various environmental and health effects. Additionally, these PTEs are taken up by aquatic organisms, crops, and other plant species and make their way to the human food chain, thereby exerting negative impacts on human health [15][16][17].
Apart from the natural and anthropogenic sources, there are two major types of wastewater pollutants—i.e., organic and inorganic pollutants. Organic pollutants include pesticides, phenols, herbicides, petroleum, dyes, oils, biphenyls, fats, proteins, starches, and medicines, while inorganic pollutants contain chemical fertilizers, PTEs, and excessive nutrients. They cause water quality deterioration and serious environmental problems [18,19]. To reduce the environmental and health risks posed by wastewater, multiple technologies are used that are based on varying degrees of treatments, chemical reactions, and processes, such as membrane filtration, reverse osmosis, chemical precipitation, solvent extraction, oxidation, and adsorption [20,21,22,23].
Apart from the natural and anthropogenic sources, there are two major types of wastewater pollutants—i.e., organic and inorganic pollutants. Organic pollutants include pesticides, phenols, herbicides, petroleum, dyes, oils, biphenyls, fats, proteins, starches, and medicines, while inorganic pollutants contain chemical fertilizers, PTEs, and excessive nutrients. They cause water quality deterioration and serious environmental problems [18][19]. To reduce the environmental and health risks posed by wastewater, multiple technologies are used that are based on varying degrees of treatments, chemical reactions, and processes, such as membrane filtration, reverse osmosis, chemical precipitation, solvent extraction, oxidation, and adsorption [20][21][22][23].
Among all of the above techniques, sorption using different adsorbent materials is thought to be simpler to execute and manage and is cost-efficient [24,25]. In addition to the primary benefits, this process does not cause secondary pollution from the generation of byproducts [26,27,28]. Minerals and organic and inorganic materials that are commonly used as adsorbents (such as activated clay minerals, carbon, industrial byproducts, zeolite, polymer materials, bio-fuels, farming waste, etc.) have different adsorption capacities for specific pollutants’ removal from wastewater [29].
Among all of the above techniques, sorption using different adsorbent materials is thought to be simpler to execute and manage and is cost-efficient [24][25]. In addition to the primary benefits, this process does not cause secondary pollution from the generation of byproducts [26][27][28]. Minerals and organic and inorganic materials that are commonly used as adsorbents (such as activated clay minerals, carbon, industrial byproducts, zeolite, polymer materials, bio-fuels, farming waste, etc.) have different adsorption capacities for specific pollutants’ removal from wastewater [29].
2. Organic Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment
2.1. Forestry and Wood Waste Adsorbent
Forestry waste (such as tree twigs, branches, leaves, and bark) is accumulated in large quantities in the form of solid waste and can be used as a feedstock for manufacturing adsorbents for wastewater treatments. Polysaccharides (pectin, cellulose) and polyphenol complexes (flavonoids, tannins, lignin, terpenes) have specific functional groups in combination with hydroxyl (-OH) or carboxyl (-COOH) groups with passing ions. These wastes have a high metal ion adsorption potential through the ion-exchange or chelation process [63]. Various types of forest waste—i.e., bark, chestnut borer, sawdust, pine pectin, and pine needles—have been used as adsorbents to remove PTEs. Among these biological wastes, chestnut bur has the maximum absorption value—i.e., 16.18 mg g
Forestry waste (such as tree twigs, branches, leaves, and bark) is accumulated in large quantities in the form of solid waste and can be used as a feedstock for manufacturing adsorbents for wastewater treatments. Polysaccharides (pectin, cellulose) and polyphenol complexes (flavonoids, tannins, lignin, terpenes) have specific functional groups in combination with hydroxyl (-OH) or carboxyl (-COOH) groups with passing ions. These wastes have a high metal ion adsorption potential through the ion-exchange or chelation process [30]. Various types of forest waste—i.e., bark, chestnut borer, sawdust, pine pectin, and pine needles—have been used as adsorbents to remove PTEs. Among these biological wastes, chestnut bur has the maximum absorption value—i.e., 16.18 mg g
−1
—and its bark has the value of 9.31 mg g
−1 [64]. Forestry wastes are also used to make biochar, an absorbent carbon material attained through slow pyrolysis. Biochar has the highest removal efficiency in removing PTEs—i.e., 264 mg g
[31]. Forestry wastes are also used to make biochar, an absorbent carbon material attained through slow pyrolysis. Biochar has the highest removal efficiency in removing PTEs—i.e., 264 mg g
−1—from wastewater [65]. It has been reported that the waste produced from the forest products has been used with an efficacy of more than 69%.
—from wastewater [32]. It has been reported that the waste produced from the forest products has been used with an efficacy of more than 69%.
2.2. Agricultural Waste as an Efficient Wastewater Adsorbent
Agricultural wastes are very popular feedstocks for making adsorbents due to their availability and cost-effectiveness. Agriculture waste has been used for many purposes, as mentioned in
. They usually consist of lignin and cellulose as the main components and have -OH and -COOH groups. These groups can be combined with metal ions by providing electron pairs to form complexes. Agricultural wastes such as grape straw, tea and coffee grounds, nutshells, papaya and plant leaves, waste grains, algae, crab apple shells, rice bowls, and sunflower plants have been used by many scientists to remove PTEs such as As, Cd(II), Cr(IV), Hg, Pb, and Ni. Used tea or coffee powder is an example of farming waste that is produced in large quantities and needs little or no treatment. As with other biomass waste products, these wastes symbolize unused resources (
Supplementary Information Table S2
).
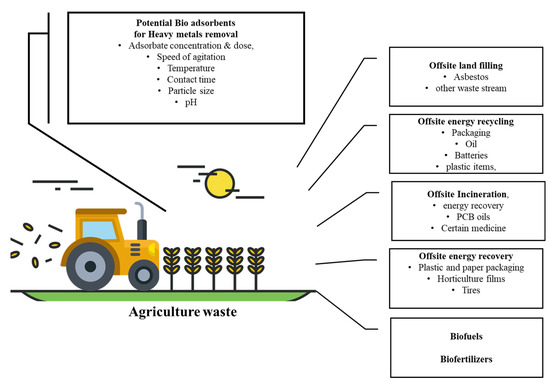
Figure 1.
Agricultural waste product usage in different processes.
Agricultural waste-derived adsorbents can be modified by different chemical pre-treatments to increase the potential of functional groups, thereby increasing the adsorption capacity of adsorbents [66]. Facts have also shown that lignocellulose biomass obtained from agricultural waste-based products could be an efficient feedstock for the manufacture of carbonaceous materials such as biochar, which has a higher surface area, pore volume, and pore distribution [67].
Agricultural waste-derived adsorbents can be modified by different chemical pre-treatments to increase the potential of functional groups, thereby increasing the adsorption capacity of adsorbents [33]. Facts have also shown that lignocellulose biomass obtained from agricultural waste-based products could be an efficient feedstock for the manufacture of carbonaceous materials such as biochar, which has a higher surface area, pore volume, and pore distribution [34].
Fruit and Vegetable Peels
In most kitchen waste containers, fruit and vegetable waste and peel make up the highest proportion. Many fruit and vegetable peels are disposed of in debris or fed to livestock directly. Vegetable and fruit wastes and byproducts that are produced in significant quantities during industrial processing/secondary product manufacturing constitute a severe problem. They must be managed or recycled due to their harmful environmental impact. Fruit and vegetable peels and skins are a natural, environmentally friendly, and economical source of adsorbents that can eliminate different types of water contaminants and reduce pollution, and are therefore a renewable and promising resource [88].
In most kitchen waste containers, fruit and vegetable waste and peel make up the highest proportion. Many fruit and vegetable peels are disposed of in debris or fed to livestock directly. Vegetable and fruit wastes and byproducts that are produced in significant quantities during industrial processing/secondary product manufacturing constitute a severe problem. They must be managed or recycled due to their harmful environmental impact. Fruit and vegetable peels and skins are a natural, environmentally friendly, and economical source of adsorbents that can eliminate different types of water contaminants and reduce pollution, and are therefore a renewable and promising resource [35].
Fruit shells—i.e., coconut shell—contain the dynamic functional groups of -OH and -COOH present in cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin which are involved in PTE (Cd, Pb, As, Cr, Cu, and Ni) binding and removal [89]. Feng et al. [90] examined the efficiency of fruit shell-based adsorbents to eliminate Cu(II) from galvanic wastewater. In 50 mL of wastewater samples holding 14.33 mg L
Fruit shells—i.e., coconut shell—contain the dynamic functional groups of -OH and -COOH present in cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin which are involved in PTE (Cd, Pb, As, Cr, Cu, and Ni) binding and removal [36]. Feng et al. [37] examined the efficiency of fruit shell-based adsorbents to eliminate Cu(II) from galvanic wastewater. In 50 mL of wastewater samples holding 14.33 mg L
−1 Cu(II) ions, the adsorption efficacy was recorded to be up to 97.1%. To evaluate the cost-effectiveness, the same process was repeated to check the adsorbent’s reusability, and it was concluded that the adsorbent could be reused for the same process multiple times [91].
Cu(II) ions, the adsorption efficacy was recorded to be up to 97.1%. To evaluate the cost-effectiveness, the same process was repeated to check the adsorbent’s reusability, and it was concluded that the adsorbent could be reused for the same process multiple times [38].
Santhi and Manonmani [92] reported that 6 g of adsorbent is enough to remove 90–95% Cr(VI) from the wastewater. The wastewater pollutant removal rate was increased with an increase in contact time to reach equilibrium after 120 min. The contaminant removal rate of citrus peel was recorded as 58.97% [93]. Citrus peel (
Santhi and Manonmani [39] reported that 6 g of adsorbent is enough to remove 90–95% Cr(VI) from the wastewater. The wastewater pollutant removal rate was increased with an increase in contact time to reach equilibrium after 120 min. The contaminant removal rate of citrus peel was recorded as 58.97% [40]. Citrus peel (
Citrus Nobilis) was also used to remove PTEs from 10 wastewater samples taken from the battery industry in Londrina (Brazil). For all samples, the remediation rate of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) by bio-adsorption was recorded to be up to 99.9% [94].
) was also used to remove PTEs from 10 wastewater samples taken from the battery industry in Londrina (Brazil). For all samples, the remediation rate of Cu(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) by bio-adsorption was recorded to be up to 99.9% [41].
2.3. Peat
The use of peat in wastewater remediation has gained attention in the past few decades due to its high porosity and adsorptive capacity. Many researchers classify peat into four groups: moor peat, wood peat, herbaceous peat, and sediment peat [95]. It has the properties of being rich, cheap, and versatile and has a sturdy adsorption capability for various toxins such as PTEs and organic contaminants [96]. Unprocessed peat contains many integral constituents such as lignin; cellulose; fulvic and humic acids; and polar functional groups such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and phenol hydroxides [97]. Peat also has a strong cation exchange capacity [98]. Its removal efficiency is higher for dyes when treated with acids. Peat collected from Panaga, Brunei Darussalam, showed a great affinity for the adsorption of congo red dye from wastewater.
The use of peat in wastewater remediation has gained attention in the past few decades due to its high porosity and adsorptive capacity. Many researchers classify peat into four groups: moor peat, wood peat, herbaceous peat, and sediment peat [42]. It has the properties of being rich, cheap, and versatile and has a sturdy adsorption capability for various toxins such as PTEs and organic contaminants [43]. Unprocessed peat contains many integral constituents such as lignin; cellulose; fulvic and humic acids; and polar functional groups such as alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and phenol hydroxides [44]. Peat also has a strong cation exchange capacity [45]. Its removal efficiency is higher for dyes when treated with acids. Peat collected from Panaga, Brunei Darussalam, showed a great affinity for the adsorption of congo red dye from wastewater.
2.4. Biochar
Agricultural waste-derived biochars have attracted greater attention among cheap and effective adsorbents for wastewater treatment [99]. They have a porous, stable structure and are an insoluble and carbon-rich solid material produced by pyrolysis (300–700 °C) under anaerobic conditions [100]. They can be produced from a broad range of agricultural and other biomass waste products such as crop straws, rice husks, yeast, sawdust, mud, kitchen waste, tea residue, and many others [101,102,103]. Biochar has been adopted as an efficient means of treating wastewater. Its ability to adsorb PTEs has been studied very critically in the past decade [104], showing that biochar is inexpensive, environmentally friendly, and more effective even than activated charcoal. The chemical properties of the biochar surface undergo complex and unpredictable changes during pyrolysis [105]. Although its low adsorptive efficiency of PTEs restricts its use into the field of sewage treatment, this is thought to be due to its low porosity, specific surface area, few adsorption sites, and functional groups [106].
Agricultural waste-derived biochars have attracted greater attention among cheap and effective adsorbents for wastewater treatment [46]. They have a porous, stable structure and are an insoluble and carbon-rich solid material produced by pyrolysis (300–700 °C) under anaerobic conditions [47]. They can be produced from a broad range of agricultural and other biomass waste products such as crop straws, rice husks, yeast, sawdust, mud, kitchen waste, tea residue, and many others [48][49][50]. Biochar has been adopted as an efficient means of treating wastewater. Its ability to adsorb PTEs has been studied very critically in the past decade [51], showing that biochar is inexpensive, environmentally friendly, and more effective even than activated charcoal. The chemical properties of the biochar surface undergo complex and unpredictable changes during pyrolysis [52]. Although its low adsorptive efficiency of PTEs restricts its use into the field of sewage treatment, this is thought to be due to its low porosity, specific surface area, few adsorption sites, and functional groups [53].
In general, the remediation of PTEs by biochar containing aqueous solutions may be carried out by physical and chemical interaction procedures such as the complexation of the outer and inner sphere, electrostatic attractiveness, ion exchange, and surface precipitation [107] (
In general, the remediation of PTEs by biochar containing aqueous solutions may be carried out by physical and chemical interaction procedures such as the complexation of the outer and inner sphere, electrostatic attractiveness, ion exchange, and surface precipitation [54] (
Figure 2). Following the results of adsorption kinetic trials and characterization experiments using Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM-eds), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), etc., the adsorbing process of biochar on PTEs commonly comprises physical adsorption, electrostatic attraction, ion-exchange, and complexation [108].
). Following the results of adsorption kinetic trials and characterization experiments using Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (SEM-eds), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), etc., the adsorbing process of biochar on PTEs commonly comprises physical adsorption, electrostatic attraction, ion-exchange, and complexation [55].
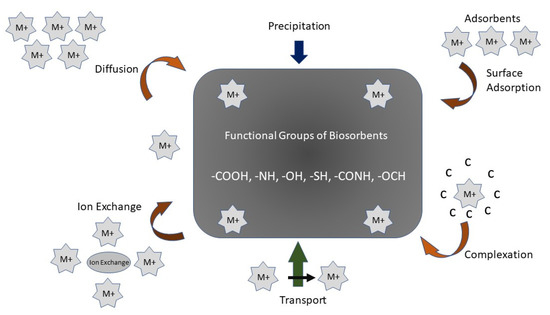
A schematic diagram of the mechanism of biochar/biosorbent to remediate contaminants.
The interior and surface structure of biochar comprise a blended allocation of macropores, mesopores, and micropores, whereby biochar maintains PTEs in its internal and surface pore structure. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy imaging has demonstrated that the functional groups of -COOH and -OH changed before and after adsorption because of complexation with Pb and Cd. The O-metal bond causes the electron density of O
2
to decrease, which drastically reduces the bound energy of the O
2-containing functional groups and improves its stability. The metal interaction can be interrupted by trembling in the C-C bonds [109]. Additionally, O
-containing functional groups and improves its stability. The metal interaction can be interrupted by trembling in the C-C bonds [56]. Additionally, O
2
which includes functional groups emits H
+
when ions are exchanged with PTEs, which leads to a reduction in the pH of the solution. Its surface charge properties are some of the standards used to determine the power of raw material in the electrostatic adsorbing process (
Figure 2). The pH and redox potential plays a crucial role in the adsorption of PTEs in wastewater [110].
). The pH and redox potential plays a crucial role in the adsorption of PTEs in wastewater [57].
2.5. Coal Based Adsorbents
Coal is an organic material that contains different minerals. Moreover, organic materials normally make up 85–95% (wt/wt) of coal’s dry biomass. Coal is a complicated sedimentary rock that mainly consists of the byproducts of plant residues and their derivatives. It is the source of carbon, although it also has different elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen. Coal and its derivatives are used not just as fuels, but as precious materials in various environmental protection processes as well. Coal is cheap and present abundantly, even some countries have numerous reserves of coal as mines. However, it has exciting properties that make it an efficient adsorptive material for removing various organic contaminants and PTEs [111].
Coal is an organic material that contains different minerals. Moreover, organic materials normally make up 85–95% (wt/wt) of coal’s dry biomass. Coal is a complicated sedimentary rock that mainly consists of the byproducts of plant residues and their derivatives. It is the source of carbon, although it also has different elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen. Coal and its derivatives are used not just as fuels, but as precious materials in various environmental protection processes as well. Coal is cheap and present abundantly, even some countries have numerous reserves of coal as mines. However, it has exciting properties that make it an efficient adsorptive material for removing various organic contaminants and PTEs [58].
Coal can form stable complexes with multiple PTEs because of the -COOH groups and phenol groups connected to its highly cross-linked aromatic structures. Carboxyl or hydroxyl groups can participate in ion exchange reactions [111]. Arpa et al. [112] reported that using inferior Turkish coal has the ability to efficiently remove Hg(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) ions from mining wastewater. Karabulut et al. [113] reported that inferior Turkish coal can also remove Cu and Zn from sewage sludge. The adsorption phenomenon appears to keep up with the Langmuir isotherm model. An analysis of crude coal and exchanged coal using FTIR showed that a significant amount of PTEs were removed and seen on the coal surface due to the development of exchange metal carboxylates. Multiple studies have also been carried out to unveil the removal of Cr at different oxidation levels from waste solutions by utilizing low-grade coal [114,115].
Coal can form stable complexes with multiple PTEs because of the -COOH groups and phenol groups connected to its highly cross-linked aromatic structures. Carboxyl or hydroxyl groups can participate in ion exchange reactions [58]. Arpa et al. [59] reported that using inferior Turkish coal has the ability to efficiently remove Hg(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) ions from mining wastewater. Karabulut et al. [60] reported that inferior Turkish coal can also remove Cu and Zn from sewage sludge. The adsorption phenomenon appears to keep up with the Langmuir isotherm model. An analysis of crude coal and exchanged coal using FTIR showed that a significant amount of PTEs were removed and seen on the coal surface due to the development of exchange metal carboxylates. Multiple studies have also been carried out to unveil the removal of Cr at different oxidation levels from waste solutions by utilizing low-grade coal [61][62].
3. Nanomaterials: Potential Use in Wastewater Treatment
Nanotechnology exists within the field of nanoscience. Nanomaterials are the world’s tiniest structures synthesized by humans, with a magnitude of a couple of nanometers [145]. More specifically, nanoparticles (NPs) are fragments which have a structural component in a dimension of not more than 100 nm [146]. NPs are being developed in numerous forms, such as nanowires, colloids, films, quantum dots, particles, and nanotubes [147]. For wastewater treatment, highly effective, environmentally friendly, and inexpensive NPs with unique functions have been developed to purify industrial wastewater, river water, groundwater, and drinking water [148]. Due to their unique properties, they can be divided into three types: nanoadsorbents, nanocatalysts, and nanofilms [149,150]. Nano-adsorbents can be produced by utilizing atoms of such components which are chemically effective and possess a high adsorbing capability on their surfaces [151,152,153].
Nanotechnology exists within the field of nanoscience. Nanomaterials are the world’s tiniest structures synthesized by humans, with a magnitude of a couple of nanometers [63]. More specifically, nanoparticles (NPs) are fragments which have a structural component in a dimension of not more than 100 nm [64]. NPs are being developed in numerous forms, such as nanowires, colloids, films, quantum dots, particles, and nanotubes [65]. For wastewater treatment, highly effective, environmentally friendly, and inexpensive NPs with unique functions have been developed to purify industrial wastewater, river water, groundwater, and drinking water [66]. Due to their unique properties, they can be divided into three types: nanoadsorbents, nanocatalysts, and nanofilms [67][68]. Nano-adsorbents can be produced by utilizing atoms of such components which are chemically effective and possess a high adsorbing capability on their surfaces [69][70][71].
3.1. Nano-Adsorbents
The use of nano-adsorbents for wastewater treatment is a positive approach for the removal of different contaminants. The potential of nano-adsorbents has been investigated in recent years. Smaller particle sizes increase their chemical activity and adsorption capacity [154]. Because of their role in the adsorption process, nano-adsorbents are roughly divided into different groups. These include metal nanoparticles (NPs), nanostructured mixed oxides, magnetic NPs, and metal oxide NPs. In addition, the latest developments include carbon nanomaterials, carbon NPs, and carbon nanosheets. In addition, various types of silicon NPs are being used as nano-adsorptive silicon nanotubes, silicon NPs, and silicon nanosheets. In one study, nano-tones, polymer-based nanomaterials, nanofibers, and aerogels were some type of NPs that has been utilized to remove PTEs from wastewater [155].
The use of nano-adsorbents for wastewater treatment is a positive approach for the removal of different contaminants. The potential of nano-adsorbents has been investigated in recent years. Smaller particle sizes increase their chemical activity and adsorption capacity [72]. Because of their role in the adsorption process, nano-adsorbents are roughly divided into different groups. These include metal nanoparticles (NPs), nanostructured mixed oxides, magnetic NPs, and metal oxide NPs. In addition, the latest developments include carbon nanomaterials, carbon NPs, and carbon nanosheets. In addition, various types of silicon NPs are being used as nano-adsorptive silicon nanotubes, silicon NPs, and silicon nanosheets. In one study, nano-tones, polymer-based nanomaterials, nanofibers, and aerogels were some type of NPs that has been utilized to remove PTEs from wastewater [73].
Chemical composition, structure, solubility, shape, fractal dimension, size, and surface chemistry are factors that affect the performance of NPs used as adsorbents [156]. Chemical activities as well as particle size are two important features of NPs. In comparison to other ingredients (such as titanium dioxide and aluminum oxide on a normal scale), NPs have outstanding advantages [154]. In addition, NPs may be modified with a specific reagent to improve their pre-concentration performance for metal ions [157]. The adsorption process will depend upon the adsorption coefficient and the regeneration and distribution of pollutants in accordance with the equilibrium conditions [158]. In addition, a redox reaction with persistent inorganic pollutants facilitates the start of the transformation of the ion structure [159]. Still, some scientists agree that variations in the redox conditions affect the toxic effects of those toxins [160]. The most used NPs as adsorbents for PTEs are graphene, iron oxide, magnesium oxide, activated carbon, manganese oxide, zinc oxide, titanium oxide, and CNTs [161].
Chemical composition, structure, solubility, shape, fractal dimension, size, and surface chemistry are factors that affect the performance of NPs used as adsorbents [74]. Chemical activities as well as particle size are two important features of NPs. In comparison to other ingredients (such as titanium dioxide and aluminum oxide on a normal scale), NPs have outstanding advantages [72]. In addition, NPs may be modified with a specific reagent to improve their pre-concentration performance for metal ions [75]. The adsorption process will depend upon the adsorption coefficient and the regeneration and distribution of pollutants in accordance with the equilibrium conditions [76]. In addition, a redox reaction with persistent inorganic pollutants facilitates the start of the transformation of the ion structure [77]. Still, some scientists agree that variations in the redox conditions affect the toxic effects of those toxins [78]. The most used NPs as adsorbents for PTEs are graphene, iron oxide, magnesium oxide, activated carbon, manganese oxide, zinc oxide, titanium oxide, and CNTs [79].
3.2. Nanocomposites in Wastewater Treatment
Nanocomposites (NCs) are usually a mixture of components (two or more) with different properties that are usually processed into a single substance with a comprehensive set of properties [162]. The key advantage of using composite materials is the ability to combine the characteristics of two materials for certain applications. Under the current circumstances, NPs have achieved popularity in different areas, such as the construction, aviation, vehicle, and biomedicine industries [163,164]. Researchers are focusing on the use of these materials in wastewater treatment [165].
Nanocomposites (NCs) are usually a mixture of components (two or more) with different properties that are usually processed into a single substance with a comprehensive set of properties [80]. The key advantage of using composite materials is the ability to combine the characteristics of two materials for certain applications. Under the current circumstances, NPs have achieved popularity in different areas, such as the construction, aviation, vehicle, and biomedicine industries [81][82]. Researchers are focusing on the use of these materials in wastewater treatment [83].
It is known that NPs have a high surface area to volume ratio and can significantly improve the matrix properties (metal/polymer/ceramic) of NPs built into them to form composite materials. In recent years, nano particles (NPs) have been used to remove micropollutants due to their large surface area, adhesion properties, cost effectiveness, antifouling properties, thermal stability, and excellent mechanical characteristics [166]. A cerium oxide NC structure was developed and has the possibility to remove carbon monoxide and contaminants from wastewater [167]. Another important strategy for the use of NCs is to magnetize CNTs with iron (zero valence) and then optimize the adsorption behavior in order to eliminate nitrates, chlorinated organic toxins, and metals from water [164,168].
It is known that NPs have a high surface area to volume ratio and can significantly improve the matrix properties (metal/polymer/ceramic) of NPs built into them to form composite materials. In recent years, nano particles (NPs) have been used to remove micropollutants due to their large surface area, adhesion properties, cost effectiveness, antifouling properties, thermal stability, and excellent mechanical characteristics [84]. A cerium oxide NC structure was developed and has the possibility to remove carbon monoxide and contaminants from wastewater [85]. Another important strategy for the use of NCs is to magnetize CNTs with iron (zero valence) and then optimize the adsorption behavior in order to eliminate nitrates, chlorinated organic toxins, and metals from water [82][86].
3.3. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are widely researched materials that can remediate PTEs and different organic contaminants from wastewater by an adsorption mechanism [169]. Yet, their inadequate disposability, problems in their separation, and tiny particle sizes are the problems with using CNT as adsorbents. In order to address these issues, researchers altered ordinary CNTs to modified CNTs such as multi-walled CNTs [170]. The modified magnetic CNTs have an elevated disposability and could easily be eliminated from wastewater or applied media with magnets [171]. Various studies have described the use of multi-walled CNTs to remove Pb, Mn [170], and Cu [172]. Gupta et al. [173] examined the adsorption capacities of treated and un-treated CNTs for Al removal. It was revealed that the coated CNTs showed a greater removal capacity than uncoated CNTs.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are widely researched materials that can remediate PTEs and different organic contaminants from wastewater by an adsorption mechanism [87]. Yet, their inadequate disposability, problems in their separation, and tiny particle sizes are the problems with using CNT as adsorbents. In order to address these issues, researchers altered ordinary CNTs to modified CNTs such as multi-walled CNTs [88]. The modified magnetic CNTs have an elevated disposability and could easily be eliminated from wastewater or applied media with magnets [89]. Various studies have described the use of multi-walled CNTs to remove Pb, Mn [88], and Cu [90]. Gupta et al. [91] examined the adsorption capacities of treated and un-treated CNTs for Al removal. It was revealed that the coated CNTs showed a greater removal capacity than uncoated CNTs.
The surface alteration of CNTs can improve their whole adsorptive activity. Numerous researchers have reported various surface modification techniques, including acid treatment [174], metal impregnation [175], and functional molecule/group transplantation [176]. The modification of the properties of CNTs is another method to improve their efficiency for pollutant removal. This can be carried out in several ways—e.g., through plasma technology, chemical alteration, and microwaves [175]. Among these technologies, plasma technology is considered one of the most suitable because of its lower energy consumption and environmentally friendly process. Chen et al. [176] described the usefulness of modified CNTs spliced with different functional groups for the remediation of PTE-contaminated water. In addition, CNTs altered with metals/metal oxides such as MnO
The surface alteration of CNTs can improve their whole adsorptive activity. Numerous researchers have reported various surface modification techniques, including acid treatment [92], metal impregnation [93], and functional molecule/group transplantation [94]. The modification of the properties of CNTs is another method to improve their efficiency for pollutant removal. This can be carried out in several ways—e.g., through plasma technology, chemical alteration, and microwaves [93]. Among these technologies, plasma technology is considered one of the most suitable because of its lower energy consumption and environmentally friendly process. Chen et al. [94] described the usefulness of modified CNTs spliced with different functional groups for the remediation of PTE-contaminated water. In addition, CNTs altered with metals/metal oxides such as MnO
2
and Al
2
O
3 have shown promising results for their adsorption mechanism [173,177,178].
have shown promising results for their adsorption mechanism [91][95][96].
3.4. Graphene Based Nano-Adsorbents
Besides the utilization of NPs, NCs, and CNTs in wastewater treatment, graphene also has special properties to be used individually and in combination with other NPs. Graphene oxide (GO) is a carbon nanomaterial with a two-dimensional structure which is manufactured through the chemical oxidation of a graphite coating [179]. Due to its large surface area, high mechanical strength, low weight, flexibility, and chemical stability, GO has attracted increasing attention as an adsorbent for removing PTEs [180]. Ding et al. [181] effectively used GO in column reactors to remove PTEs from wastewater. Lee and Yang [182] modified GO with TiO
Besides the utilization of NPs, NCs, and CNTs in wastewater treatment, graphene also has special properties to be used individually and in combination with other NPs. Graphene oxide (GO) is a carbon nanomaterial with a two-dimensional structure which is manufactured through the chemical oxidation of a graphite coating [97]. Due to its large surface area, high mechanical strength, low weight, flexibility, and chemical stability, GO has attracted increasing attention as an adsorbent for removing PTEs [98]. Ding et al. [99] effectively used GO in column reactors to remove PTEs from wastewater. Lee and Yang [100] modified GO with TiO
2
and applied hybrid composites to adsorb Zn, Cd, and Pb from wastewater. The adsorption capacity of the hybrid complex for Pb, Cd, and Zn reached 65.6 mg g
−1
, 72.8 mg/g, and 88.9 mg g
−1
, respectively. Graphene as well as other composite materials displays an extremely high removal of PTEs from wastewater [27].
3.5. Magnetic Nanocomposites
Magnetic NCs are a unique category of nanomaterials. They have core-shell nanostructures that can be quickly and easily restored by exterior magnetic fields. Functional group NPs may be grafted as well as fixed on Fe
3
O
4 NPs through chemical bonding or direct deposition [183]. Raw materials which can be coated are Ag, TiO
NPs through chemical bonding or direct deposition [101]. Raw materials which can be coated are Ag, TiO
2
, CNT, GO, Pd, and SiO
2
. Silicon oxide coating can offer a large surface area as well as echo porosity while at the same time keeping the magnetic core from erosion (
Supplementary Information Table S3). After coating, the resulting magnetic NCs generally show improved adsorption capacities and have fast kinetics for the removal of pollutants such as PTEs, pigments, phenolic substances, and microorganisms [184]. In the last few years, Cui et al. [185] synthesized a sequence of porous magnetic nanowires based on manganese that have been synthesized to remediate PTEs and various organic contaminants. A straightforward one-step solvothermal process was also proposed to produce hollow magnetic carbon spheres that are very effective in removing PTEs.
). After coating, the resulting magnetic NCs generally show improved adsorption capacities and have fast kinetics for the removal of pollutants such as PTEs, pigments, phenolic substances, and microorganisms [102]. In the last few years, Cui et al. [103] synthesized a sequence of porous magnetic nanowires based on manganese that have been synthesized to remediate PTEs and various organic contaminants. A straightforward one-step solvothermal process was also proposed to produce hollow magnetic carbon spheres that are very effective in removing PTEs.
Jin et al. [110] concluded that amino acid-modified magnetic NPs can adsorb up to 94% of the bacteria cells in a pH spectrum of 4–10 within 20 min. Zhang et al. [186] developed other multifunctional magnetic NPs coated with a polyethylene core which can inactivate bacteria by penetrating the cell membrane and remove PTEs by chelation. In addition, these NCs can be regenerated by Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and NaOH and reused.
Jin et al. [57] concluded that amino acid-modified magnetic NPs can adsorb up to 94% of the bacteria cells in a pH spectrum of 4–10 within 20 min. Zhang et al. [104] developed other multifunctional magnetic NPs coated with a polyethylene core which can inactivate bacteria by penetrating the cell membrane and remove PTEs by chelation. In addition, these NCs can be regenerated by Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and NaOH and reused.
3.6. Combination of Biological-Nano Technology Processes
There are various technologies to harvest algal biomass, such as deposition, centrifugation, and air flotation, in which condensed chemicals are used as a carrier. However, these technologies cannot be used on a large scale due to their high costs [187]. In these advanced technologies, membrane technology is the utmost advantageous method for algae growth and biomass production, in which the cultivation of algae with a high density is only completed by membrane bioreactors [188]. The advantage of membrane technology is that no coagulants need to be added for membrane filtration, which promotes the reuse of filtered water and simplifies the separation of algal biomass [189]. Scientific and technical technologies on a nanoscale show that many existing problems with water quality can be solved using nanostructured catalytic membranes, nano-catalysts, nano-absorbents, nanotubes, nano-powder, and micro-molecules [190]. These are all NPs and colloids that have a significant impression on the quality of water in the treatment procedure [191]. A study has demonstrated that combining wastewater treatment processes with advanced nanotechnology can produce highly effective water treatment systems [192]. The cultivation of algae in wastewater is one of the most useful approaches for energy generation and wastewater treatment. Many types of algae show effectiveness due to the presence of PTEs [156]. Nutrients are mixed with water to form a solution which provide the essential growth conditions required for algae. In addition, algae biomass is recovered more efficiently than conventional methods without damaging the cells, and the energy requirement for the algae harvest is less than other methods [193]. Polyvinylidene fluoride, poly sulfone, and polyether sulfone membranes are widely useful because of their physiochemical stability, although the main problem is membrane material and the microbial cells between the hydrophobic mechanism and membrane contamination [194]. Research has indicated that NPs can improve hydrophilicity and decrease membrane contamination—for example, CNTs and TiO
There are various technologies to harvest algal biomass, such as deposition, centrifugation, and air flotation, in which condensed chemicals are used as a carrier. However, these technologies cannot be used on a large scale due to their high costs [105]. In these advanced technologies, membrane technology is the utmost advantageous method for algae growth and biomass production, in which the cultivation of algae with a high density is only completed by membrane bioreactors [106]. The advantage of membrane technology is that no coagulants need to be added for membrane filtration, which promotes the reuse of filtered water and simplifies the separation of algal biomass [107]. Scientific and technical technologies on a nanoscale show that many existing problems with water quality can be solved using nanostructured catalytic membranes, nano-catalysts, nano-absorbents, nanotubes, nano-powder, and micro-molecules [108]. These are all NPs and colloids that have a significant impression on the quality of water in the treatment procedure [109]. A study has demonstrated that combining wastewater treatment processes with advanced nanotechnology can produce highly effective water treatment systems [110]. The cultivation of algae in wastewater is one of the most useful approaches for energy generation and wastewater treatment. Many types of algae show effectiveness due to the presence of PTEs [74]. Nutrients are mixed with water to form a solution which provide the essential growth conditions required for algae. In addition, algae biomass is recovered more efficiently than conventional methods without damaging the cells, and the energy requirement for the algae harvest is less than other methods [111]. Polyvinylidene fluoride, poly sulfone, and polyether sulfone membranes are widely useful because of their physiochemical stability, although the main problem is membrane material and the microbial cells between the hydrophobic mechanism and membrane contamination [112]. Research has indicated that NPs can improve hydrophilicity and decrease membrane contamination—for example, CNTs and TiO
2 [192].
[110].
The performance of microbial fuel cells can be improved by using inexpensive NCs such as nanoscale carbon in electrodes, as electrodes are mechanically stable and have a large surface area, great electrical conductivity, and good electrochemical catalyst activity [195]. Because of all the unique properties of platinum (Pt), commercial Pt cathode catalysts can therefore be replaced by CNT/Pt in microbial fuel cells [196]. To increase the adhesion of microorganisms and decrease toxicity, CNTs were also coated by numerous anemic polymers such as polyaniline and poly-pyrrole to constitute NCs. These NCs comprise in the negative charged CNTs, which are combined by electrostatic interaction with positively charged polycationic polymers as microbial fuel cells anodes [197].
The performance of microbial fuel cells can be improved by using inexpensive NCs such as nanoscale carbon in electrodes, as electrodes are mechanically stable and have a large surface area, great electrical conductivity, and good electrochemical catalyst activity [113]. Because of all the unique properties of platinum (Pt), commercial Pt cathode catalysts can therefore be replaced by CNT/Pt in microbial fuel cells [114]. To increase the adhesion of microorganisms and decrease toxicity, CNTs were also coated by numerous anemic polymers such as polyaniline and poly-pyrrole to constitute NCs. These NCs comprise in the negative charged CNTs, which are combined by electrostatic interaction with positively charged polycationic polymers as microbial fuel cells anodes [115].
References
- Stackelberg, P.E.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Zaugg, S.D.; Henderson, A.K.; Reissman, D.B. Persistence of pharmaceutical compounds and other organic wastewater contaminants in a conventional drinking-water-treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 329, 99–113.
- Bartolomeu, M.; Neves, M.; Faustino, M.; Almeida, A. Wastewater chemical contaminants: Remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 1573–1598.
- Bueno, P.D.L.C.; Gillerman, L.; Gehr, R.; Oron, G. Nanotechnology for sustainable wastewater treatment and use for agricultural production: A comparative long-term study. Water Res. 2017, 110, 66–73.
- Salgot, M.; Folch, M. Wastewater treatment and water reuse. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 2, 64–74.
- Inyinbor, A.A.; Bello, O.S.; Oluyori, A.P.; Inyinbor, H.E.; Fadiji, A.E. Wastewater conservation and reuse in quality vegetable cultivation: Overview, challenges and future prospects. Food Control 2019, 98, 489–500.
- Ganjegunte, G.; Ulery, A.; Niu, G.; Wu, Y. Organic carbon, nutrient, and salt dynamics in saline soil and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) irrigated with treated municipal wastewater. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 80–90.
- Launay, M.A.; Dittmer, U.; Steinmetz, H. Organic micropollutants discharged by combined sewer overflows–characterisation of pollutant sources and stormwater-related processes. Water Res. 2016, 104, 82–92.
- Chowdhary, P.; Raj, A.; Bharagava, R.N. Environmental pollution and health hazards from distillery wastewater and treatment approaches to combat the environmental threats: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 229–246.
- Rashed, M.N. Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater. Org. Pollut. Monit. Risk Treat. 2013, 167–194.
- Roccaro, P.; Sgroi, M.; Vagliasindi, F.G. Removal of xenobiotic compounds from wastewater for environment protection: Treatment processes and costs. Chem. Eng. Trans 2013, 32.
- Zheng, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Z.; Li, A. Treatment technologies for organic wastewater. Water Treat. 2013, 11, 250–286.
- Ariffin, N.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Zainol, M.R.R.M.A.; Murshed, M.F.; Faris, M.A.; Bayuaji, R. Review on adsorption of heavy metal in wastewater by using geopolymer. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, 5–6 August 2016; p. 01023.
- Mohammed, A.S.; Kapri, A.; Goel, R. Heavy metal pollution: Source, impact, and remedies. In Biomanagement of Metal-Contaminated Soils; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–28.
- Hussain, M.M.; Wang, J.; Bibi, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Iqbal, J.; Mian, I.A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Bashir, S.; Shah, N.S. Arsenic speciation and biotransformation pathways in the aquatic ecosystem: The significance of algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 403, 124027.
- Barakat, M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377.
- Akpor, O.; Otohinoyi, D.; Olaolu, D.; Aderiye, B. Pollutants in wastewater effluents: Impacts and remediation processes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Earth Sci. 2014, 3, 50–59.
- Harvey, P.; Handley, H.; Taylor, M. Identification of the sources of metal (lead) contamination in drinking waters in north-eastern Tasmania using lead isotopic compositions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12276–12288.
- Ali, M. Assessment of some water quality characteristics and determination of some heavy metals in Lake Manzala, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2008, 12, 133–154.
- Alssgeer, H.M.A.; Gasim, M.B.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Abdulhadi, E.R.A.; Azid, A. GIS-based analysis of water quality deterioration in the Nerus River, Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 112, 334–343.
- Bolan, N.S. Water Encyclopedia: Domestic, Municipal, and Industrial Water Supply and Waste Disposal. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1299.
- Lehr, J.H.; Keeley, J.; Lehr, J. Domestic, Municipal, and Industrial Water Supply and Waste Disposal; Wiley Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005.
- Caicedo, C.; Rosenwinkel, K.-H.; Exner, M.; Verstraete, W.; Suchenwirth, R.; Hartemann, P.; Nogueira, R. Legionella occurrence in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants and risks of reclaimed wastewater reuse. Water Res. 2019, 149, 21–34.
- Choudhary, M.; Peter, C.; Shukla, S.K.; Govender, P.P.; Joshi, G.M.; Wang, R. Environmental issues: A challenge for wastewater treatment. In Green Materials for Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–12.
- Sharahi, F.J.; Shahbazi, A. Melamine-based dendrimer amine-modified magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient Pb (II) adsorbent for wastewater treatment: Adsorption optimization by response surface methodology. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 291–300.
- De Gisi, S.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40.
- Dubey, S.P.; Gopal, K.; Bersillon, J. Utility of adsorbents in the purification of drinking water: A review of characterization, efficiency and safety evaluation of various adsorbents. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 327–332.
- Santhosh, C.; Velmurugan, V.; Jacob, G.; Jeong, S.K.; Grace, A.N.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 1116–1137.
- Ersan, G.; Apul, O.G.; Perreault, F.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption of organic contaminants by graphene nanosheets: A review. Water Res. 2017, 126, 385–398.
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24.
- Cutillas-Barreiro, L.; Paradelo, R.; Igrexas-Soto, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Fernández-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Álvarez-Rodriguez, E.; Garrote, G.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M. Valorization of biosorbent obtained from a forestry waste: Competitive adsorption, desorption and transport of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 131, 118–126.
- Kim, N.; Park, M.; Park, D. A new efficient forest biowaste as biosorbent for removal of cationic heavy metals. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 629–632.
- Aghababaei, A.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M. Optimized removal of oxytetracycline and cadmium from contaminated waters using chemically-activated and pyrolyzed biochars from forest and wood-processing residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 28–36.
- Pyrzynska, K. Removal of cadmium from wastewaters with low-cost adsorbents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102795.
- Nor, N.M.; Lau, L.C.; Lee, K.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Synthesis of activated carbon from lignocellulosic biomass and its applications in air pollution control—A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 658–666.
- Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Agricultural waste peels as versatile biomass for water purification—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 244–271.
- Abdolali, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Lu, S.; Chen, S.-S.; Nguyen, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. A breakthrough biosorbent in removing heavy metals: Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism analyses in a lab-scale study. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 603–611.
- Feng, N.; Guo, X.; Liang, S. Adsorption study of copper (II) by chemically modified orange peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1286–1292.
- Rao, R.A.K.; Kashifuddin, M. Pottery glaze—An excellent adsorbent for the removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution. Chin. J. Geochem. 2012, 31, 136–146.
- Santhi, T.; Manonmani, S. Malachite green removal from aqueous solution by the peel of Cucumis sativa fruit. Clean–SoilAirWater 2011, 39, 162–170.
- Devi, R.; Singh, V.; Kumar, A. COD and BOD reduction from coffee processing wastewater using Avacado peel carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1853–1860.
- Inagaki, C.S.; Caretta, T.d.O.; Alfaya, R.V.d.S.; Alfaya, A.A.d.S. Mexerica mandarin (Citrus nobilis) peel as a new biosorbent to remove Cu (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II) from industrial effluent. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5537–5546.
- Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Hu, J.; Zhou, C.; Cai, X.; Wang, W.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, J. Durably antibacterial and bacterially antiadhesive cotton fabrics coated by cationic fluorinated polymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6124–6136.
- Chwastowski, J.; Staroń, P.; Kołoczek, H.; Banach, M. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions using Canadian peat and coconut fiber. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 981–989.
- Zehra, T.; Priyantha, N.; Lim, L.B. Removal of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution using yeast-treated peat as adsorbent: Thermodynamics, kinetics, and equilibrium studies. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 357.
- Vecino, X.; Devesa-Rey, R.; Cruz, J.; Moldes, A. Entrapped peat in alginate beads as green adsorbent for the elimination of dye compounds from vinasses. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1448.
- Bardestani, R.; Roy, C.; Kaliaguine, S. The effect of biochar mild air oxidation on the optimization of lead (II) adsorption from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 404–420.
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Tankpa, V.; Bai, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, X. Mechanisms and reutilization of modified biochar used for removal of heavy metals from wastewater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1298–1309.
- Semerjian, L. Removal of heavy metals (Cu, Pb) from aqueous solutions using pine (Pinus halepensis) sawdust: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 12, 91–103.
- Gong, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, R.; Wei, J.; Huang, C.; Xu, P.; Wan, J.; Zhang, C. Pyrolysis and reutilization of plant residues after phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated sediments: For heavy metals stabilization and dye adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 64–71.
- Hubadillah, S.K.; Othman, M.H.D.; Harun, Z.; Ismail, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J. A novel green ceramic hollow fiber membrane (CHFM) derived from rice husk ash as combined adsorbent-separator for efficient heavy metals removal. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 4716–4720.
- Zheng, W.; Guo, M.; Chow, T.; Bennett, D.N.; Rajagopalan, N. Sorption properties of greenwaste biochar for two triazine pesticides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 121–126.
- Huggins, T.M.; Pietron, J.J.; Wang, H.; Ren, Z.J.; Biffinger, J.C. Graphitic biochar as a cathode electrocatalyst support for microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 195, 147–153.
- Liu, W.-J.; Zeng, F.-X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.-S. Preparation of high adsorption capacity bio-chars from waste biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8247–8252.
- Uddin, M.K. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462.
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Fang, J.; Sun, Y.; Cao, X. Sorption of heavy metals on chitosan-modified biochars and its biological effects. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 512–518.
- Karunanayake, A.G.; Todd, O.A.; Crowley, M.L.; Ricchetti, L.B.; Pittman Jr, C.U.; Anderson, R.; Mlsna, T.E. Rapid removal of salicylic acid, 4-nitroaniline, benzoic acid and phthalic acid from wastewater using magnetized fast pyrolysis biochar from waste Douglas fir. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 319, 75–88.
- Jin, H.; Capareda, S.; Chang, Z.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. Biochar pyrolytically produced from municipal solid wastes for aqueous As (V) removal: Adsorption property and its improvement with KOH activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 622–629.
- Simate, G.S.; Maledi, N.; Ochieng, A.; Ndlovu, S.; Zhang, J.; Walubita, L.F. Coal-based adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2291–2312.
- Arpa, Ç.; Başyilmaz, E.; Bektaş, S.; Genç, Ö.; Yürüm, Y. Cation exchange properties of low rank Turkish coals: Removal of Hg, Cd and Pb from waste water. Fuel Process. Technol. 2000, 68, 111–120.
- Karabulut, S.; Karabakan, A.; Denizli, A.; Yürüm, Y. Batch removal of copper (II) and zinc (II) from aqueous solutions with low-rank Turkish coals. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 18, 177–184.
- Gode, F.; Pehlivan, E. Adsorption of Cr (III) ions by Turkish brown coals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 875–884.
- Anwar, J.; Shafique, U.; Salman, M.; Anwar, S.; Anzano, J.M. Removal of chromium (III) by using coal as adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 797–801.
- Chaturvedi, S.; Dave, P.N.; Shah, N. Applications of nano-catalyst in new era. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2012, 16, 307–325.
- Amin, M.; Alazba, A.; Manzoor, U. A review of removal of pollutants from water/wastewater using different types of nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 825910.
- Lubick, N.; Betts, K. Silver Socks Have Cloudy Lining|Court Bans Widely Used Flame Retardant; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Theron, J.; Walker, J.; Cloete, T. Nanotechnology and water treatment: Applications and emerging opportunities. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 34, 43–69.
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Pan, K.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y. Removal of Cu (II) by loofah fibers as a natural and low-cost adsorbent from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 401–407.
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, R.; Xu, P.; Chen, R.; He, Q.; Zhong, J.; Gu, X. Performance study of ZrO2 ceramic micro-filtration membranes used in pretreatment of DMF wastewater. Desalination 2014, 346, 1–8.
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Nanoadsorbents for pollutants removal: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 203, 159–168.
- El Saliby, I.; Shon, H.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Nanotechnology for wastewater treatment: In brief. Encycl. Life Support Syst. Eolss 2008, 7.
- Oppong, S.O.; Anku, W.W.; Shukla, S.K.; Govender, P.P. Lanthanum doped–TiO2 decorated on graphene oxide nanocomposite: A photocatalyst for enhanced degradation of acid blue 40 under simulated solar light. Adv. Mater. Lett 2017, 8, 295–302.
- Kalfa, O.M.; Yalçınkaya, Ö.; Türker, A.R. Synthesis of nano B2O3/TiO2 composite material as a new solid phase extractor and its application to preconcentration and separation of cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 455–461.
- Anjum, M.; Miandad, R.; Waqas, M.; Gehany, F.; Barakat, M. Remediation of wastewater using various nano-materials. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4897–4919.
- Abou-Shanab, R.A.; Ji, M.-K.; Kim, H.-C.; Paeng, K.-J.; Jeon, B.-H. Microalgal species growing on piggery wastewater as a valuable candidate for nutrient removal and biodiesel production. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 115, 257–264.
- Khajeh, M.; Sanchooli, E. Synthesis and evaluation of silver nanoparticles material for solid phase extraction of cobalt from water samples. Appl. Nanosci. 2011, 1, 205–209.
- Mehrizad, A.; Zare, K.; Dashti, K.H.; Dastmalchi, S.; Aghaie, H.; Gharbani, P. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol on nano-TiO2. JPTC 2011, 8, 33–37.
- Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.; Sadegh, H.; Ghoshekandi, R.S.; Makhlouf, A.S.H. Nanoparticles as adsorbent; a positive approach for removal of noxious metal ions: A review. Sci. Technol. Dev. 2017, 34, 195–214.
- Ray, P.C. Size and shape dependent second order nonlinear optical properties of nanomaterials and their application in biological and chemical sensing. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5332–5365.
- Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Dubey, B.K. Hybrid nanoadsorbents for drinking water treatment: A critical review. Hybrid Nanomater. Adv. Energy Environ. Polym. Nanocompos. 2017, 199.
- Singh, L.; Goga, G.; Rathi, M.K. Latest developments in composite materials. IOSR J. Eng. IOSRJEN 2012, 2, 152–158.
- Mahajan, G.; Aher, V. Composite material: A review over current development and automotive application. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2012, 2, 1–5.
- Anku, W.W.; Oppong, S.O.-B.; Shukla, S.K.; Agorku, E.S.; Govender, P.P. Chitosan–sodium alginate encapsulated Co-doped ZrO 2–MWCNTs nanocomposites for photocatalytic decolorization of organic dyes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 7231–7245.
- Jaspal, D.; Malviya, A. Composites for wastewater purification: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125788.
- Beyene, H.D.; Ambaye, T.G. Application of sustainable nanocomposites for water purification process. In Sustainable Polymer Composites and Nanocomposites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 387–412.
- Zhong, L.-S.; Hu, J.-S.; Cao, A.-M.; Liu, Q.; Song, W.-G.; Wan, L.-J. 3D flowerlike ceria micro/nanocomposite structure and its application for water treatment and CO removal. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1648–1655.
- Azari, A.; Babaie, A.-A.; Rezaei-Kalantary, R.; Esrafili, A.; Moazzen, M.; Kakavandi, B. Nitrate removal from aqueous solution by carbon nanotubes magnetized with nano zero-valent iron. J. Maz. Univ. Med Sci. 2014, 23, 15–27.
- Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Nagatsu, M.; Wang, X. Carbon nanotubes as adsorbents in environmental pollution management: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 395–410.
- Tarigh, G.D.; Shemirani, F. Magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as an adsorbent for preconcentration and determination of lead (II) and manganese (II) in various matrices. Talanta 2013, 115, 744–750.
- Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Bagheri, H. Removal of some cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using magnetic-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 109–114.
- Tang, W.-W.; Zeng, G.-M.; Gong, J.-L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Liu, Z.-F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.-R.; Tu, D.-Z. Simultaneous adsorption of atrazine and Cu (II) from wastewater by magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211, 470–478.
- Gupta, V.K.; Agarwal, S.; Saleh, T.A. Synthesis and characterization of alumina-coated carbon nanotubes and their application for lead removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 17–23.
- Al-Khaldi, F.A.; Abusharkh, B.; Khaled, M.; Atieh, M.A.; Nasser, M.; Saleh, T.A.; Agarwal, S.; Tyagi, I.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorptive removal of cadmium (II) ions from liquid phase using acid modified carbon-based adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 204, 255–263.
- Zhang, C.; Sui, J.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Cai, W. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions by thiol-functionalized superparamagnetic carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 45–52.
- Chen, H.; Li, J.; Shao, D.; Ren, X.; Wang, X. Poly (acrylic acid) grafted multiwall carbon nanotubes by plasma techniques for Co (II) removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 475–481.
- Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X.; Dong, H.; Zeng, G.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Hua, S.; Zhang, S. Facile synthesis of alumina-decorated multi-walled carbon nanotubes for simultaneous adsorption of cadmium ion and trichloroethylene. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 273, 101–110.
- Tawabini, B.S. Removal of methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) from contaminated water using UV-assisted nano composite materials. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 55, 549–554.
- Qi, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, W. Aggregation morphology is a key factor determining protein adsorption on graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1303–1309.
- Gopalakrishnan, A.; Krishnan, R.; Thangavel, S.; Venugopal, G.; Kim, S.-J. Removal of heavy metal ions from pharma-effluents using graphene-oxide nanosorbents and study of their adsorption kinetics. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 30, 14–19.
- Ding, Z.; Hu, X.; Morales, V.L.; Gao, B. Filtration and transport of heavy metals in graphene oxide enabled sand columns. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 257, 248–252.
- Lee, Y.-C.; Yang, J.-W. Self-assembled flower-like TiO2 on exfoliated graphite oxide for heavy metal removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1178–1185.
- Gómez-Pastora, J.; Dominguez, S.; Bringas, E.; Rivero, M.J.; Ortiz, I.; Dionysiou, D.D. Review and perspectives on the use of magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs) in water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 407–427.
- Sharma, S. ZnO nano-flowers from Carica papaya milk: Degradation of Alizarin Red-S dye and antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Optik 2016, 127, 6498–6512.
- Cui, H.-J.; Cai, J.-K.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, B.; Ai, C.; Fu, M.-L. One step solvothermal synthesis of functional hybrid γ-Fe2O3/carbon hollow spheres with superior capacities for heavy metal removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 425, 131–135.
- Zhang, H.; Wu, Q.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z. Thermal conductivity of polyethylene glycol nanofluids containing carbon coated metal nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 124304.
- Brennan, L.; Owende, P. Biofuels from microalgae—A review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 557–577.
- Stephenson, T.; Brindle, K.; Judd, S.; Jefferson, B. Membrane Bioreactors for Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2000.
- Ríos, S.D.; Salvadó, J.; Farriol, X.; Torras, C. Antifouling microfiltration strategies to harvest microalgae for biofuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 406–418.
- Gupta, S.K.; Behari, J.; Kesari, K.K. Low frequencies ultrasonic treatment of sludge. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2006, 3, 101–105.
- Diallo, M.S.; Savage, N. Nanoparticles and Water Quality; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005.
- Yin, J.; Zhu, G.; Deng, B. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs)/polysulfone (PSU) mixed matrix hollow fiber membranes for enhanced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 237–248.
- Gordon, R.; Seckbach, J. The Science of Algal Fuels: Phycology, Geology, Biophotonics, Genomics and Nanotechnology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 25.
- Maximous, N.; Nakhla, G.; Wan, W. Comparative assessment of hydrophobic and hydrophilic membrane fouling in wastewater applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 93–99.
- Yuan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhuang, L. Polypyrrole/carbon black composite as a novel oxygen reduction catalyst for microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 3490–3493.
- Ghasemi, M.; Ismail, M.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Saeedfar, K.; Daud, W.R.W.; Hassan, S.H.; Heng, L.Y.; Alam, J.; Oh, S.-E. Carbon nanotube as an alternative cathode support and catalyst for microbial fuel cells. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 1050–1056.
- Sun, J.-J.; Zhao, H.-Z.; Yang, Q.-Z.; Song, J.; Xue, A. A novel layer-by-layer self-assembled carbon nanotube-based anode: Preparation, characterization, and application in microbial fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3041–3047.
