The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention considers saliva contact the lead transmission mean of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Saliva droplets or aerosols expelled by sneezing, coughing, breathing, and talking may carry this virus. People in close distance may be exposed directly to these droplets or indirectly when touching the droplets that fall on surrounding surfaces and ending up contracting COVID-19 after touching the mucosa tissue of their faces. It is of great interest to quickly and effectively detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in an environment, but the existing methods only work in laboratory settings, to the best of our knowledge. However, it may be possible to detect the presence of saliva in the environment and proceed with prevention measures. However, detecting saliva itself has not been documented in the literature. On the other hand, many sensors that detect different organic components in saliva to monitor a person’s health and diagnose different diseases, ranging from diabetes to dental health, have been proposed and they may be used to detect the presence of saliva.
- saliva sensor
- human saliva
- COVID-19
- virus detection
- multi-modal saliva detection
- droplet detection
- humidity sensor
- virus sensor
- SARS-CoV-2 detection
1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has claimed hundreds of thousands of lives, disrupted day-to-day human activity all around the world, and affected local and global economies [1]. While scientists and health-care professionals are still learning about it, this virus has proved to be highly contagious and deadly in some cases [2]. Therefore, there is an effort to develop and test vaccines to reduce the number of infections of this disease. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has suggested that COVID-19 mainly spreads from person to person through saliva droplets [3]. These droplets are expelled by coughing, sneezing, talking, or even breathing. They fall on surfaces that people may touch, and eventually bring them in contact with their mucosa tissue at their nose, mouth, or eyes by touching their face. They may eventually contract COVID-19 after the virus enters their system. Moreover, there are also concerns that airborne droplets can be suspended in the air for several minutes [4]. Such airborne droplets may spread very effectively as they can enter the nose when a person breaths air. Currently, SARS-CoV-2 can be detected in a patient after he or she is exposed to the virus and contracts COVID-19.
A sensor that can quickly and accurately detect SARS-CoV-2 in an ad-hoc environment before a person is exposed to it is desirable, but a system that can achieve this has not yet been reported. The complexity of SARS-CoV-2 detection and the lack of knowledge about the virus lead us to wonder how to determine whether an environment presents a high risk for contracting COVID-19 for its occupants. In such case, one can detect the presence of human saliva and take preventative measures. The detection of saliva in an environment may not ensure the presence of the virus but it may indicate the need for taking septic measures that may minimize the possibility of infection. Therefore, this paper focuses on the detection of the presence of saliva. Portable and robust sensors that detect SARS-CoV-2 in the field seem to be complex to realize at this time. On the other hand, there has been interest in detecting different saliva components for health monitoring and disease diagnosis in recent years. Such sensors may identify a saliva droplet by detecting one or a few of its components.
Saliva is a complex mixture of components secreted by three major salivary glands, namely the submandibular, parotid and sublingual glands, and other small parts of the mouth that also produce saliva but in small quantity, such as the gingival fold and oral mucosa [5][6]. The components of human saliva include water, organic proteins, such as amylase, peroxidase, lysozyme, cortisol, and mucin, glucose, cholesterol, urea, and inorganic components or electrolytes [7][8]. The concentration of these components has been used as an indicator or an auxiliary means of diagnosis of various diseases [9][10][11]. Saliva-producing glands have been shown to host SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19 while being asymptomatic [12]. Saliva tests for COVID-19 have received recent emergency approval as a non-invasive COVID-19 test by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May (COVID-19 molecular laboratory developed test, LDT, by Rutgers Clinical Genomics Laboratory) [13] and August (SalivaDirect COVID-19 diagnostic test by Yale School of Public Health) [14], 2020.
Saliva is a complex mixture of components secreted by three major salivary glands, namely the submandibular, parotid and sublingual glands, and other small parts of the mouth that also produce saliva but in small quantity, such as the gingival fold and oral mucosa [5,6]. The components of human saliva include water, organic proteins, such as amylase, peroxidase, lysozyme, cortisol, and mucin, glucose, cholesterol, urea, and inorganic components or electrolytes [7,8]. The concentration of these components has been used as an indicator or an auxiliary means of diagnosis of various diseases [9,10,11]. Saliva-producing glands have been shown to host SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with COVID-19 while being asymptomatic [12]. Saliva tests for COVID-19 have received recent emergency approval as a non-invasive COVID-19 test by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May (COVID-19 molecular laboratory developed test, LDT, by Rutgers Clinical Genomics Laboratory) [13] and August (SalivaDirect COVID-19 diagnostic test by Yale School of Public Health) [14], 2020.
2. Components of Saliva
Human saliva comprises water (98.5%), organic (1.0%), and inorganic (0.5%) components as shown in
Figure 1. Organic components include proteins, enzymes, mucin and nitrogenous products, such as urea, generated by the human body. Inorganic components are a variety of electrolytes found in saliva and the human body. While the daily average flow of saliva is between 1 to 1.5 L, the concentration of the organic and inorganic components in saliva is small. The small concentrations of these components in saliva impose challenges for their detection in saliva. For example, some components can be detected in saliva, such as amylase, mucin, glucose, cholesterol, urea, peroxidase, lysozyme, and cortisol, while others, such as immunoglobulin and other glycoproteins are found in saliva in such small concentrations that sensors that detect these components focus on serum obtained from blood [15][16]. Inorganic components detectable in saliva are cations, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, and anions, such as chloride, phosphate, and sulphate.
. Organic components include proteins, enzymes, mucin and nitrogenous products, such as urea, generated by the human body. Inorganic components are a variety of electrolytes found in saliva and the human body. While the daily average flow of saliva is between 1 to 1.5 L, the concentration of the organic and inorganic components in saliva is small. The small concentrations of these components in saliva impose challenges for their detection in saliva. For example, some components can be detected in saliva, such as amylase, mucin, glucose, cholesterol, urea, peroxidase, lysozyme, and cortisol, while others, such as immunoglobulin and other glycoproteins are found in saliva in such small concentrations that sensors that detect these components focus on serum obtained from blood [15,16]. Inorganic components detectable in saliva are cations, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, and anions, such as chloride, phosphate, and sulphate.
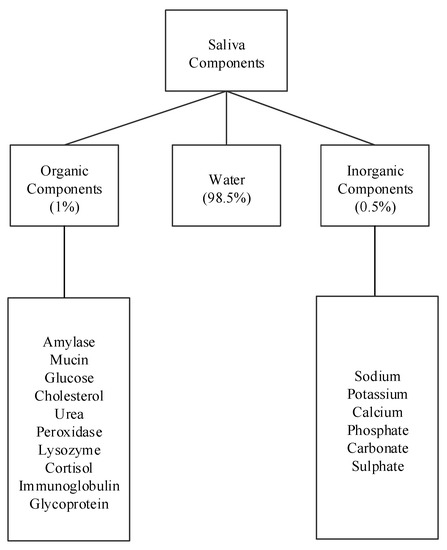
Figure 1.
Components of human saliva.
shows the concentrations of saliva components in
μ
g/mL and their percentage compared to other components. Among the listed components, amylase (42%), mucin (17%), and urea (17%) appear in higher concentrations, while cholesterol and cortisol appear in the smallest concentrations. The remaining concentration are other peptides. The remainder of this section describes these saliva components and some of their properties and uses.
Table 1. Concentration of components in saliva [7].
Concentration of components in saliva [7].
| Components | Concentration (μg/mL) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Amylase | 476 | 42 |
| Mucin | 200 | 17 |
| Urea | 200 | 17 |
| Lysozyme | 9.5 | 1 |
| Glucose | 10 | 1 |
| Cholesterol | 0.14 | ≈0 |
| Cortisol | 0.2 | ≈0 |
| Peroxidase | 50 | 4 |
3. Sensors for Organic and Inorganic Components of Human Saliva
Many of the organic components of human saliva, such as immunoglobulin, glycoprotein, glucose, cholesterol, etc., are also found in blood and have been used as indicators to monitor a person’s health. Therefore, there is an interest in detecting and measuring their concentration in saliva.
The following sensors are designed to detect the organic salivary components and measure their concentration. The paper presents a classification of sensors according to their working principle, target component, and technology used.
shows the surveyed salivary component sensors and their different detection working principles: electrochemical, optical, chemical, capacitive, and fluorescence.
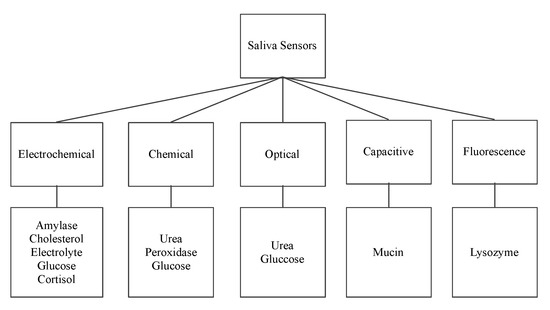
Figure 2.
Saliva sensors and their working principle.
3.1. Electrochemical Sensors
Electrochemical sensors involve a transfer of charges due to spontaneous reaction that takes place in the electrolytic solution when a suitable voltage is applied between the Working Electrode (WE) and the Reference Electrode (RE) [17][18][19][20][21][22]. This transfer of charges results in output current between the WE and the Counter Electrode (CE) corresponding to the change in the concentration of a specific component.
Electrochemical sensors involve a transfer of charges due to spontaneous reaction that takes place in the electrolytic solution when a suitable voltage is applied between the Working Electrode (WE) and the Reference Electrode (RE) [20,21,22,23,24,25]. This transfer of charges results in output current between the WE and the Counter Electrode (CE) corresponding to the change in the concentration of a specific component.
3.1.1. Enzyme Modified Alpha Amylase Sensor
Zheng et al. [17] proposed a biosensor that detects alpha-amylase using electrochemical working principle. During the detection of amylase, a KCl-saturated calomel electrode (SCE) is used as the reference, a platinum wire as the counter electrode, and an enzyme modified screen-printed electrode as the working electrode. The starch solution acts as the substrate. The measured output is the current generated by applying different voltages. This sensor uses encapsulation of both glucose oxidase (GOD) and
Zheng et al. [20] proposed a biosensor that detects alpha-amylase using electrochemical working principle. During the detection of amylase, a KCl-saturated calomel electrode (SCE) is used as the reference, a platinum wire as the counter electrode, and an enzyme modified screen-printed electrode as the working electrode. The starch solution acts as the substrate. The measured output is the current generated by applying different voltages. This sensor uses encapsulation of both glucose oxidase (GOD) and
α
-glucosidase in a composite film of sol–gel and Nafion. Here, Nafion immobilizes 1-dimethyl-3-2-amino-1-hydroxyethyl ferrocene (DMAHFc), as an electron transferring mediator, on the surface of the screen-printed electrode. DMAHFc, sol–gel, and Nafion enhance electron transfer, and improve the sensitivity and long-term stability of the biosensor. This electrochemical sensor has a detection limit of 10 to 656.6 mg/L. The detection limit is the minimum and maximum amounts of the component under test that can be measured.
3.1.2. Platinum Nano-Cluster Combination as a Cholesterol Sensor
Eom et al. [18] proposed a platinum nano-cluster combination (Pt-NC) sensor that detects cholesterol. For the detection of cholesterol, a three-electrode cell configuration is used where Pt-NC, enzyme (mixture of cholesterol esterase, cholesterol oxidase, and peroxidase), and Nafion (Pt-NC/enzyme/Nafion). Nafion acts as the working electrode, Pt as the counter electrode, and Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode. This is an enzyme-based biosensor that detects low concentrations of cholesterol in saliva. The biosensor exhibits a linear response in the range of 2 to 486
Eom et al. [21] proposed a platinum nano-cluster combination (Pt-NC) sensor that detects cholesterol. For the detection of cholesterol, a three-electrode cell configuration is used where Pt-NC, enzyme (mixture of cholesterol esterase, cholesterol oxidase, and peroxidase), and Nafion (Pt-NC/enzyme/Nafion). Nafion acts as the working electrode, Pt as the counter electrode, and Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode. This is an enzyme-based biosensor that detects low concentrations of cholesterol in saliva. The biosensor exhibits a linear response in the range of 2 to 486
μ
M and a detection limit of about 2
μ
M. The reported sensitivity of the sensor is 132
μ
A/mMcm
2
.
shows the Pt-NC sensor for cholesterol detection.
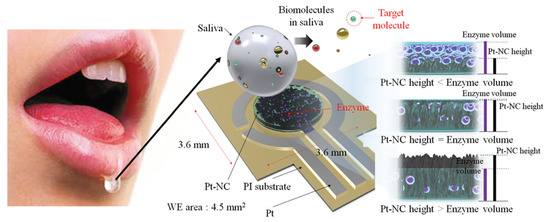
Figure 3. Biosensor with a Pt nano-cluster and strategy on changing the concentration of enzyme over the surface area of the substrate may improve sensor’s performance by optimizing the effective surface area and enzyme volume [18].
Biosensor with a Pt nano-cluster and strategy on changing the concentration of enzyme over the surface area of the substrate may improve sensor’s performance by optimizing the effective surface area and enzyme volume [21].
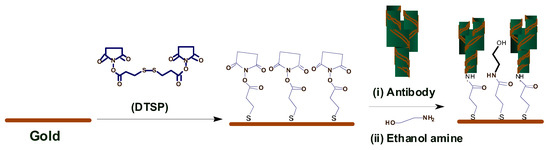
3.1.3. Immunosensor: Interdigitated Microelectrodes-Based Cortisol Sensor
Pasha et al. [19] proposed a simple, low-cost, label-free, electrochemical immunosensing platform for a highly sensitive and selective detection of cortisol in saliva. Electrochemical immunosensing platform has been utilized for a low-cost and label-free detection of cortisol via covalent immobilization of anti-cortisol antibodies (Anti-Cab) on self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of dithiobis succinimidylpropionte (DTSP) with modified microfabricated interdigitated microelectrodes (IDEs). The sensor is binded using ethyleneamine (EA). The non-binding sites of the immunosensor’s surface are blocked using EA. The concentration of cortisol produces an electrochemical response using cyclic voltametry. The sensor exhibits a detection that ranges from 10 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL, a detection limit of 10 pg/mL, and a sensitivity of 6
Pasha et al. [22] proposed a simple, low-cost, label-free, electrochemical immunosensing platform for a highly sensitive and selective detection of cortisol in saliva. Electrochemical immunosensing platform has been utilized for a low-cost and label-free detection of cortisol via covalent immobilization of anti-cortisol antibodies (Anti-Cab) on self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of dithiobis succinimidylpropionte (DTSP) with modified microfabricated interdigitated microelectrodes (IDEs). The sensor is binded using ethyleneamine (EA). The non-binding sites of the immunosensor’s surface are blocked using EA. The concentration of cortisol produces an electrochemical response using cyclic voltametry. The sensor exhibits a detection that ranges from 10 pg/mL to 100 ng/mL, a detection limit of 10 pg/mL, and a sensitivity of 6
μ
A/(pg/mL), with a regression coefficient of 0.99.
3.1.4. Antibody Modified Gold Microarray Electrode Cortisol Sensor
Arya et al. [20] proposed a microarray electrode sensor that detects cortisol hormone in saliva. This sensor is similar to the one in
Arya et al. [23] proposed a microarray electrode sensor that detects cortisol hormone in saliva. This sensor is similar to the one in
with functionalized gold (Au) microelectrode array. This sensor uses an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technique to make cortisol measurements. It monitors the change on resistance by the different currents. The EA/C-Mab/DTSP/Au-based biosensor can accurately detect cortisol in the range of 1 pM to 1
μ
M with a sensitivity of 1 pM.
shows the operation of the EA/C-Mab/DTSP/Au bio-electrode.
3.1.5. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Sensor
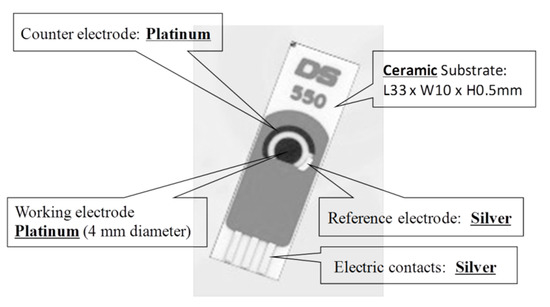
Du et al. [21] proposed a single-walled carbon nanotube sensor to detect salivary glucose. For the detection of glucose three metallic electrodes are used: a Pt WE, a silver (Ag) RE, and a Pt CE. These salivary glucose sensors are built using layer-by-layer self-assembled single-walled carbon nanotubes, chitosan, gold nanoparticles, and glucose oxidase onto a screen-printed platinum electrode. An electrochemical sensor is utilized for a quantitative detection of glucose in both buffer solution and saliva samples. The buffer solution is used as a reference. The WE and CE are used to detect changes of glucose concentrations. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) electro-analytical tests can be conducted with these sensors. In such tests, a suitable voltage is applied between the WE and RE. The current between the WE and CE corresponds to the concentration of glucose.
Du et al. [24] proposed a single-walled carbon nanotube sensor to detect salivary glucose. For the detection of glucose three metallic electrodes are used: a Pt WE, a silver (Ag) RE, and a Pt CE. These salivary glucose sensors are built using layer-by-layer self-assembled single-walled carbon nanotubes, chitosan, gold nanoparticles, and glucose oxidase onto a screen-printed platinum electrode. An electrochemical sensor is utilized for a quantitative detection of glucose in both buffer solution and saliva samples. The buffer solution is used as a reference. The WE and CE are used to detect changes of glucose concentrations. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) electro-analytical tests can be conducted with these sensors. In such tests, a suitable voltage is applied between the WE and RE. The current between the WE and CE corresponds to the concentration of glucose.
shows this electrochemical glucose sensor and its parts.
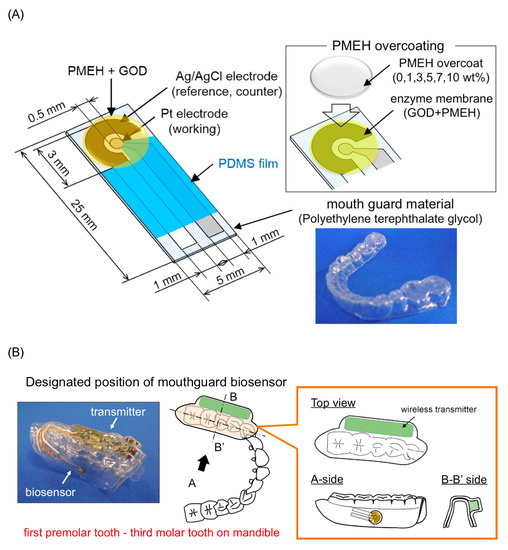
3.1.6. Mouthguard Cavitas Sensor
Arakawa et al. [22] proposed a mouthguard cavitas sensor to detect salivary glucose. This glucose sensor consists of a platinum and silver/silver chloride electrode (Ag/AgCl), with glucose oxidase (GOD) immobilized by poly2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine-co-2-ethylhexylmethacrylate (PMEH) on a custom-fitted monolithic mouth-guard. It has a wireless transmitter for telemetric measurement of saliva glucose. A 0.5 mm-thick layer of polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) is selected as part of the structure to demonstrate a strong adhesion of Pt and Ag to PETG. This sensor has GOD and a PMEH overcoat applied to the sensing region. PMEH over-coating increases the sensitivity of the sensor. The biosensor is capable of real-time continuous wireless measurement of glucose in artificial saliva from 5–1000
Arakawa et al. [25] proposed a mouthguard cavitas sensor to detect salivary glucose. This glucose sensor consists of a platinum and silver/silver chloride electrode (Ag/AgCl), with glucose oxidase (GOD) immobilized by poly2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine-co-2-ethylhexylmethacrylate (PMEH) on a custom-fitted monolithic mouth-guard. It has a wireless transmitter for telemetric measurement of saliva glucose. A 0.5 mm-thick layer of polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) is selected as part of the structure to demonstrate a strong adhesion of Pt and Ag to PETG. This sensor has GOD and a PMEH overcoat applied to the sensing region. PMEH over-coating increases the sensitivity of the sensor. The biosensor is capable of real-time continuous wireless measurement of glucose in artificial saliva from 5–1000
μ
mol/L with a phantom jaw.
shows the mouthguard sensor and its operation.
3.2. Chemical Colorimetric Sensors
Colorimetric detection involves the use of substances that react chemically to detect the presence of a specific component [23][24][25]. The following sensors use colorimetric detection.
Colorimetric detection involves the use of substances that react chemically to detect the presence of a specific component [26,27,28]. The following sensors use colorimetric detection.
3.2.1. Colorimetric Urea Sensor
Evans et al. [23] proposed a colorimetric sensor to detect urea in saliva. The change of color on the testpad indicates the presence of Urea. The Salivary Urea Nitrogen (SUN) dipstick method determines the amount of urea in saliva. This method can be applied to unstimulated saliva, from which 50
Evans et al. [26] proposed a colorimetric sensor to detect urea in saliva. The change of color on the testpad indicates the presence of Urea. The Salivary Urea Nitrogen (SUN) dipstick method determines the amount of urea in saliva. This method can be applied to unstimulated saliva, from which 50
μL are used to moisten the test pad of a colorimetric SUN dipstick. Unstimulated saliva is obtained from a subject fasting for at least 15 min prior to the sample collection. The change in color of the test pad is assessed after one minute of being moistened. The color of the test pad is compared to the color of the six reference pads corresponding to increasing SUN concentrations: 5 to 14 mg/dL (pad 1), 15 to 24 mg/dL (pad 2), 25 to 34 mg/dL (pad 3), 35 to 54 mg/dL (pad 4), 55 to 74 mg/dL (pad 5), and ≥75 mg/dL (pad 6). This sensor has a sensitivity of 12.82% and a specificity of 97.33% in the detection of acute kidney disease. Another optical portable sensor of urea has also been reported [26].
L are used to moisten the test pad of a colorimetric SUN dipstick. Unstimulated saliva is obtained from a subject fasting for at least 15 min prior to the sample collection. The change in color of the test pad is assessed after one minute of being moistened. The color of the test pad is compared to the color of the six reference pads corresponding to increasing SUN concentrations: 5 to 14 mg/dL (pad 1), 15 to 24 mg/dL (pad 2), 25 to 34 mg/dL (pad 3), 35 to 54 mg/dL (pad 4), 55 to 74 mg/dL (pad 5), and ≥75 mg/dL (pad 6). This sensor has a sensitivity of 12.82% and a specificity of 97.33% in the detection of acute kidney disease. Another optical portable sensor of urea has also been reported [29].
3.2.2. Colorimetric Glucose Sensor
Agrawal et al. [24] proposed a colorimetric sensor that detects glucose. For glucose detection, glucose oxidase acts as a catalyst and reacts with saliva to generate a red color complex. The quantitative estimation of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and fasting saliva glucose (FSG) is performed by a glucose oxidase method using enzymatic kit Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase (GOD-POD). GOD catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid. The formed hydrogen peroxide (H
Agrawal et al. [27] proposed a colorimetric sensor that detects glucose. For glucose detection, glucose oxidase acts as a catalyst and reacts with saliva to generate a red color complex. The quantitative estimation of fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and fasting saliva glucose (FSG) is performed by a glucose oxidase method using enzymatic kit Glucose Oxidase-Peroxidase (GOD-POD). GOD catalyses the oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid. The formed hydrogen peroxide (H
2
O
2
) is detected by a chromogenic oxygen acceptor phenol, 4-AP, 4-aminophenazone in the presence of peroxidase. The red-colored complex quinoneimine is measured colorimetrically and the intensity of the color formed is directly proportional to the concentration of glucose in the sample. The mean FSG of the subjects in a non-diabetic group was reported as 6.08 ± 1.16 mg/dL and the mean FSG of subjects in a diabetic group was 10.93 ± 1.93 mg/dL.
There are portable [27][28][29][30] and non portable [26][31][32][33][34][35] sensors of salivary glucose reported in the literature. These sensors are based on chemical, electrochemical and optical working principles.
There are portable [30,31,32,33] and non portable [29,34,35,36,37,38] sensors of salivary glucose reported in the literature. These sensors are based on chemical, electrochemical and optical working principles.
3.2.3. Chemical Peroxidase Sensor
The salivary peroxidase (SP) system is one of the non-immunoglobulin defense systems in saliva. Vučićević-Boras et al. [25] proposed a sensor that detects peroxidase using a chemical working principle. In peroxidase detection, 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) reacts with saliva to generate a red color complex indicating the presence of peroxidase in saliva. The reagents used for salivary analysis are 20 mM 2.2 azino-di-3-etil-benzotiazolin-6-sulphonic acid diammonium acid (ABTS) in 67 mM phosphate buffer with pH of 6.0 and 10 mM hydrogen peroxide and peroxidase in quantity of 250 J/kg. The assay is based on 0.5 mL of saliva sample, which is diluted with 1.5 mL of phosphate buffer with a pH of 6.0. The reactive mixture consists of 2 mL of diluted saliva, 0.2 mL of ABTS solution, and 0.2 mL of hydrogen peroxide, which are all mixed in a reactive cuvette and analyzed by a spectrometer at 405 nm and at 25
The salivary peroxidase (SP) system is one of the non-immunoglobulin defense systems in saliva. Vučićević-Boras et al. [28] proposed a sensor that detects peroxidase using a chemical working principle. In peroxidase detection, 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) reacts with saliva to generate a red color complex indicating the presence of peroxidase in saliva. The reagents used for salivary analysis are 20 mM 2.2 azino-di-3-etil-benzotiazolin-6-sulphonic acid diammonium acid (ABTS) in 67 mM phosphate buffer with pH of 6.0 and 10 mM hydrogen peroxide and peroxidase in quantity of 250 J/kg. The assay is based on 0.5 mL of saliva sample, which is diluted with 1.5 mL of phosphate buffer with a pH of 6.0. The reactive mixture consists of 2 mL of diluted saliva, 0.2 mL of ABTS solution, and 0.2 mL of hydrogen peroxide, which are all mixed in a reactive cuvette and analyzed by a spectrometer at 405 nm and at 25
∘
C. The absorbance becomes red between the first and fifth minutes when using the reagent as a blind trial to indicate the presence of peroxidase.
3.3. Optical
Optical sensors either uses colorimetric optical absorption or measure a change in wavelength when there is light absorption by the component [36][37].
Optical sensors either uses colorimetric optical absorption or measure a change in wavelength when there is light absorption by the component [39,40].
3.3.1. Optical Urea Sensor
Soni et al. [36] proposed an optical sensor to detect urea in saliva. This component is detected using colorimetric optical absorption where a strip changes color upon reacting with urea in saliva. The color change is determined using a smartphone application. The sensor is used to detect on sight of kidney disease. The used amount of saliva is 10
Soni et al. [39] proposed an optical sensor to detect urea in saliva. This component is detected using colorimetric optical absorption where a strip changes color upon reacting with urea in saliva. The color change is determined using a smartphone application. The sensor is used to detect on sight of kidney disease. The used amount of saliva is 10
μ
L. The sensor is fabricated using a simple methodology; by immobilizing enzyme urease along with a pH indicator on a filter paper-based strip. The strip changes color upon the reaction of urea in saliva. This color change is determined using a smartphone application; based on Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) profiling. Calibration of the sensor is carried out using saliva spiked with synthetic urea samples with various concentrations. The reported sensitivity of the sensor is 10.9 mg/dL.
3.3.2. Optical Amylase Sensor
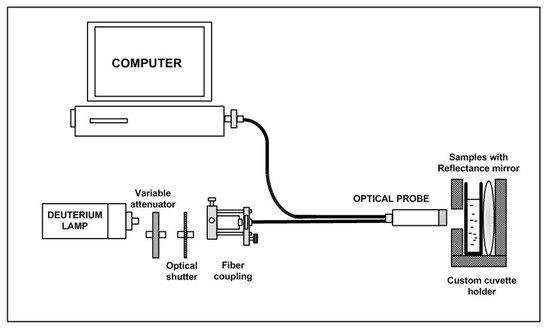
Yazid et al. [37] proposed an optical sensor to detect dental caries by detecting the amount of amylase in saliva. Amylase can be detected on the basis of optical absorption using an ultraviolet-visible (UV-VIS) spectrometer. The alpha-amylase is absorbed by light at a specific wavelength. When the light at those wavelengths passes through the saliva specimen, some of the light is absorbed by the solute and some other passes through the sample. This difference in the original and transmitted light is called absorbance. The spectrometer detects the absorbance at around 280 nm. The quantity of saliva used for the detection is 2 mL. Six core fibers deliver the UV light to the saliva sample and one fiber in the middle collects the reflected light back to the other end. The sample is placed in a special 350
Yazid et al. [40] proposed an optical sensor to detect dental caries by detecting the amount of amylase in saliva. Amylase can be detected on the basis of optical absorption using an ultraviolet-visible (UV-VIS) spectrometer. The alpha-amylase is absorbed by light at a specific wavelength. When the light at those wavelengths passes through the saliva specimen, some of the light is absorbed by the solute and some other passes through the sample. This difference in the original and transmitted light is called absorbance. The spectrometer detects the absorbance at around 280 nm. The quantity of saliva used for the detection is 2 mL. Six core fibers deliver the UV light to the saliva sample and one fiber in the middle collects the reflected light back to the other end. The sample is placed in a special 350
μ
L quartz cuvette, which allows the transmission of UV light. The reflected UV light is measured by the high-resolution UV–VIS spectrometer, which is capable of detecting a wavelength range from 200 nm to 1100 nm at 0.01 nm resolution. It is observed that the absorbance of the saliva samples of a healthy group are the lowest as compared to that of a low caries group and high caries group, because of the amylase concentration.
shows the optical detection of amylase.
3.4. Capacitive
Capacitive sensors are non-contact devices that can detect the presence or absence of virtually any object regardless of material. They utilize the electrical property of capacitance and the change of capacitance based on a change in the electrical field around the active face of the sensor [38][39].
Capacitive sensors are non-contact devices that can detect the presence or absence of virtually any object regardless of material. They utilize the electrical property of capacitance and the change of capacitance based on a change in the electrical field around the active face of the sensor [41,42].
Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Mucin Biosensors
Guha et al. [38] and Soltani et al. [39] proposed two complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) biosensors that detect mucin using a capacitive working principle. The operation of the sensors are based on the detection of change in the dielectric constant of the sputum-mucin due to varying viscosity. A planar interdigitated capacitor (IDC) is embedded in a CMOS oscillator, which works as the sensor. The two models considered for estimation and understanding of variation of viscosity are a) glycerol water mixture and b) glycerol ethanol mixture. The reported sensors use CMOS and bi-polar CMOS (BiCMOS) integrated technology. The sensing principle of these two sensors is based on the detection of a dielectric change of the capacitor embedded in a resonant CMOS oscillator. The operating frequency of the sensors is 12 GHz. The sensors can distinguish between a highly viscous clot of sputum-mucin and diluted sputum-mucin.
Guha et al. [41] and Soltani et al. [42] proposed two complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) biosensors that detect mucin using a capacitive working principle. The operation of the sensors are based on the detection of change in the dielectric constant of the sputum-mucin due to varying viscosity. A planar interdigitated capacitor (IDC) is embedded in a CMOS oscillator, which works as the sensor. The two models considered for estimation and understanding of variation of viscosity are a) glycerol water mixture and b) glycerol ethanol mixture. The reported sensors use CMOS and bi-polar CMOS (BiCMOS) integrated technology. The sensing principle of these two sensors is based on the detection of a dielectric change of the capacitor embedded in a resonant CMOS oscillator. The operating frequency of the sensors is 12 GHz. The sensors can distinguish between a highly viscous clot of sputum-mucin and diluted sputum-mucin.
3.5. Fluorescence
Fluorescence detection often includes a source of excitation light (e.g., LED photo-diodes), a fluorophore particle, wavelength filters to isolate photon emissions from excitable molecules, and a detector that records changes in fluorescence intensity and generates a measurable value [40][41].
Fluorescence detection often includes a source of excitation light (e.g., LED photo-diodes), a fluorophore particle, wavelength filters to isolate photon emissions from excitable molecules, and a detector that records changes in fluorescence intensity and generates a measurable value [43,44].
Fluorescence Lysozyme Biosensor
Liu et al. [40] proposed a fluorescence-based sensor to detect the presence of lysozyme in saliva. The anti-lysozyme DNA aptamer labeled with fluorescein (FAM) is used as a probe to recognize and transduce a fluorescence signal. The mixture gets adsorbed on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) via strong binding and hydrophobic interactions between the Single-Stranded DNA (ssDNA) and GO. In this case, the FAM and the acceptor (i.e., GO) come in close proximity. As a result, the intensity of fluorescence decreases due to energy transfer from FAM to GO. When lysozyme comes in contact with the FAM aptamer, it gets combined with FAM aptamer and the resulting FAM-lysozyme structure gets separated from GO. Due to this separation, the intensity of fluorescence is increased and the maximum intensity of the signal is found at a wavelength of 480 nm, indicating the presence of lysozyme. This fluorometric lysozyme sensor has a detection sensitivity of 2
Liu et al. [43] proposed a fluorescence-based sensor to detect the presence of lysozyme in saliva. The anti-lysozyme DNA aptamer labeled with fluorescein (FAM) is used as a probe to recognize and transduce a fluorescence signal. The mixture gets adsorbed on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) via strong binding and hydrophobic interactions between the Single-Stranded DNA (ssDNA) and GO. In this case, the FAM and the acceptor (i.e., GO) come in close proximity. As a result, the intensity of fluorescence decreases due to energy transfer from FAM to GO. When lysozyme comes in contact with the FAM aptamer, it gets combined with FAM aptamer and the resulting FAM-lysozyme structure gets separated from GO. Due to this separation, the intensity of fluorescence is increased and the maximum intensity of the signal is found at a wavelength of 480 nm, indicating the presence of lysozyme. This fluorometric lysozyme sensor has a detection sensitivity of 2
μg/mL with a detection limit of 21.8 pM. The specificity of this sensor is 85%, defined in terms of flurorescence recovery and under the presence of six other proteins as 500 pM along with 250 pM of lysozyme. This sensor does not require cleaning or replacement and it can be used for long periods of time. Khan et al. [41] recently proposed another portable lysozyme sensor. There are other proposed lysozyme sensors that are; however, not portable [42][43].
g/mL with a detection limit of 21.8 pM. The specificity of this sensor is 85%, defined in terms of flurorescence recovery and under the presence of six other proteins as 500 pM along with 250 pM of lysozyme. This sensor does not require cleaning or replacement and it can be used for long periods of time. Khan et al. [44] recently proposed another portable lysozyme sensor. There are other proposed lysozyme sensors that are; however, not portable [45,46].
3.6. Sensors for Inorganic Components of Human Saliva
Rumenjak et al. [44] proposed a potentiometric sensor to detect the electrolyte concentration of a substance in saliva. This method determines concurrent concentrations of potassium, calcium, and chloride using ion-selective electrodes. The instrument consists of three ion-selective electrodes and a reference electrode, two peristaltic pumps for collecting samples and washing the electrodes after use, and a computer. Prior to the measurement, the instrument is calibrated using undiluted standard samples containing potassium, calcium, and chloride with different concentrations. The saliva sample is diluted by a magnesium acetate solution at 1:10. The development of this sensor is motivated for the detection of dental problems by determining the calcium concentrations. Urbanowicz et al. [45] also proposed a portable electrolyte sensor to determine the ionic profiles in human saliva.
Rumenjak et al. [47] proposed a potentiometric sensor to detect the electrolyte concentration of a substance in saliva. This method determines concurrent concentrations of potassium, calcium, and chloride using ion-selective electrodes. The instrument consists of three ion-selective electrodes and a reference electrode, two peristaltic pumps for collecting samples and washing the electrodes after use, and a computer. Prior to the measurement, the instrument is calibrated using undiluted standard samples containing potassium, calcium, and chloride with different concentrations. The saliva sample is diluted by a magnesium acetate solution at 1:10. The development of this sensor is motivated for the detection of dental problems by determining the calcium concentrations. Urbanowicz et al. [48] also proposed a portable electrolyte sensor to determine the ionic profiles in human saliva.
There are other portable sensors of urea [46], glucose [27][28][29][30], lysozyme [41], and inorganic components [45] reported in the literature that may present some similarities to the ones described above.
There are other portable sensors of urea [49], glucose [30,31,32,33], lysozyme [44], and inorganic components [48] reported in the literature that may present some similarities to the ones described above.