We have thus far seen in all of the foregoing[1][2][3][4] that the TheoryTheory of Entropicity (ToE) of Entropicity (ToE) [first formulated and developed by John Onimisi Obidi][5][6][7] indeed advances a bold reimagining of gravitational dynamics by proposing that entropy, not spacetime geometry, is the fundamental source of physical interactions. In this section of the Treatise, we compare this framework against the most prominent precedents in entropic and gravitational theory—namely the classical gravitation of Newton, the geometric gravitation of Einstein, the entropic emergent gravity of Verlinde, and the thermodynamic gravity of Padmanabhan. While these frameworks offer powerful insights into the structure of gravity, they either treat entropy as derivative, statistical, or holographic, or anchor gravitational phenomena in spacetime curvature. We have seen that ToE radically departs from these traditions by promoting entropy to a fundamental, causal field with its own local dynamics, variational principles, and quantum excitations (entropions). This entropic field replaces the geometric curvature of General Relativity and the emergent statistical reasoning of Verlinde with a Lagrangian-based field theory governed by the ObidiObidi Action Action and its corresponding Master Entropic Equation (MEE). In this submission, we have further detailed how ToE re-derives Einstein’s results—such as Mercury’s perihelion precession and the deflection of starlight—via an entropically modified Binet equation, without invoking curved spacetime. The result is not merely a reinterpretation of gravity, but a comprehensive replacement of its ontological and mathematical foundation. The originality of ToE lies in its systemic unification of entropy, force, time asymmetry, and quantum behavior, positioning entropy as the true source of constraint and curvature in nature. The current Chapter thus sets the stage for ToE’s broader implications in cosmology and black hole dynamics.
- Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum Theory
- Field Theory
- Gravity
- Newton and Einstein
- Entropy
- Theory of Entropicity(ToE)
- Verlinde and Padmanabhan's Gravity
- General Relativity
1. Special Notes on Obidi's Gravity from Newton and Einstein in the Theory of Entropicity(ToE)
Obidi's Gravity from Newton, Einstein, Verlinde, Padmanabhan, and Others
The Theory of Entropicity (ToE), [1][2][3][4] as formulated in this treatise, offers a profound departure from prior approaches to gravity, including those of Newton, Einstein, Verlinde, Padmanabhan, and other entropic and geometric theorists. This section systematically outlines the comparative landscape, highlighting ToE's originality, mathematical innovations, and foundational shifts [5][6][7].
Setup of the Derivation of Newtonian Gravity from Entropy Gradient
Consider a static, spherically symmetric mass \(M\) localized at the origin. To leading order, the entropy field \(S(x)\) obeys a Poisson-like equation (see §7.4):
\[
\nabla^2 S(x) \;=\; -\,\eta\,\rho_M(x)
\quad\text{with}\quad
\rho_M(x) = M\,\delta^3(x)\,,
\]
Outside the mass distribution we have \(\nabla^2 S = 0\). Solving Laplace’s equation in spherical symmetry gives
where \(S_\infty\) is the asymptotic (far-field) value of the entropy.
Entropic Force
A test particle of mass \(m\) moves so as to increase the total entropy. Its equation of motion follows from the entropic variational principle (see §5.2):
\[
\mathbf{F}_{\mathrm{entropy}}
= -\,m\,\nabla \Phi_S(r)
\,,\qquad
\Phi_S(r) \equiv S(r).
\]
Substitute the radial solution for \(S(r)\):
\[
\frac{\eta}{4\pi} \;=\; G
\]
thus reproduces Newton’s law of universal gravitation:
\[
\mathbf{F}_{\mathrm{entropy}}
= -\,\frac{G\,M\,m}{r^2}\,\hat{\mathbf{r}}\,,
\]
an attractive \(1/r^2\) force arising from the gradient of the entropy field in the Theory of Entropicity (ToE).
ToE Reinterprets Entropy as a Source of Constraint Curvature
The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) breaks with tradition by proposing that:
- All observed curvatures in spacetime and trajectories are not due to spacetime geometry itself, but arise from entropy gradients and their associated field constraints.
- Thus, the entropy field directly modifies the effective force, not only in a Newtonian sense but in a fully relativistic, irreversible, and time-asymmetric manner.
- From this perspective, ToE extends the classical Binet equation with an entropic source term that naturally accounts for observed relativistic corrections.
This extension is therefore entirely novel:
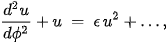
where the additional terms arise from entropic field constraints (e.g., via ) and are derived from the Master Entropic Equation (MEE) or the entropy-constrained geodesic equation of the Theory of Entropicity.
In doing so, ToE redefines the source of curvature from a purely geometrical model to a field-theoretic model governed by entropy, rendering the Binet equation once again a valid and powerful tool—now enriched by entropic effects.
We begin by contrasting the ToE with Erik Verlinde's entropic gravity, arguably the most well-known recent attempt to link gravitation to entropy:
2.
Comparison with Verlinde's Entropic Gravity
Comparison of Verlinde's Entropic Gravity and the Theory of Entropicity (ToE)
Aspect
Verlinde's Entropic Gravity
Theory of Entropicity (ToE)
Nature of Entropy
Emergent and statistical; linked to coarse-graining and information loss on holographic screens
Fundamental and field-like; a causal, dynamic entity that propagates as a physical field
Origin of Gravity
Gravity Source
Curved spacetime geometry
Emerges from entropy gradients ; derived from the Obidi Action
Entropic field gradients
Role of Holography
Central to formulation via equipartition and boundary information
Not essential; entropy is local and volumetric
Emergent from information change on holographic surfaces
Mathematical Formulation
Thermodynamic analogies (e.g., ); lacks field equations
Derived from a full action principle; includes the Master Entropic Equation (MEE) and entropy-modified Binet equation
Quantization
No formal quantum formulation
Introduces the entropion, the quantum of the entropy field
Correction Terms
Geodesic deviation in curved space
Constraint terms from entropy flow
Field Equation
Einstein Field Equation
Master Entropic Equation (MEE)
Particle Path
Geodesic
Entropic constrained least-action path
Binet Usage
Not applicable
Emergent from entropy potential
Temporal Asymmetry
Time-symmetric
Irreversibility built in via the No-Rush Theorem and Entropic CPT violation
Equation Structure
Analogical use of thermodynamic relations
First-principles derivations from entropy-based variational dynamics
Scope
Gravitational reinterpretation
Unification of gravity, quantum mechanics, thermodynamics, and information theory
Experimental Predictions
Limited; mostly conceptual
Predicts 232 attosecond entanglement delay, entropy lensing, entropion spectra, time-asymmetric collapse, and more
Einstein's Gravity in General Relativity and Obidi's Gravity in the Theory of Entropicity(ToE)
Einstein's Gravity in General Relativity and Obidi's Gravity in the Theory of Entropicity(ToE)
Feature
General Relativity (GR)
Theory of Entropicity (ToE)
3. Unique Insights and Innovations in ToE on Gravity from the Binet-Obidi Equation
3.1.
1.
Entropy as a Real Dynamical Field
- Unlike Verlinde, who treats entropy as a boundary phenomenon, ToE promotes entropy to a local scalar field with physical dynamics, satisfying wave equations and variational principles. This represents a fundamental ontological shift.
3.2.
2.
The Obidi Action and the Master Entropic Equation (MEE)
- The Obidi Action introduces a new variational principle from which the MEE arises. This equation governs the entropic field's evolution and its interaction with matter and motion:
where is a nonlinear operator encoding entropy, curvature, and irreversibility.
3.3.
3.
The Vuli-Ndlela Integral
- The Vuli-Ndlela Integral is a reformulated path integral for entropic dynamics:
This integral incorporates gravitational entropy , irreversible entropy , and an entropy-modified action.
3.4.
4.
Entropic Binet Equation
- The classical Binet equation is resurrected and extended in ToE as the following Binet-Obidi Equation [1][2][3][4]Binet-Obidi Equation:[1][2][3][4]
where and is derived from entropic corrections. This formulation reproduces Einsteinian results for Mercury's perihelion precession and light deflection without invoking spacetime curvature.
- The No-Rush Theorem and Entropic Time Limit (ETL)
1. The No-Rush Theorem and Entropic Time Limit (ETL)
- These principles posit a finite lower bound on all physical interaction durations due to entropy propagation constraints. This leads to predictions like the finite 232 attosecond delay in entanglement formation.
- Black Hole Dynamics via Entropy Field
2. Black Hole Dynamics via Entropy Field
- Black hole evaporation is reinterpreted as a loss of entropy field energy and the emission of quantized entropic particles (entropions), rather than Hawking’s pair production.
-
- Entanglement formation delay (232 attoseconds)
- Entropy lensing near strong fields
- Entropic collapse asymmetry in quantum measurements
- Testable Predictions
3. Testable Predictions
- Quantized black hole entropy spectra
4. Why the Modified Binet Equation (the Binet-Obidi Equation) in ToE is Revolutionary
Traditionally, the Binet equation: is limited to Newtonian central force problems. GR bypasses it in favor of spacetime geodesics derived from the Schwarzschild metric. ToE reinvigorates the Binet equation by embedding it in an entropic variational principle, where the effective force arises from entropy gradients: Although does not appear explicitly in the final Binet-Obidi form, it is the generator of the correction term , making the entropy field the true origin of curvature and force.
5. Summary and Final Word on Gravity from ToE's Binet-Obidi Formulation
Verlinde makes gravity emergent from entropy; Obidi’s ToE makes all physics emergent from entropy.
In ToE, entropy is no longer a passive measure of disorder or information, but a fundamentalfundamental force-field force-field shaping motion, structure, and time. Through the Obidi Action, MEE, the Vuli-Ndlela Integral, and the Entropic Binet-Obidi Equation, ToE offers a unified, causal, and testable alternative to traditional gravity and quantum theories. This redefines the conceptual foundations of physics and signals a new era in theoretical science.
References
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Corrections to the Classical Shapiro Time Delay in General Relativity (GR) from the Entropic Force-Field Hypothesis (EFFH). Cambridge University. (11 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-v7m6c
- Obidi, John Onimisi. How the Generalized Entropic Expansion Equation (GEEE) Describes the Deceleration and Acceleration of the Universe in the Absence of Dark Energy. Cambridge University. (12 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-6d843
- Obidi, John Onimisi. The Theory of Entropicity (ToE): An Entropy-Driven Derivation of Mercury’s Perihelion Precession Beyond Einstein’s Curved Spacetime in General Relativity (GR). Cambridge University. (16 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-g55m9
- Obidi, John Onimisi. The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) Validates Einstein’s General Relativity (GR) Prediction for Solar Starlight Deflection via an Entropic Coupling Constant η. Cambridge University. (23 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-1cs81
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Einstein and Bohr Finally Reconciled on Quantum Theory: The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) as the Unifying Resolution to the Problem of Quantum Measurement and Wave Function Collapse. Cambridge University. (14 April 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-vrfrx
- Obidi, John Onimisi . "On the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty, Probability and CPT-Theorem Symmetry-Breaking in the Standard Model of Particle Physics: More Revolutionary Insights from the Theory of Entropicity (ToE)". Cambridge University. (14 June 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-n4n45
- Obidi, John Onimisi. A Critical Review of the Theory of Entropicity (ToE) on Original Contributions, Conceptual Innovations, and Pathways towards Enhanced Mathematical Rigor: An Addendum to the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty. Cambridge University.(2025-06-30). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-hmk6nI
| Aspect | Verlinde's Entropic Gravity | Theory of Entropicity (ToE) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature of Entropy | Emergent and statistical; linked to coarse-graining and information loss on holographic screens | Fundamental and field-like; a causal, dynamic entity that propagates as a physical field | |||
| Origin of Gravity | |||||
| Gravity Source | Curved spacetime geometry | Emerges from entropy gradients ; derived from the Obidi Action | |||
| Entropic field gradients | Role of Holography | Central to formulation via equipartition and boundary information | Not essential; entropy is local and volumetric | ||
| Emergent from information change on holographic surfaces | Mathematical Formulation | Thermodynamic analogies (e.g., ); lacks field equations | Derived from a full action principle; includes the Master Entropic Equation (MEE) and entropy-modified Binet equation | ||
| Quantization | No formal quantum formulation | Introduces the entropion, the quantum of the entropy field | |||
| Correction Terms | Geodesic deviation in curved space | Constraint terms from entropy flow | |||
| Field Equation | Einstein Field Equation | Master Entropic Equation (MEE) | |||
| Particle Path | Geodesic | Entropic constrained least-action path | |||
| Binet Usage | Not applicable | Emergent from entropy potential | Temporal Asymmetry | Time-symmetric | Irreversibility built in via the No-Rush Theorem and Entropic CPT violation |
| Equation Structure | Analogical use of thermodynamic relations | First-principles derivations from entropy-based variational dynamics | |||
| Scope | Gravitational reinterpretation | Unification of gravity, quantum mechanics, thermodynamics, and information theory | |||
| Experimental Predictions | Limited; mostly conceptual | Predicts 232 attosecond entanglement delay, entropy lensing, entropion spectra, time-asymmetric collapse, and more |
| Feature | General Relativity (GR) | Theory of Entropicity (ToE) |
|---|
- Entanglement formation delay (232 attoseconds)
- Entropy lensing near strong fields
- Entropic collapse asymmetry in quantum measurements
- Quantized black hole entropy spectra
Why the Modified Binet Equation (the Binet-Obidi Equation) in ToE is Revolutionary
Traditionally, the Binet equation: is limited to Newtonian central force problems. GR bypasses it in favor of spacetime geodesics derived from the Schwarzschild metric. ToE reinvigorates the Binet equation by embedding it in an entropic variational principle, where the effective force arises from entropy gradients: Although does not appear explicitly in the final Binet-Obidi form, it is the generator of the correction term , making the entropy field the true origin of curvature and force.
5. Summary and Final Word on Gravity from ToE's Binet-Obidi Formulation
Verlinde makes gravity emergent from entropy; Obidi’s ToE makes all physics emergent from entropy.
In ToE, entropy is no longer a passive measure of disorder or information, but a fundamentalfundamental force-field force-field shaping motion, structure, and time. Through the Obidi Action, MEE, the Vuli-Ndlela Integral, and the Entropic Binet-Obidi Equation, ToE offers a unified, causal, and testable alternative to traditional gravity and quantum theories. This redefines the conceptual foundations of physics and signals a new era in theoretical science.
References
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Corrections to the Classical Shapiro Time Delay in General Relativity (GR) from the Entropic Force-Field Hypothesis (EFFH). Cambridge University. (11 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-v7m6c
- Obidi, John Onimisi. How the Generalized Entropic Expansion Equation (GEEE) Describes the Deceleration and Acceleration of the Universe in the Absence of Dark Energy. Cambridge University. (12 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-6d843
- Obidi, John Onimisi. The Theory of Entropicity (ToE): An Entropy-Driven Derivation of Mercury’s Perihelion Precession Beyond Einstein’s Curved Spacetime in General Relativity (GR). Cambridge University. (16 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-g55m9
- Obidi, John Onimisi. The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) Validates Einstein’s General Relativity (GR) Prediction for Solar Starlight Deflection via an Entropic Coupling Constant η. Cambridge University. (23 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-1cs81
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Einstein and Bohr Finally Reconciled on Quantum Theory: The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) as the Unifying Resolution to the Problem of Quantum Measurement and Wave Function Collapse. Cambridge University. (14 April 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-vrfrx
- Obidi, John Onimisi . "On the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty, Probability and CPT-Theorem Symmetry-Breaking in the Standard Model of Particle Physics: More Revolutionary Insights from the Theory of Entropicity (ToE)". Cambridge University. (14 June 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-n4n45
- Obidi, John Onimisi. A Critical Review of the Theory of Entropicity (ToE) on Original Contributions, Conceptual Innovations, and Pathways towards Enhanced Mathematical Rigor: An Addendum to the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty. Cambridge University.(2025-06-30). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-hmk6nI
Verlinde makes gravity emergent from entropy; Obidi’s ToE makes all physics emergent from entropy.
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Corrections to the Classical Shapiro Time Delay in General Relativity (GR) from the Entropic Force-Field Hypothesis (EFFH). Cambridge University. (11 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-v7m6c
- Obidi, John Onimisi. How the Generalized Entropic Expansion Equation (GEEE) Describes the Deceleration and Acceleration of the Universe in the Absence of Dark Energy. Cambridge University. (12 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-6d843
- Obidi, John Onimisi. The Theory of Entropicity (ToE): An Entropy-Driven Derivation of Mercury’s Perihelion Precession Beyond Einstein’s Curved Spacetime in General Relativity (GR). Cambridge University. (16 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-g55m9
- Obidi, John Onimisi. The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) Validates Einstein’s General Relativity (GR) Prediction for Solar Starlight Deflection via an Entropic Coupling Constant η. Cambridge University. (23 March 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-1cs81
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Einstein and Bohr Finally Reconciled on Quantum Theory: The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) as the Unifying Resolution to the Problem of Quantum Measurement and Wave Function Collapse. Cambridge University. (14 April 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-vrfrx
- Obidi, John Onimisi . "On the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty, Probability and CPT-Theorem Symmetry-Breaking in the Standard Model of Particle Physics: More Revolutionary Insights from the Theory of Entropicity (ToE)". Cambridge University. (14 June 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-n4n45
- Obidi, John Onimisi. A Critical Review of the Theory of Entropicity (ToE) on Original Contributions, Conceptual Innovations, and Pathways towards Enhanced Mathematical Rigor: An Addendum to the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty. Cambridge University.(2025-06-30). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-hmk6nI
References
- Obidi, John Onimisi. ''A Critical Review of the Theory of Entropicity (ToE) on Original Contributions, Conceptual Innovations, and Pathways towards Enhanced Mathematical Rigor: An Addendum to the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty''. Cambridge University.(2025-06-30). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-hmk6nI
- Obidi, John Onimisi. Master Equation of the Theory of Entropicity (ToE). Encyclopedia; 2025. https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/58596
- Obidi, John Onimisi . "On the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty, Probability and CPT-Theorem Symmetry-Breaking in the Standard Model of Particle Physics: More Revolutionary Insights from the Theory of Entropicity (ToE)". Cambridge University. (14 June 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-n4n45
- Obidi, John Onimisi. ''Einstein and Bohr Finally Reconciled on Quantum Theory: The Theory of Entropicity (ToE) as the Unifying Resolution to the Problem of Quantum Measurement and Wave Function Collapse''. Cambridge University. (14 April 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-vrfrx
- Physics:Gravity from Newton and Einstein in the Theory of Entropicity(ToE), https://handwiki.org/wiki/index.php?title=Physics:Gravity_from_Newton_and_Einstein_in_the_Theory_of_Entropicity(ToE)&oldid=3741982 (last visited August 6, 2025).
- Obidi, John Onimisi . "On the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty, Probability and CPT-Theorem Symmetry-Breaking in the Standard Model of Particle Physics: More Revolutionary Insights from the Theory of Entropicity (ToE)". Cambridge University. (14 June 2025). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-n4n45.
- Obidi, John Onimisi. A Critical Review of the Theory of Entropicity (ToE) on Original Contributions, Conceptual Innovations, and Pathways towards Enhanced Mathematical Rigor: An Addendum to the Discovery of New Laws of Conservation and Uncertainty. Cambridge University.(2025-06-30). https://doi.org/10.33774/coe-2025-hmk6nI.
