1. Introduction
γδ T cells are an unconventional T cell subset, making up about 1–5% of circulating lymphocytes in most healthy animal species
[1]. However, in healthy mucosal or epithelial tissue, these cells can comprise up to 50% of the T cell population
[2]. Furthermore, γδ T cell population increases dramatically in response to invading pathogens
[3]. Along with Mucosal associated invariant T cells (MAIT), Natural Killer T cells (NKT), and Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL), and other unconventional T cell subsets, γδ T cells are non-MHC restricted, can recognize a host of diverse self- and foreign molecules, and have both innate and adaptive immune cell features
[4].
γδ T cells are classified by their TCRγ and TCRδ chain usage. In humans, this is primarily divided into Vδ1+ and Vδ2+ subsets, which arise during fetal development. Vδ1+ subsets typically associate with the Vγ1+ group, including Vγ2,3,4,5, and 8
[5], and are found in the mucosal epithelium
[6][7][6,7]. Vδ2+ subsets typically only associate with the Vγ2+ group, including Vγ9
[5], and form the largest γδ T cell population in the peripheral blood
[6][7][6,7]. The functions of human Vγ9Vδ2+ T cells are well studied, including cytokine production, killing of infected target cells, regulation of monocyte and Dendritic cell (DC) differentiation and maturation, and antigen presentation
[8][9][10][11][8,9,10,11].
In mice, however, γδ T cells are classified primarily via their Vγ chain expression and can be resident to specific tissues with non-redundant functions
[12]. The first γδ T cell population to arise in the thymus are Vγ5Vδ1 T cells, which migrate to the epidermis and become dendritic epidermal T cells (DETCs), a population not found in humans
[13]. DETC progenitors are found between embryonic days 14–16
[14]. In the dermis, however, γδ T cells are primarily Vγ6+, arising at around embryonic day 5, but found obviously on day 3 in mice
[12]. These cells are bona fide resident dermal cells and are essential in neonatal skin immunity
[12]. Vγ4+ cells increase in number through development
[12]. Vγ4+ γδ T cells typically make IFNγ cytokine, while Vγ6+ γδ T cells typically make IL-17 and IL-22
[15]. Thymic signals regulate these cells’ subsequent effector function and critical role during early infection stages
[16].
γδ T cells may also have memory functions, although it is unclear if these functions are entirely analogous to αβ T cell memory functions
[17][18][19][20][17,18,19,20]. Though not fully elucidated, human Vγ9Vδ2 T cells respond to (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP), an intermediate in the non-mevalonate (MEP) pathway of isoprenoid synthesis in some pathogenic bacterial species
[8][9][21][22][8,9,21,22]; isopentenyl phosphate (IPP) an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid synthesis
[21]; and superantigens
[23]. Other subsets of γδ T cells respond to antigens such as CMV virus and MHC-related molecules
[24].
γδ T cells are thus important in understanding the host response to bacterial infection. Part of the host immune response includes metabolic reprogramming, coined as immunometabolism, driving subsequent cytokine, chemokine, and interferon responses
[25].
2. Immunometabolism of γδ T Cells during Bacterial Infection
Murine γδ T cells can be functionally divided into two subsets via the expression of CD27 and their subsequent metabolic states
[26][27][26,27]. CD27+ γδ T cells are generally splenic-resident, ligand-experienced, and secrete IFNγ
[26][27][26,27]. Alternatively, CD27− γδ T cells are found in the lymph nodes (LNs), are ligand naive, and secrete IL-17
[26][27][26,27]. The transcription factor c-Maf is an essential regulator of IL-17 producing γδ T cells by increasing chromatin availability of genes involved in producing Th17 cytokines,
Rorc,
Il17a, and
Blk, and downregulating
TCF1, which limits IL-17 producing γδ T cell differentiation
[28]. These two cell sets have differential metabolic states established during thymic development
[29]. IFNγ producing cells are dependent on glycolysis, while IL-17-producing cells rely on oxidative phosphorylation
[29], controlled by c-Maf regulation of rate-limiting enzyme isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2)
[30].
While glucose metabolic pathways may mark differential γδ T cell subsets by cytokine production, lipid metabolic changes may impact the severity of inflammation in inflammatory disease. In a psoriasis model, dietary cholesterol metabolites, such as oxysterol, regulate IL-17+ γδ T cell development and trafficking to the skin, with a higher fat diet in mice being associated with more severe psoriasis
[31]. Similarly, IL-17+ γδ T cells had increased lipid metabolism and storage in murine breast adenocarcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, and melanoma models
[29].
Amino acid metabolism in T cells has been well studied, particularly in the context of cancer; however, recent studies aim to relate amino acid metabolism in γδ T cells to changes in inflammation severity in psoriasis and polymicrobial sepsis. For example, glutamine metabolism was upregulated in IL-17+ γδ T cells during psoriasis, promoting acetylation of the
Il17a promoter and increasing IL-17 production
[32][33][32,33]. Additionally, CD69 interacted with the heterodimeric LAT1-CD98 amino acid transporter to upregulate tryptophan uptake during psoriasis, leading to mTORC- and AhR-mediated IL-22 production and increased inflammation
[33]. Furthermore, glutamine metabolism is also implicated in mouse models of polymicrobial sepsis. Mice treated with glutamine administration had increased γδ T cell populations, decreased inflammatory lesions, and reduced lung damage compared with mice treated with saline
[34]. While these metabolic states were established and studied in both an inflammatory and tumor microenvironment, these metabolic changes have not yet been fully elucidated during bacterial infection.
3. The Site-Specific γδ T Cell Response to Staphylococcus aureus Infection
S. aureus is a gram-positive bacterium that is highly pathogenic and is the major cause of skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), infective endocarditis, bone and joint infection, medical device-related infection, and bacteremia.
[35][39]. Mainly, community-associated methicillin-resistant
S. aureus (CA-MRSA) infection is a looming threat, claiming over 20,000 lives in the US annually
[36][40]. Furthermore, vaccine efforts against
S. aureus to date have been unsuccessful
[37][38][41,42]. As a result, alternative approaches to combat the threat have become essential, and immunotherapies against
S. aureus infection have emerged in recent years
[39][40][43,44].
There are various non-pore-forming toxins, pore-forming toxins, and bacterial components from
S. aureus that are antigenic to the host. γδ T cells have been reportedly involved in early immune responses to
S. aureus infection. γδ T cells respond to staphylococcal superantigens, including staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1)
[41][45]. In conventional T cells, staphylococcal superantigens bind outside the MHCII-TCR antigen presenting complex, leading to rapid T cell expansion and inflammation
[42][46].
In human adults, Vγ2+ T cell response and proliferation to SEA in specific requires APC presentation, particularly on MHC II
[23][43][23,47]. SEA recognition requires the N terminal third of the toxin for partial γδ T cell activity and the N terminal two-thirds of the protein for optimal activity, most critically needing amino acid residues 20–27
[23]. Subsequent reactivity to SEA was also dependent on and specific to the Vγ9 region of the TCR, which may explain why Vγ2+ cells are largely extrathymic
[43][47].
The γδ T cell cytokine response to superantigens primarily involves IFNγ and IL-17A. IFNγ production by γδ T cells in response to SEA proceeds through an IL-12-dependent pathway and helps induce the expansion of memory-like CD45RO+ Vγ9Vδ2 T cells
[37][41][41,45]. This finding was echoed in bovine WC1+ γδ T cells
[44][48]. On the other hand, SEA-induced IL-17A production by γδ T cells has a unique role in lung host response. In a lung immunity model, Kumar and colleagues found that γδ T cells were the primary source of proinflammatory cytokine IL-17A after the SEA challenge
[45][49].
Interestingly, however, after the SEA challenge, there was no decrease in neutrophil and monocyte recruitment in TCRδ(−/−) mice, and αβ T cells were found to be responsible for neutrophil and monocyte recruitment to the infection site
[45][49]. Neutrophil recruitment is critical for clearance of
S. aureus: individuals with impaired neutrophil function or decreased neutrophil count display increased infection susceptibility
[46][50]. Since IL-17A is known to play a critical role in neutrophil recruitment
[47][51], the researchers hypothesized that IL-17A production was being compensated by CD3 + CD8− αβ T cells in TCRδ(−/−) mice
[45][49]. In a follow-up study, IL-17 producing γδ T cells in the lung were termed lung granular γδ T cells due to their increased side scatter measured during flow cytometry analysis
[48][52]. Lung granular γδ T cells were activated by inflammasome-derived IL-1β and IL-2 to produce IL-17 in a JAK/STAT-dependent manner, marking a novel mechanism by which γδ T cells respond to superantigen exposure
[48][52]. Interestingly, this finding contrasts the widely accepted paradigm of IL-2 inhibition of Th17 differentiation
[49][53], though the exact function of γδ T cell-derived IL-17 in this context has not yet been elucidated.
Unlike SEA stimulation, TSST-1 stimulation of γδ T cells upregulated secretion of proinflammatory cytokines IFNγ, TNFα, and IL-2 and suppressed anti-inflammatory IL-10 production
[50][54]. This response was specific to TSST-1 stimulation and was not demonstrated in other staphylococcal toxins
[50][54].
While staphylococcal superantigens were shown to activate the inflammatory response of γδ T cells,
S. aureus α toxin was contrastingly found to delay IL-17+ γδ T cell recruitment to the infection site, slowing neutrophil recruitment and worsening infection in a mouse dermonecrosis model
[51][55]. These studies indicate a critical role for γδ T cells in activating or suppressing host immune responses against
S. aureus in response to toxins the bacterium produces. The following parts will explore current literature elucidating the host γδ T cell response to
S. aureus in different infection sites and contexts.
3.1. Cutaneous Infection
4.1. Cutaneous Infection
Cutaneous γδ T cells are important in early immune defense against
S. aureus skin infection
[52][56] (
Figure 1). In a murine in vivo study of
S. aureus skin infection, epidermal Vγ5+ γδ T cells induced by IL-1R and IL-23 signaling were protective against worsened infection; γδ T cell deficient mice had more significant lesion sizes, increased bacterial burdens, and lessened neutrophil recruitment and activity compared to both αβ T cell deficient mice and wild type (WT) mice
[53][57]. This protective role is mediated by IL-17 production. γδ T cells comprise most of the IL-17-producing cells in
S. aureus-infected skin
[53][54][57,58]. Treatment of γδ T cell-deficient mice with a single dose of IL-17 abrogated the detrimental effects of γδ T cell deficiency
[53][57]. IL-17+ γδ T and Th17 cells also play a compensatory role, promoting neutrophil recruitment in IL-1β deficient mice
[55][59].
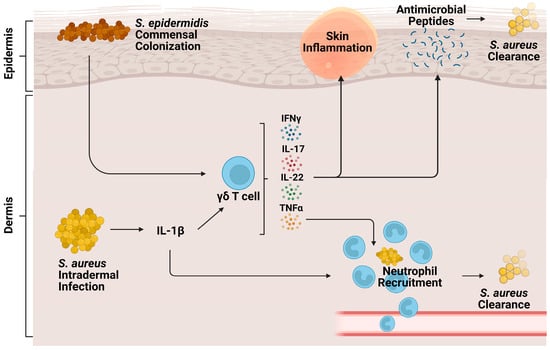
Figure 1. Role of γδ T cells during cutaneous S. aureus infection. Intradermal S. aureus infection and subsequent IL-1β signaling stimulate cutaneous γδ T cells to produce proinflammatory cytokines IFNy, TNFα, IL-22, and IL-17. These cytokines contribute to neutrophil recruitment, production of antimicrobial peptides, skin inflammation, and eventual bacterial clearance. Commensal S. epidermidis, skin colonization, stimulates γδ T cells to produce perforin-2, a pore-forming cytolysin that helps clear S. aureus infection.
A study from
our research
ers's group supported the importance of IL-17 producing γδ T cell populations during
S. aureus skin infection, finding that these cells were being trafficked from the LNs
[56][60]. T cell receptor (TCR) RNA sequencing revealed clonotypic expansion of Vγ6+ Vδ4+ T cells but not Vγ5+ γδ T cells in the skin and LNs
[56][60]. This expansion was specific to
S. aureus infection; however, during
P. aeruginosa infection, both TRGV6 and V5 were expanded
[56][60]. The trafficked Vγ6 + Vδ4+ T cells enhanced the neutrophilic response during secondary
S. aureus infection in IL-1β deficient mice
[57][61]. These cells produced not only IL-17 but also other proinflammatory cytokines like TNFα, IL-22, and IFNγ
[56][60]. IL-17A and IL-17F produced by LN-trafficked γδ T cells have compensatory roles to one another in the skin, as they do during mucocutaneous
S. aureus infection
[58][62]. Both cytokines had to be neutralized to note any differences in mouse lesion size or bacterial burden after cutaneous
S. aureus infection
[56][60]. While IL-17 plays a critical role in γδ T cell signaling in cutaneous infection, it is important to note that this is not the case in all infection contexts. For example, response to early IL-1R signaling, but surprisingly not IL-17 or TNFα signaling, in γδ T cells promotes host survival and monocyte recruitment to the spleen in an
S. aureus-induced bacteremia model
[59][63].
γδ T cells also have memory-like function during skin inflammation and
S. aureus infection
[57][60][61,64]. In an imiquimod model of inflammation, IL-17 producing Vγ4+ γδ T cells leave the LNs and are trafficked to the skin, with previously sensitized mice showing more significant γδ T cell-induced inflammation proliferation and IL-17 production, indicating a memory-like role
[60][64]. In the context of
S. aureus infection,
our
esearcher colleagues found that while the primary challenge of IL-1β deficient mice led to decreased bacterial clearance, greater lesions, and impaired neutrophil abscess formation, these functions were restored upon secondary infection by LN draining γδ T cells through TLR2/MyD88 signaling to produce IFNγ and TNF
[57][61]. Overall, inflammatory cytokine production in the skin by LN-draining γδ T cells seems to confer protective immunity against primary and secondary
S. aureus infections.
Along with inherent host protective responses to
S. aureus infection, commensal bacteria may protect the host against
S. aureus infection by driving host antimicrobial peptide production by γδ T cells
[61][65]. One study finds that
S. epidermidis commensal colonization of the skin induces γδ T cells to upregulate perforin-2 expression, a cytolysin constitutively expressed by γδ T cells to form pores in bacterial membranes
[62][66], along with upregulating other cytotoxicity markers against MRSA infection
[63][67]. As such,
S. epidermidis co-colonization with
S. aureus on the skin led to an increased anti-
S. aureus effect
[63][67].
Lactobacilli have also been identified as commensal bacteria that may modulate host immune protection (
Figure 1). One study found that in vitro co-colonization of human PBMCs with
S. aureus and Lactobacillus strains dampened IFNγ secretion in γδ T cells, MAIT cells, and NK cells stimulated by
S. aureus cell free supernatants
[64][68]. However, recent other studies utilize Lactobacillus recombinant strains as vaccine models against
S. aureus due to the commensal bacteria’s ability to induce a robust immune response
[65][66][69,70]. Thus, it is evident that during
S. aureus infection, lactobacilli have differential effects in vitro versus in vivo and must be studied contextually.
3.2. Pneumonia
4.2. Pneumonia
In the lung, the major subsets of γδ T cells are Vγ1+ and Vγ4+ and accumulate after
S. aureus-induced pneumonia
[67][71]. While murine γδ T cells are involved in decreasing the bacterial burden and increasing neutrophil infiltration, with corresponding increases in keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC), MIP2, GM-CSF, IL-6, and TNFα, acute lung damage was decreased in γδ T cell deficient mice, likely due to tamped inflammation from reduced neutrophil recruitment
[67][71]. An early burst of γδ T cell-produced IL-17 was also implicated in increased lung damage post-pneumonia
[67][71], indicating a possibly detrimental role for γδ T cells in this model.
Interestingly, nociceptor sensory neurons in the lung may have an immunosuppressive role on pulmonary γδ T cell function during MRSA infection. Selective ablation of TRPV1+, an ion channel expressed on nociceptors mediating airway allergic pathways, increased absolute Vγ1+ γδ T cell population, increased survival, and increased bacterial clearance
[68][72]. This neuroimmunological finding is important as it marks sensory neurons as targets to protect against
S. aureus pneumonia.
Cell death pathways, including the necroptotic pathway, may also suppress the host immune response against
S. aureus-induced pneumonia by targeting IL-17 signaling by lung γδ T cells
[69][73]. α toxin from
S. aureus is known to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in vitro
[70][74]. NLRC4, an NLR family protein involved in inflammasome assembly, is upregulated during
S. aureus-induced pneumonia in myeloid and non-myeloid cells
[69][73]. Furthermore, α toxin from
S. aureus induces necroptosis leading to increased IL-18 and IL-1β production and suppressed γδ T cell recruitment, dampening the IL-17 response, leading to decreased neutrophil recruitment and inflammation
[69][73]. However, necroptotic suppression of IL-17 response is site-specific; in a surgical site
S. aureus infection model, IL-17 producing γδ T cells at the wound site relied by NLRP3/IL-1β signaling for IL-17A production. It is interesting to note that these observed during infection with SH1000
S. aureus strain, but not PS80
[71][37].
Therefore, the pneumonia model indicates the necessity of balance in the γδ T cell response; too much IL-17 signaling may lead to excessive inflammation and tissue damage, while too little may hinder bacterial clearance.
3.3. Peritonitis
4.3. Peritonitis
Similar to cutaneous and pulmonary infection, γδ T cells are the primary source of IL-1β-dependent IL-17 in a primary challenge during a recurrent peritonitis murine model of
S. aureus infection
[18]. Some mice in this study were also found to have a biphasic wave of IL-17 production, with one peak at 3 h and the second at 72 h post-infection, with V
γ4+ γδ T cells at 72 h being primed for later infection and IL-1β independent IL-17 production
[18], suggesting a memory function for γδ T cells during acute peritonitis as well. In the kidney, chronic systemic
S. aureus infection induced the expansion of a population of kidney-resident γδ T cells that constitutively express CD69 and provide protection against
S. aureus [15]. Thus, in mice,
S. aureus infection seems to expand both resident and memory γδ T cells.
In human peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients, on the other hand, it is unclear whether
S. aureus-induced peritonitis expands γδ T cells or not. In one study, peritoneal Vδ2+ γδ T cells were reduced during acute peritonitis
[71][37]. However, this was not specific to
S. aureus-induced peritonitis and was used partially as an immune fingerprint to classify gram-positive acute peritonitis
[71][37]. On the other hand, other studies found Vδ2+ γδ T cell recruitment and response to
S. aureus-induced peritonitis in PD patients, possibly due to superantigen recognition
[22][23][22,23].