Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Stavros P. Papadakos and Version 2 by Lindsay Dong.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a global health challenge with limited treatment options and a poor prognosis for advanced-stage patients. Recent advancements in cancer immunotherapy have generated significant interest in exploring novel approaches to combat HCC. One such approach involves the unique and versatile subset of T cells known as γδ T cells. γδ T cells represent a distinct subset of T lymphocytes that differ from conventional αβ T cells in terms of antigen recognition and effector functions. They play a crucial role in immunosurveillance against various malignancies, including HCC.
- γδ T cells
- hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- immunotherapy
1. Introduction
1.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Understanding, Challenges, and Therapeutic Horizons
In 2020, approximately 906,000 individuals worldwide received a diagnosis of liver cancer, mainly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), ranking it as the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths [1][2][1,2], accompanied by a 5-year survival rate of merely 18% [3]. HCC mostly affects individuals aged 60–70 years and is more prevalent in men. The causative factors show regional and ethnic variations, mainly attributed to distinct risk factors. Chronic liver diseases arising from hepatitis B (HBV) or C (HCV), alcohol abuse, fatty liver diseases, obesity, diabetes, and certain rare conditions contribute significantly to its development [4]. Predominantly, 80% of cases occur in sub-Saharan Africa and eastern Asia, where chronic hepatitis B and exposure to aflatoxin B1 are primary risk factors. For hepatitis B patients, the incidence correlates with viral load, infection duration, and liver disease severity. Occult hepatitis B virus infection also heightens the risk due to DNA damage induced by virus integration [5]. In the USA, Europe, and Japan, hepatitis C, coupled with excessive alcohol intake, stands as the primary risk factor. The epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma exhibits dynamic temporal trends, with Japan and Europe experiencing plateauing or declining incidence, contrasting with the ongoing increase in the USA, predicted to stabilize by 2020 [5]. Concurrently, there is a noticeable rise in the incidence of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)/metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH)-related liver cancers, now standing as the most prevalent chronic liver diseases globally, impacting approximately 25% of the population [6]. Lifestyle factors, such as obesity, diabetes, alcohol consumption, and genetic variants (PNPLA3, TM6SF2, HSD17B13), are associated with an increased risk of HCC, even in the absence of cirrhosis [7]. Notably, enhancing glycemic control and maintaining a healthy weight are independently linked to a reduced HCC risk [8]. Interestingly, while alcohol-related liver disease is more common in men, women face a higher relative risk of developing HCC [9]. Epigenetic mechanisms significantly influence the progression of HCC [10].
1.2. Decoding γδ T Cell Diversity: Bridging Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Lymphocytes in the vertebrate adaptive immune system utilize somatic recombination to generate diverse antigen receptor repertoires, enabling recognition of a wide range of pathogens. B cells, αβ T cells, and γδ T cells, evolving over approximately 500 million years, are crucial components of this system [11][26]. While research on T cells has traditionally focused on the αβ compartment, groundbreaking studies revealed the existence of a separate lineage, γδ T lymphocytes, distinguished by a distinct somatically recombined γδ T cell receptor (TCR) and non-MHC restriction [12][27]. Despite proposing diverse roles in immunity, such as protection against pathogens, tumor immunosurveillance, and the maintenance of epithelial surfaces, the functions and antigen recognition requirements of γδ T cells remain unclear [13][28]. Regarding human peripheral γδ T cells, two major subsets, innate-like Vγ9Vδ2 T cells and adaptive-like subsets, exhibit distinct immunobiologies [12][27]. Innate-like Vγ9Vδ2 T cells, predominant in peripheral blood (PB), undergo a phenotypic transition from rare and naïve in cord blood to mature effector cells with CD45RO expression in early childhood [14][29]. They respond universally to pathogen-derived phosphoantigens (pAgs), including microbial-derived 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMBPP), in a TCR-dependent manner [15][30]. This subset displays a semi-invariant TCR repertoire, resembling innate lymphocytes, such as i-NKT and mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells. On the other hand, adaptive-like subsets, such as Vδ2neg γδ T cells and Vγ9negVδ2 T cells, constitute a minority in PB [11][26]. Vδ2neg T cells, enriched in solid tissues, respond to viral infections and display clonal expansions, exhibiting an adaptive-like immunobiology [12][27]. These cells undergo clonal expansions in response to various infections, including CMV, suggesting an adaptive response [16][31]. Vγ9negVδ2 T cells, unable to respond to pAgs, adopt a Tnaive phenotype, but in rare instances, they can transition to a Teffector phenotype with clonal expansion upon stimulation [11][26]. In summary, recent studies reveal a complex landscape of γδ T cell subsets with distinct immunobiologies, combining features of both innate and adaptive immunity [17][32]. The transition from naïve to effector status in these subsets appears linked to environmental exposures, particularly infections, resembling conventional adaptive immune responses [11][26]. γδ T cells possess unique characteristics that make them well suited for recognizing and responding to transformed cells, including HCC. γδ T cells exhibit distinct advantages over conventional αβ T cells. Unlike αβ T cells that mainly recognize peptide antigens presented by major histocompatibility complexes (MHC), γδ T cells recognize a diverse array of non-peptide antigens, including stress-induced molecules and phosphorylated metabolites. γδ T cells provide a rapid response to antigens, acting as a frontline defense in epithelial tissues and mucosa. Their innate-like immune functions enable immediate responses without prior sensitization, contributing to immune surveillance against infections and tumors. Importantly, γδ T cells can recognize antigens independently of MHC presentation, broadening their capacity to detect various stress-related molecules. In contrast, αβ T cells primarily function as adaptive immune cells, requiring specific antigen recognition and prior activation [18][33].1.3. γδ T Cells: Dynamic Modulators of Inflammation in Chronic Liver Diseases
γδ T cells play a crucial role in the establishment and regulation of inflammatory processes, with their involvement varying based on disease etiology and specific subsets [19][35]. The involvement of γδ T cells in various inflammatory processes is underscored by several studies, with their role dependent on disease etiology and the specific subset engaged. Notably, Vδ1 and Vγ9Vδ2 T cells can adopt a CD103+ liver tissue-resident memory (TRM) phenotype, exhibiting higher levels of C-X-C chemokine receptor (CXCR) 6 and CXCR3 compared to circulating γδ T cells in HCC patients [18][33]. In acute viral HBV, γδ T cells are depleted in blood but accumulate in the liver, potentially driven by CXCR3 and C-C chemokine receptor (CCR)5 [20][36]. In chronic HCV infection, Vδ1 T cells are enriched in the liver, correlating with increased liver inflammation [21][37]. In models of acute liver injury, γδ T cells contribute to pro-fibrotic processes through IL-17A production [22][38]. However, in humans, γδ T cells are more likely to exhibit type 1 effector functions, producing interferon (IFN)-γ and engaging in tumor-killing activities [23][39]. In liver transplantation for chronic liver disease, Vγ9+Vδ2+ T cells decrease in circulation and liver sinusoids, particularly in acute-on-chronic liver failure [24][41]. Chronically activated, these cells exhibit reduced antibacterial effector functions in response to microbial metabolites, possibly contributing to bacterial infections. In decompensated cirrhosis, bacterial translocation in the peritoneal cavity leads to a comparable fraction of γδ T cells as in the blood, but with a TRM phenotype [25][26][34,42]. This phenotype is associated with enhanced local inflammation in response to a bacterial infection. The detection of both migratory and resident γδ T cell populations suggest a possible redistribution between the gut, liver, circulation, and peritoneum [26][42].2. Exploring Epigenetic Regulation of γδ T Cells: Insights into Development, Function, and Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer Immunotherapy
Epigenetic regulation plays a crucial role in the process of carcinogenesis [27][28][29][30][31][44,45,46,47,48]. γδ T cells, positioned at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity, exhibit a unique repertoire that necessitates in-depth investigation. As our comprehension of the epigenetic landscape evolves, the analysis of the molecular pathways regulating the behavior of γδ T cells becomes invaluable for the comprehension of immune regulation [32][49]. For example, the utilization of single-cell RNA-sequencing technology and immune functional assays provided evidence that bacille Calmette –Guerin (BCG) induces changes in the epigenetic transcriptional programs of γδ T cells at the chromatin level [33][50] and at histone H3 acetylation at lysine 27 (H3K27ac) [34][51], enhancing their responsiveness to heterologous bacterial and fungal stimuli, such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and Candida albicans [35][52], characterized by a higher production of TNF and IFN-γ several weeks after the vaccination [35][52]. Taking a step further, distinct and temporally restricted epigenetic mechanisms regulate the development of TCRαβ and TCRγδ T cells [36][53]. Chromatin accessibility dynamics exhibit stage specificity, with T cell lineage commitment marked by the GATA binding protein 3 (GATA3)- and B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11B (BCL11B)-dependent closing of PU.1 sites. Notably, β-selection is characterized by a temporary increase in histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) without open chromatin modifications. Emerging γδ T cells, originating from common precursors of β-selected cells, exhibit significant chromatin accessibility changes due to strong TCR signaling [36][53]. Chromatin modifiers, particularly histone-modifying factors, play a significant role in the differentiation of γδ T cells [37][54]. Specifically, an upregulation of chromatin modifiers is evident during the differentiation trajectories of γδ T cell subsets (γδ T17 and IFN-γ-producing T cells). The late activated molecules during effector differentiation, particularly in the γδ T17 lineage, showed an increased expression of histone-modifying factors, such as histone–lysine N-methyltransferase (Kmt)2a, Kmt2c, lysine demethylase (Kdm)5a, Kdm5b, and the histone deacetylase (Hdac)7 [37][54]. These modifications are involved in shaping the functional characteristics and phenotypic diversity of γδ T cell subsets. A growing body of evidence suggests that distinct epigenetic patterns at certain gene loci differentiate the IL-17-producing CD27− γδ T cells from the IFN-γ-expressing CD27+ γδ T cells [38][55]. In CD27− γδ T cells, active H3K4me2 marks were found to accumulate at the Il17a, IL17f, and Il22 loci, indicating permissive chromatin configurations. However, in γδ CD27+ T cells, these marks were notably absent at these loci. Conversely, the Ifng locus displayed H3K4me2 marks in both γδ cell subsets, suggesting a shared epigenetic regulation for Ifng in both subsets. An additional investigation into histone modifications revealed that acetylation of histone H3 (H3ac) was exclusive to the Il17a locus in γδ CD27− cells, while both CD27+ and γδ CD27− T cells exhibited H3ac marks at the Ifng locus. These epigenetic modifications were associated with differential cytokine gene expression levels. Il17a was highly expressed in γδ CD27− T cells, while Ifng showed higher expression in CD27+ γδ T cells, consistent with the epigenetic patterns observed [38][55]. The combination of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) and epigenetic modifiers significantly enhances γδ T cell functions, providing a promising strategy for improving clinical outcomes in immunotherapy [39][57]. Using 3D melanoma models, it is observed that γδ T cells infiltrated rapidly but exhibited exhausted phenotypes, limiting tumor killing. ICB enhances γδ T cell killing, and epigenetic modifiers (Entinostat, Vorinostat) improve functions by regulating MHC class I chain-related protein A (MICA)/ MHC class I chain-related protein B (MICB) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). γδ T cells, serving as innate immune sentinels, infiltrate melanoma spheroids effectively, with early IFN-γ production and enhanced effector functions. However, they display exhausted phenotypes. Combining γδ T cells with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1)/cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) enhanced functions and reduced spheroid size. Epigenetic modifiers such as Tubastatin-A, Ricolinostat, and Vorinostat inhibit HDAC6/7 pathways, improving γδ T cell antitumor functions. These modifiers increase MICA/MICB expression and decrease NKG2A expression in tumor cells.3. Insights into the Utilization of γδ T Cells in HCC Immunotherapy Clinical Evidence
HCC treatment necessitates innovative immunotherapeutic strategies. The HCC tumor microenvironment (TME) is acknowledged for its immunosuppressive characteristics, attributed to various regulatory factors, such as a low pH, hypoxia, a nutritional deficiency, metabolic remodeling, and inflammation [40][22]. γδ T cells have emerged as potential assets in this landscape, and their role is currently under intense investigation in patients with chronic liver disease [25][34]. HCC transcriptomic data reveal a significant upregulation of inhibitory checkpoint molecules in HCC tissues compared to normal tissues [41][58]. Notably, these molecules, including CTLA4, hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 (HAVCR2), lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3), programmed cell death protein 1 (PDCD1), programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PDCD1LG2), T cell immunoreceptor with immunoglobulin (Ig) and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) domains (TIGIT), and sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 15 (SIGLEC15), show consistent expression across different patient pTNM stages, suggesting a uniform responsiveness to ICB therapy. Hu et al. uncovered a distinct immunosuppressive profile in the HCC TME. This is characterized by increased infiltration of regulatory T cells (Tregs), activated mast cells, and M0 macrophages, coupled with the suppression of γδ T cell infiltration and hindrance in the differentiation of macrophages from M0 to M2. Strikingly, these immune cell infiltrations exhibited no statistical differences among different pTNM stages, affirmin g the highly immunosuppressive nature of the HCC TME across various disease stages. The authors further extended their investigation to the phenotypic profiles of circulating γδ T cells in HCC and healthy populations [41][58]. The analysis reveals a dominance of the Vδ2+ subset in the PB of healthy individuals, while under immune-suppressed conditions in HCC, the Vδ2+ subset is significantly depleted. The proposed Vδ1+/Vδ2+ ratio emerges as a potential indicator for clinical prognosis, with higher ratios associating with more suppressed immunity and poorer outcomes. The study also identified reduced NKG2D expression in the Vδ1+ population, suggesting depressed cell activation and enhanced survival ability, while a higher pPD1 expression in the Vδ2+ population indicated suppressed cytotoxicity [41][58]. Employing the CIBERSORT algorithm and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), they identified γδ T cell-specific genes associated with immunological activity and notably T cell activation. A risk signature comprising 11 hub genes demonstrated robust prognostic capabilities. This signature exhibited correlations with clinical features and tumor grade and stage, providing valuable prognostic insights. High-risk HCC samples exhibited an immune-activated phenotype and increased susceptibility to ICB pathways. The risk signature demonstrated associations with chemotherapy drug sensitivity, suggesting its potential utility in guiding treatment strategies. They also investigated the role of the Rieske Fe-S domain-containing (RFESD) gene in HCC, identifying it as a poor prognosis predictor and correlating it with immune cell infiltration and HCC cell line proliferation. Collectively, they underscored the significance of immune infiltration of γδ T cells in the context of HCC, while the constructed risk signature may serve as a valuable tool for risk stratification and treatment decision making in HCC [42][59]. Sun et al. explored the immune characteristics of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and focused on the changes in peripheral immunity in patients with HBV-HCC [43][61]. They documented that the expression of NKp46, a marker associated with cytotoxicity, is up-regulated in the PB of HBV-HCC patients. Additionally, they investigated γδ T cells, highlighting an increase in PD-1 expression on Vd1 cells in HBV-HCC patients. They suggested a correlation between T cell Ig and mucin domain 3 (TIM3) expression on γδ T cells and disease progression, with increased TIM3+ γδ T cells in the PB of advanced HBV-HCC patients. This highlights the need for further exploration of the liver immune microenvironment in HBV-HCC patients, while single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) could serve towards a more comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis and treatment strategies of HCC [43][61].4. The Role of γδ T Cell in the Immune Landscape of HCC
4.1. γδ Τ Cell Features and Interactions in the HCC TME
Research has highlighted unique characteristics of γδ Τ cells in the HCC TME. These features determine the interactions between γδ Τ cells and neoplastic cell and the distribution of different γδ Τ cells between the PB and the liver tissue, thus affecting antitumor immunity. Toutirais investigated the interaction between Vγ9Vδ2 T cells and HCC cells, focusing on the role of DNAM-1 and CD96, two activating NK receptors expressed by Vγ9Vδ2 T cells [44][64]. The ligands for these receptors, Nectin-like-5, Nectin-2, and CD96, were found on all analyzed HCC cell lines. Through mAb-mediated masking experiments, they demonstrated that DNAM-1 plays a crucial role in the cytotoxicity against HCC cells and IFN-γ production in Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. Specifically, Nectin-like-5, but not Nectin-2, was identified as the ligand responsible for DNAM-1-dependent functions in Vγ9Vδ2 T cells. CD96, however, did not appear to contribute to the killing of HCC cells. Moreover, they revealed that DNAX accessory molecule-1 (DNAM-1) and NKG2D could cooperate in the cell lysis of HCC, providing insights into potential therapeutic targets for antitumor immunotherapy involving γδ T cells [44][64]. Given the liver’s abundance of tissue-resident γδ T cells and the established efficacy of allogeneic Vδ2+ γδ T cell adoptive transfer in liver cancer control, Hu et al. investigated the mechanisms underlying γδ T cell repression in the HCC TMΕ [41][58]. Analyzing circulating γδ T cells in healthy individuals and HCC patients, they observed a significant imbalance in subset proportions. Specifically, the Vδ1+ subset exhibited a substantial increase, while the Vδ2+ subset showed a marked reduction in the HCC population, resulting in a noteworthy elevation of the Vδ1+/Vδ2+ ratio. Furthermore, they revealed a significant decrease in NKG2D expression within the Vd1+ subset, suggesting a potential impairment in antitumor immunity. In contrast, the Vδ2+ subset in the HCC group displayed a notable increase in PD1 expression, indicative of compromised cytotoxicity in Vδ2+ γδ T cells.4.2. γδ Τ Cell Reshaping the HCC Tumor Microenvironment
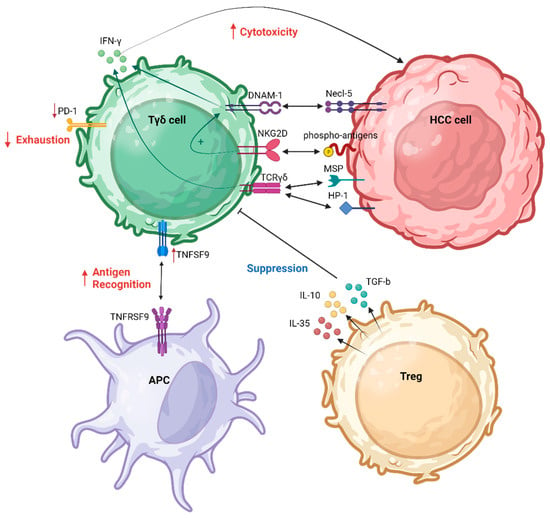
The immune TME plays a critical role in the dynamics of HCC, influencing its progression and response to treatment [45][65]. Comprising a complex interplay of immune cells, stromal elements, and signaling molecules, the TME significantly impacts the trajectory of HCC [46][47][18,66]. In this context, the immune TME often takes on an immunosuppressive profile, fostering conditions conducive to tumor growth and immune evasion [48][49][19,20]. Several T cell populations comprise the immune HCC TME [50][67]. Within the tumor, an increased presence of cells expressing CD137, and inducible T cell co-stimulator (ICOS) suggested recent antigenic activation. Notably, distinct T cell populations were identified, such as functionally impaired proliferating CD4+ cells co-expressing ICOS and TIGIT, functionally active CD8+ cells co-expressing CD38 and PD1, and CD4-CD8 double-negative T cell receptor αβ and γδ cells [non-major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-restricted T cells)]. Histologic classification correlated with the accumulation of activated T cells, indicating an immune-inflamed HCC phenotype [50][67]. Recent findings indicate a synergistic interaction between γδ T cells and NK cells within the HCC TME [44][51][52][60,64,68]. γδ T cells exhibit a capacity to recognize human tumor cells in a non-restricted MHC manner. The mechanisms for malignant cell recognition by γδ T cells involve both TCR-dependent pathways and activation through NK receptors [44][64]. Toutirais et al. explored the role of two NK receptors, DNAM-1 and CD96, in the lytic function of γδ T cells, as was analyzed previously. These specific interactions between DNAM-1 and Necl-5 on HCC cells was highlighted as a novel regulatory mechanism for γδ T cell cytotoxicity, enhancing IFN-γ production. Moreover, the authors suggested a cooperative role of DNAM-1 and NKG2D receptors in triggering the cytotoxic effector function of γδ T cells [44][64]. Numerous molecules play pivotal roles in shaping the immune TME of HCC, impacting the abundance and functionality of γδ T cells. Emerging evidence suggests that transforming growth factor (TGF)-b1 is associated with a poor prognosis in HCC [53][71]. Specifically, seven members of the TGF-b family, including bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)2, BMP6, growth differentiation factor (GDF)6, GDF7, GDF10, left-right determination factor 2 (LEFTY2), and TGF-b1, were identified as potential independent prognostic factors for HCC. Figure 1 summarizes the interactions between γδ Τ cells and HCC cells as well as with other immune cells responsible for the regulation of γδ Τ cell functions in the HCC TME.
Figure 1. γδ Τ cell interaction in HCC TME. APC, antigen-presenting cell; DNAM-1, DNAX accessory molecule-1; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; MSP, macrophage-stimulating protein; NKG2D, natural killer group 2D; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; TCR, T cell receptor; TNFSF9, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily member 9; Treg, regulatory T cell. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 4 December 2023).
5. γδ T Cells: An Immunotherapeutic Odyssey for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
5.1. Strategies to Enhance γδ T Cell Antitumor Efficacy
5.1.1. γδ T Cells in CAR T Therapies: Targeting HCC Breakthroughs
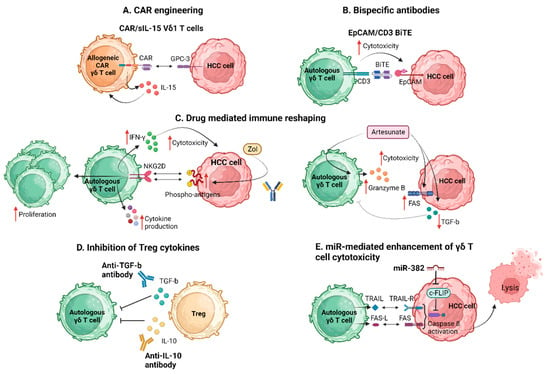
The development of allogeneic Vδ1 T cells expressing a glypican-3 (GPC-3)-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) [54][73] and secreting IL-15 is explored as a potential cell therapy for HCC and other GPC-3-expressing tumors [55][74]. Autologous CAR T cell therapy has shown success in hematologic malignancies, but challenges exist in treating solid tumors due to issues such as poor T cell homing, CAR target antigen variability, and the immunosuppressive TME. GPC-3 is an attractive target for immunotherapy, being highly expressed in HCC [18][56][33,75]. Autologous GPC-3.CAR αβ T cells have shown promise, but logistical challenges and concerns about immune fitness have hindered widespread adoption. Allogeneic cell therapies, derived from healthy donors, present a potential solution by overcoming manufacturing challenges. In fact, recent evidence exploring the safety and efficacy of combining locoregional therapy with the adoptive transfer of allogeneic γδ T cells for advanced HCC and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) demonstrated that adverse events were manageable, indicating the safety of this novel combination therapy [57][76], as opposed to allogeneic αβ T cells that may pose a risk of graft-versus-host disease (GvVHD), necessitating complex gene editing [58][77].
5.1.2. Zoledronic Acid/Artesunate and γδ T Cells Reshaping HCC Therapeutics
Ongoing research in the field of HCC investigates the interplay between zoledronic acid (Zol) and γδ T cells [19][59][60][61][35,78,79,80]. Zol has demonstrated immunomodulatory properties, notably activating γδ T cells, which show antitumor capabilities. The exploration of combining Zol with γδ T cell therapy emerges as a prospective approach to enhance the immune response against HCC. Zakeri et al. investigated the potential of Zol in enhancing the antitumor activity of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells in the context of HCC with a focus on the TRM subset of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells found in the human liver [19][35]. They began characterizing the liver-resident Vγ9Vδ2 TRM, highlighting their tissue-homing capabilities through the expression of chemokine receptors CXCR6 and CXCR3. These TRMs displayed a reduced expression of the endothelial homing receptor CX3CR1 and lacked the expression of the lymph node homing receptor CD62L. Functionally, the intrahepatic Vγ9Vδ2 TRMs exhibited an activated profile with higher expression of the T cell activation marker HLA-DR. However, they showed reduced cytotoxic potential, marked by a lower expression of the serine protease granzyme B and a significant capacity for rapid production of the pro-survival cytokine IL-2 and IFN-γ. The authors also explored the antitumor potential of Vγ9Vδ2 TRM against Zol-sensitized HCC cell lines. While fresh intrahepatic Vγ9Vδ2 T cells exhibited minimal effector function in response to co-culture with HCC cell lines, Zol pre-treatment of the tumor cells significantly enhanced the effector function of CD69+CD49a+ Vγ9Vδ2 TRM. This response was further observed with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) isolated from HCC tumors, suggesting the potential for Zol to boost the antitumor function of intratumoral Vγ9Vδ2 T cells [19][35]. The above are further supported by Sugai et al., who demonstrated that Vγ9Vδ2 T cells, activated by Zol-induced phosphoantigens, exhibited significant antitumor activity against various HCC cell lines (HepG2, HLE, HLF, HuH-1, JHH5, JHH7, and Li-7). Zol treatment not only increased HCC cell susceptibility to T cell killing but also triggered T cell proliferation and induced cytokine production (IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IFN-γ, GM-CSF, TNF-α) and grandzyme B [59][78]. Towards the same direction, Tian et al. utilized Zol in combination with IL-2 in vitro, concluding that, in conjunction, they could expand circulating γδ T cells in HCC patients, enabling them to lyse HCC cells without raising immunosuppressive factors during amplification [61][80]. Importantly, they investigated immunosuppressive factors, demonstrating that Tregs, γδ T17 cells, and IL-17A do not increase during γδ T cell amplification, indicating the safety of this approach for HCC immunotherapy [61][80].5.1.3. Therapeutic Manipulation of γδ T Cells in HCC beyond Known Pathways
Yi et al. exploring the immune dynamics within the HCC TME revealed a significant attenuation in the infiltration and cytotoxic function of γδ T cells within HCC tissue [62][72]. Importantly, Treg cells within the tumor were found to directly suppress the cytotoxic ability and IFN-γ secretion of γδ T cells, with this effect being dependent on TGF-β and IL-10. They emphasized the novel insight into the distribution, cytotoxic function, and Treg-mediated suppression of γδ T cells in the TME. They documented a negative correlation between Treg cells and γδ T cells in HCC tissues. The in vitro analysis revealed a partial reversal of Treg cell-mediated suppression by anti-TGFβ or anti-IL-10 antibodies, suggesting a soluble factor-dependent mechanism in the Treg cell-mediated suppression of γδ T cells [62][72]. In conclusion, they emphasized the importance of enhancing the antitumor effect of γδ T cells and eliminating suppressive factors, particularly Treg cells, within the ΤΜΕ. The combination of these approaches is suggested as a potential strategy to improve outcomes for patients with HCC. Figure 2 summarizes the proposed strategies applied to enhance γδ Τ cell antitumor efficacy in HCC.
Figure 2. Strategies to enhance γδ Τ cell antitumor efficacy. BiTE, bispecific T cell engager; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; c-FLIP, cellular FADD-like interleukin-1b-converting enzyme-inhibitory protein; EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; FAS-L, FAS ligand; GPC-3, glypican-3; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; miR, micro RNA; NKG2D, natural killer group 2D; sIL-15, soluble interleukin 15; TGF-b, transforming growth factor b; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Zol, zolendronic acid. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 4 December 2023).
5.2. T Cell Exhaustion in γδ T Cells within HCC
In HCC, T cell exhaustion is a complex process influenced by various factors. The liver is an immunologically unique organ, and HCC often develops in the setting of chronic liver inflammation, commonly caused by viral hepatitis or cirrhosis [63][64][83,84]. The HCC TME is widely acknowledged for its immunosuppressive nature, influenced by various regulatory factors, such as low pH, hypoxia, nutritional deficiencies, and metabolic pathway alterations [65][66][85,86]. The prolonged exposure to antigens in the TME, along with the immunosuppressive signals produced by both the tumor and the liver environment, can lead to T cell exhaustion [67][87]. Transcriptomic analysis of HCC tissue indicates significantly elevated expression of genes encoding for inhibitory checkpoint molecules, including CTLA4, HAVCR2, LAG3, PDCD1, PDCD1LG2, TIGIT, and SIGLEC15, irrespective of patient pTNM stages [41][58].
More recently, increased evidence highlights the role of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in the context of γδ Τ cell function in HCC pathogenesis [68][69][70][71][70,88,89,90]. Jiang et al. documented that circulating γδ T cells from HCC patients exhibit impaired cytotoxicity compared to healthy controls, a finding attributed to a lower frequency of Vδ2 T cells and reduced IL-2 and IL-21 expression [69][88]. In vitro expansion with Zol enhanced cytotoxicity but did not fully restore it. PD-1 expression was elevated in HCC patients, and a co-culture with γδ T cells increased PD-L1 in HCC cell lines. Blocking PD-1 during the expansion improved cytotoxicity against all HCC lines, while blocking during assays enhanced it specifically against HepG2 and SNU-398, indicating a connection between reduced cytotoxicity and altered IL-2, IL-21, and PD-1 expression in circulating γδ T cells of HCC patients [69][88].
LAG-3 stands out as one of the primarily studied indicators of T cell exhaustion [71][72][90,91]. He et al. investigated the functional state of γδ T cells infiltrating HCC and explored the potential of allogenic Vδ2+ γδ T cells in HCC immunotherapy. scRNA-seq on γδ T cells from HCC tumors and healthy donor livers revealed that γδ T cells in the HCC TME exhibit G2/M cell cycle arrest, express cytotoxic molecules, and show functional exhaustion with elevated LAG3 expression. The LAG3+Vδ1+ population dominated, while Vδ2+ γδ T cells were depleted in the HCC TME. Glutamine metabolism was upregulated in γδ T cells due to glutamine deficiency in the TME, resulting in increased LAG3 expression. Ex vivo-expanded Vδ2+ γδ T cells from healthy donors complement the loss of TCRclonality and effector functions in HCC-derived γδ T cells [72][91]. They provided insight into the dysfunctional signatures of HCC-infiltrating γδ T cells and supported the potential use of allogenic Vδ2+ γδ T cells in HCC cellular therapy
Conclusively, several mechanisms contributing to exhaustion in γδ T cells have been identified. These multiple mechanisms collectively contribute to the reduced cytotoxic capacity and functional exhaustion of γδ T cells in HCC. The reversal of the identified mechanisms contributing to γδ T cell exhaustion in HCC presents a unique and promising therapeutic target.
