Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Chaoran Song and Version 2 by Wendy Huang.
The immune system protects our body from bacteria, viruses, and toxins and removes malignant cells. Activation of immune cells requires the onset of a network of important signaling proteins. Methylation of these proteins affects their structure and biological function. Under stimulation, T cells, B cells, and other immune cells undergo activation, development, proliferation, differentiation, and manufacture of cytokines and antibodies. Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs), a group of methyltransferases with a seven β-strand set, methylate proteins on arginine residues.
- arginine methylation
- PRMT1
- CARM1
- PRMT5
- PRMT6
- protein
1. Introduction
Methylation is a post-translational modification (PTM) associated with a variety of cellular functions through enzymatic modification of proteins. Transmethylation is orchestrated by writers (e.g., methyltransferases), readers (e.g., binding substrate proteins), and erasers (e.g., demethylases) with distinct roles in adding, recognizing, or removing these methyl groups. Methyltransferases transfer methyl groups from a donor, generally S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet), to different acceptor molecules [1]. At present, the AdoMet-dependent methyltransferases have been divided into three families [2]. The most abundant group (Class I) contains a seven-strand twisted β-sheet structure [3]. The methyltransferases in the second group (Class II) possess a conserved Su(var)3-9, enhancer-of-zeste and Trithorax (SET) domain structure, which is approximately 130 amino acids long [4]. Class III consists of methyltransferases that are enzymes with multiple membrane-spanning regions [5]. In eukaryotes, arginine and lysine are multiply methylated and lead to distinct outcomes. Methylation of arginine and lysine provides significant functional diversity and regulatory complexity [4].
Protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs), a group of methyltransferases with a seven β-strand set, methylate proteins on arginine residues [6]. Arginine-mediated methylation is the most prevalent type of protein methylation in mammalian cells. It is involved in signal transduction, RNA processing, chromatin stability, and transcriptional regulation [6][7][8][6,7,8]. The AdoMet-dependent methyltransferases in the PRMT family share four conserved motifs (I, post-I, II, and III), as well as a THW loop [9]. The AdoMet-binding pocket mainly consists of Motifs I, post-I, and a THW loop [9]. These motifs are highly conserved in eukaryotes, particularly in a core region that contains ~310 amino acids responsible for catalyzing the enzymatic activity of the group [10][11][12][10,11,12]. Three types of arginine methylation have been identified (Figure 1). PRMTs transfer a methyl group from AdoMet to a guanidino group of arginine, leading to monomethylarginine and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in target proteins [13]. The addition of two methyl groups to the two ω-guanidino nitrogen atoms of arginine forms symmetrically dimethylated arginine (SDMA) [14]. The structural domain of PRMTs is shown in Figure 2.
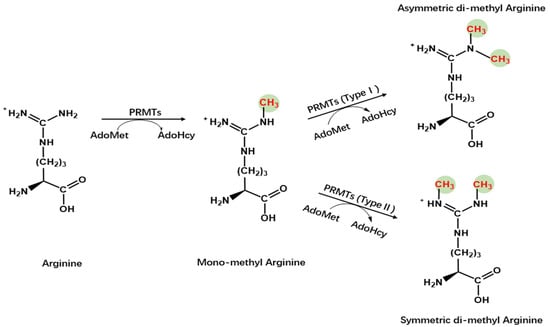
Figure 1. Chemistry of arginine methylation. Type I protein arginine methyltransferases catalyze asymmetric methylation of arginine, whereas Type II protein arginine methyltransferases catalyze symmetric demethylation in arginine.
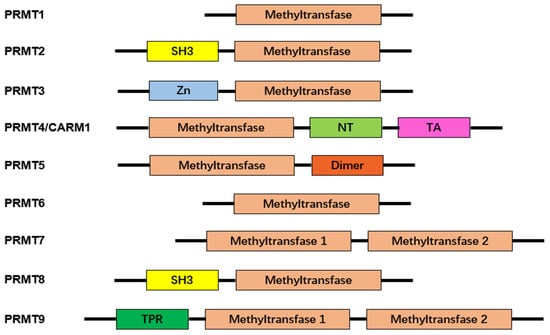
Figure 2. Characteristic domains of arginine protein methyltransferases. Arginine protein methyltransferases (PRMTs) share a common structural domain, the methyltransferase domain. Additionally, some members of PRMTs feature distinct structural domains, enhancing their functional diversity. These additional domains include Src-homology 3 (SH3), zinc-finger (Zn), nuclear translocation (NT), transactivation (TA), dimerization (Dimer), and tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR). The presence of these characteristic domains contributes to the unique roles and regulatory functions exhibited by different PRMTs.
To date, the mammalian family of PRMTs is recognized to have nine members. They are grouped into two categories according to the type of modification they catalyze [15][27]. Type I enzymes are PRMTs that add two methyl groups to the same terminal nitrogen group of arginine and form ADMA. PRMT1, -2, -3, -4, -6, and -8 belong to this type [10][16][10,28]. PRMT5, -7, and -9 are type II enzymes that transfer a second methyl group to the other terminal nitrogen, generating SDMA. In Table 1, immunopathological responses, target molecules, and molecular outcomes of protein arginine methyltransferases are summarized.
Table 1.
Regulatory mechanisms of protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs) in immunity.
| PRMTs | Pathology/Affected Field | Treatment/Model | Target Molecules (Binding Partner) |
Observations | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRMT1 | Toll-like receptor signaling | Primary and cultured cells | TRAF6 | -Decreased ubiquitin ligase activity of TRAF6 -Reduced activation of Toll-like receptor signaling -Suppressed basal NF-κB activation |
[17][29] |
| Macrophages | PRMT1 mutation PARP1−/− macrophages | p65 (p50), PARP1 | -Activated NF-κB-dependent gene expression | [18][30] | |
| Inflammatory and immune responses | Knockdown of PRMT1 | RelA, p65 (p50) | -Increased levels of NF-κB target genes | [19][31] | |
| IFN-dependent responses | Methyltransferase inhibitor | PIAS1 | -Decreased anti-viral and anti-proliferative abilities of type I interferons | [20][21][22][32,33,34] | |
| Innate immune responses | Myeloid-specific PRMT1 knockout mice | PPARγ | -Caused a lower survival rate and higher pro-inflammatory cytokine production | [23][35] | |
| Humoral immunity in B cells | PRMT1-impaired B cells | -Decreased the immune system response to T cell-dependent antigens -Reduced survival, proliferation, and differentiation of B cells |
[24][36] | ||
| T cells | NIP45-impaired mice | NIP45 (NFAT) | -Deficient expression of IFN-γ and IL-4 | [25][37] | |
| Th17 cells | Knockdown of PRMT1 by shRNA, specific PRMT1 inhibitor autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice | RORγt | -Regulated the production of Th17 cells and Th17 differentiation -Alleviated activation of EAE in mice |
[26][38] | |
| Human and mouse T cells | Transmethylation inhibition | Vav1 (Rac) | -Reduced methylation of Vav1 and IL-2 production | [27][28][39,40] | |
| CARM1 | Immune responses | CARM1−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts | p160 (ER), p300 (BRCA1), p65 | -Dampened expression of a group of NF-κB target genes | [29][30][31][41,42,43] |
| Macrophages | LPS stimulation | RNA-binding protein HuR | -Stabilized TNF-α mRNA | [32][44] | |
| Thymocytes | CARM1-deleted embryos | -Reduced the number of thymocytes | [33][45] | ||
| PRMT5 | T cell-mediated immune dysfunction | aGVHD mouse model, inhibitor of PRMT5 | ERK1/2, STAT1 | -Improved survival and reduced disease incidence and clinical severity -Decreased phosphorylation of STAT1 and ERK1/2 and transcription of pro-inflammatory genes |
[34][46] |
| T cells | Autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mouse model inhibitor of PRMT5 | -Repressed memory T cell responses -Downregulated IL-2 production and proliferation of recall Th cells |
[35][47] | ||
| Lymphoma cells | PRMT5 knockdown by shRNA | -Regulated TP53K372 methylation, cyclin D1 transcriptional activation, BCL3 production | [36][48] | ||
| Tregs | Conditional knockout of PRMT5 mice, pharmacological inhibition | FOXP3 | -Developed severe scurfy-like autoimmunity -Reduced human Treg functions |
[37][49] | |
| Natural killer T cells | T cell-specific PRMT5 conditional knockout mice | -Led to peripheral T cell lymphopenia in mice -Impaired IL-7-mediated survival and TCR-induced proliferation in vitro |
[38][50] | ||
| Pro-B and pre-B cells | Conditional deletion of PRMT5 in pro-B cells | -Severe deficit in antibody-secreting cells -Reduced pre-immune serum IgG1 |
[39][51] | ||
| PRMT6 | Tumor-associated macrophages | Tamoxifen-inducible lung-targeted PRMT6 gain-of-function mouse model | ILF2 | -Regulated pro-inflammatory genes: TNFα and iNOS | [40][52] |
| HIV | Knockdown of PRMT6 | HIV-1 Tat | -Enhanced HIV-1 production and faster viral replication | [41][53] | |
| Inflammatory responses | Transgenic mice that ubiquitously express PRMT6 fused to the hormone-binding portion of the estrogen receptor | RelA | -Regulated NF-κB target genes | [42][54] | |
| Anti-viral innate immunity | PRMT6-deficient mice | IRF3 | -Promoted the TBK1–IRF3 interaction -Enhanced IRF3 activation and type I interferon production |
[43][55] |
2. PRMT1
As the first identified PRMT in mammals, PRMT1 is involved in up to 85% of total arginine methylation activity [44][45][56,57]. In mammals, the NF-κB family is composed of five transcription factors: p50, p52, RelA (p65), c-Rel, and RelB [46][47][58,59]. The classical NF-κB pathway is essential for innate immunity through IKK-dependent IκB degradation (Figure 3) [48][60]. Additionally, the alternative pathway of NF-κB plays a distinct role in lymphoid organ development and adaptive immunity [48][60].
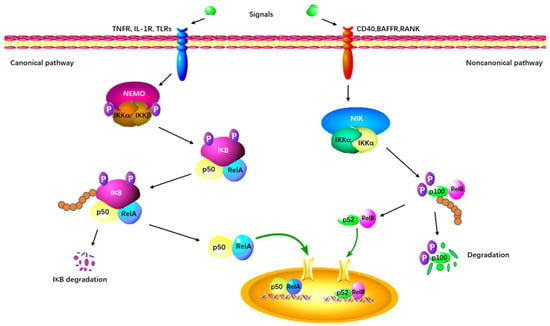
Figure 3. The canonical and non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. The canonical pathway is triggered by TLRs, TNFRs, and IL-1R, leading to the phosphorylation and degradation of the inhibitory protein IκB. NF-κB is activated by its release from the IκB-containing complex and translocates into the nucleus. The non-canonical pathway depends on the activation of p100/RelB complex by BAFFR, CD40, and RANK. This cascade involves the phosphorylation of NIK, which in turn phosphorylates IKKα. Subsequently, the p52-RelB heterodimer is activated and translocates to the nucleus.
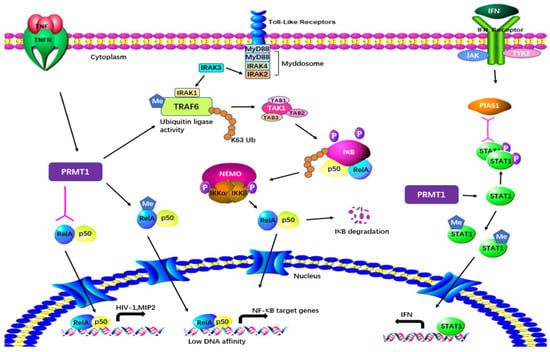
PRMT1 is considered a regulator of immunity based on its effect on NF-κB. PRMT1 directly binds to TRAF6 and reversibly methylates it at multiple sites in both primary and cultured cells (Figure 4). After being arginine-methylated by PRMT1, the ubiquitin ligase activity of TRAF6 is downregulated, leading to the suppression of basal NF-κB activation. The loss of PRMT1 enhances the activities of IRAK3 and NF-κB reporter luciferase as well as the nuclear translocation of p65 [17][29]. These data suggest that PRMT1 is essential for blocking TRAF6-dependent pathways, and that the absence of PRMT1 results in impaired Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligand constitutive activation and response [17][29]. Hassa et al. have shown direct interaction between PRMT1 and NF-κB subunit p65. The interaction activates NF-κB-dependent gene expression at the promoters of CARM1-dependent macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP2) and human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) [18][30]. Luciferase reporter gene assays have strongly indicated that PRMT1 has synergy with poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) and p300 [18][30]. Interestingly, the knockdown of PRMT1 increases the levels of NF-κB target genes by facilitating p65 recruitment to their promoters in response to TNFα. PRMT1 is a restrictive factor of NF-κB by interacting with p65 [19][31].

Figure 4. Regulatory mechanisms of PRMT1 in inflammatory responses. PRMT1 plays a multifaceted role in cellular processes by directly binding to and methylating TRAF6. The arginine methylation of TRAF6 by PRMT1 downregulates its ubiquitin ligase activity, resulting in the suppression of basal NF-κB activation. PRMT1 also methylates RelA, regulating DNA affinity and the expression of NF-κB target genes. The interaction between PRMT1 and RelA activates NF-κB-dependent gene expression at the promoters of MIP2 and HIV. Furthermore, PRMT1 methylates PIAS1, influencing IFN transcription. Additionally, PRMT1 methylates STAT1 on Arg-31, and this methylation is essential for transcriptional activation.
Weber et al. have demonstrated in both in vitro and in vivo tests that PRMT1 also methylates the protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 (PIAS1), a negative regulator of STAT1 in immune responses [20][32]. Arginine methylation of PIAS1 is vital for the inhibition of PRMT1 in interferon (IFN)-dependent transcription. The methylation also recruits PIAS1 to STAT1 target promoters in response to IFN [21][33]. Further previously reported evidence of the significance of methylation was that STAT1 is methylated by PRMT1 on Arg-31 and that methylation of STAT1 is required for transcriptional activation. Treatment with methylthioadenosine, a transmethylation inhibitor, weakens DNA–STAT1 binding by strengthening the connection between STAT1 and PIAS1. The loss of PRMT1 decreases the anti-viral and anti-proliferative capacities of type 1 IFNs, showing the role of PRMT1 in IFNα/β-receptor-associated signaling events [22][34]. A two-hybrid screening system has indicated that PRMT1 is the first enzyme in its family to bind to the cytoplasmic region of type 1 IFN receptor [49][50][61,62]. PRMT1 regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) gene expression at its promoter through H4R3me2a methylation, leading to impaired expression of PPARγ in response to interleukin-4 (IL-4) treatment. Using a myeloid-specific PRMT1 knockout mouse model, Tikhanovich et al. showed that the abolition of PRMT1 causes a lower survival rate and higher pro-inflammatory cytokine production after cecal ligation and puncture [23][35]. These results indicate that the regulation of PPAR in PRMT1-dependent macrophages can cause PRMT1 knockout mice to be susceptible to infection.
Furthermore, PRMT1 activity is crucial for proper execution of several processes that are important for humoral immunity in B cells [24][36]. The expression and activity of PRMT1 in human and mouse peripheral blood B cells increase after activation in vitro or in vivo. A marked decrease in the immune system response to T cell-dependent antigens has been observed when PRMT1 is deleted. Upon stimulation of multiple mitogens, activation of PRMT1-impaired B cells results in reduced survival, proliferation, and differentiation in vitro.
Additionally, PRMT1 alters the differentiation, generation, and activation of T cells (Figure 5). PRMT1 is located downstream of the T cell receptor in progenitor Th cells [28][40]. T cell receptor signaling promotes the expression of PRMT1 (https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/prmt1, accessed on 22 December 2023), which methylates the arginine residues of NIP45, the cofactor protein of nuclear factor of activated T cells [28][40]. Methylation facilitates its association with NFAT and leads to elevated cytokine production, whereas deficient expression of IFN-γ and IL-4 has been observed in T cells from NIP45-impaired mice [25][37].

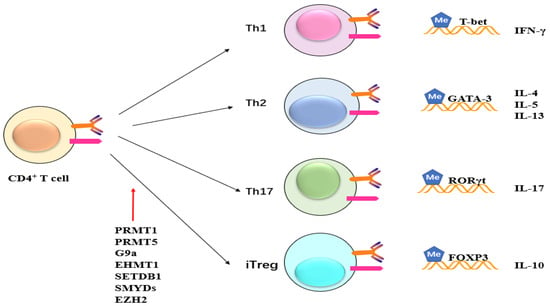
Figure 5. Potential role of methylation on CD4+ cells. Methyltransferase like PRMT1, PRMT5, G9a, EHMT1, SETDB1, SMYDs, and EZH2 exert their influence on CD4+ T cells, impacting subsequent T cell differentiation and maturation. This, in turn, leads to alterations in the expression of inflammatory factors such as IFN and ILs.
Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γt (RORγt) is a key transcription factor that mediates the differentiation of Th17 cells [26][51][38,63]. PRMT1 has been demonstrated to be related to RORγt and regulated mouse Th17 differentiation, which is promoted by PRMT1 overexpression. However, the knockdown of PRMT1 by shRNA and inactivation by specific PRMT1 inhibitors limits Th17 differentiation. The use of a specific inhibitor of PRMT1 damages the production of Th17 cells and alleviates activation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice [26][38]. Sen et al. have suggested that PRMT1 could be a new target for reducing Th17-mediated autoimmunity by decreasing the generation of pathogenic Th17 cells [26][38]. Vav1, a Rac/Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor, plays a crucial role in cytokine secretion, T cell activation, and proliferation [52][53][64,65]. Methylation of Vav1 is promoted in both human and mouse T cells and occurs in the nucleus [27][28][39,40]. The inhibition of cellular transmethylation of PRMT1 reduces methylation of Vav1 and IL-2 production, indicating potentially crucial roles for PRMT1 in T cell-mediated disorders.
3. CARM1
CARM1 (PRMT4) is a transcriptional coactivator related to the p160 family in nuclear receptor-mediated transcription [54][66]. In addition to the p160 family, CARM1 synergistically activates NF-κB-mediated transactivation with P300/CREB-binding protein [29][55][56][41,67,68]. As reported, CARM1 bound to p300 in vivo and interacted with p65, a NF-κB subunit, in vitro [31][43]. During TNFα or LPS stimulation, CARM1−/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts exhibited dampened expression of a group of NF-κB target genes [31][57][43,69]. The RNA-binding protein HuR, a novel substrate of CARM1, is methylated by CARM1 at arginine 217 [58][70]. Methylation of endogenous HuR and stabilization of TNF-α mRNA have been observed in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. The methylation of HuR was similarly increased in cells overexpressing CARM1, and methylated HuR is related to the stability of HuR-dependent mRNA [32][44]. Previous research has shown that CARM1 is associated with survival of thymocytes. Thymocytes isolated from CARM1-deleted embryos are stagnated between CD4− CD8− double-negative stage 1 and double-negative stage 2 [33][54][45,66]. A significant reduction in the number of thymocytes has been observed. Therefore, the methylation of arginine residues by CARM1 in inflammation suggests CARM1 as a therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases [54][66].
4. PRMT5
Acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) is a T cell-mediated immune dysfunction in which T cells in donated tissue recognize the recipient as foreign [54][66]. PRMT5 has been identified to play a role in T cell responses in aGVHD, suggesting it as a target of this disease [34][46]. PRMT5 is a mediator in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a well-developed animal model of autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis [59][71]. In vivo EAE mouse models have shown that PRMT5 inhibition potently repressed memory T cell responses. Delayed-type hypersensitivity and inflammation in clinical disease were also decreased. The inhibition of PRMT5 by specific inhibitors downregulates IL-2 production and proliferation of recall Th cells. These results demonstrate the importance of PRMT5 as a regulator in adaptive memory Th cell responses [35][47]. In lymphoma cells, deceased PRMT5 represses TP53K372 methylation, cyclin D1 transcriptional activation, and BCL3 production and promotes NF-κB p52–HDAC1 repressor complexes to the cyclin D1 promoter [36][48].
As Nagai et al. have reported, PRMT5 forms a complex with FOXP3 homomer in Tregs [37][49]. Therefore, a specific blockade of PRMT5 decreases methylation of FOXP3 and arrests human Treg functions. Mice with conditional knockout of PRMT5 expression in Tregs develop severe scurfy-like autoimmunity and display a limited suppressive function. This may also explain the reduced numbers of Tregs in the spleen in PRMT5 cKO mice [37][49]. Additionally, PRMT5 has been found to regulate T cell survival and proliferation through analysis of T cell-specific PRMT5 conditional knockout mice [38][50]. PRMT5 is essential for natural killer T cell development, optimal peripheral T cell maintenance, and early T cell development [38][50]. Consistently, deficient IL-7-dependent survival and TCR-induced proliferation in T cells were caused by deletion of PRMT5 in vitro [38][50]. Separately, PRMT5 has been shown to be important for antibody responses and plays essential but distinct roles in all proliferative B cell stages in mice [39][51]. PRMT5 prevents p53-mediated suppression in pro-B and pre-B cells and inhibits apoptosis of mature B cells during simultaneous activation via p53-independent pathways [39][51]. The inhibition of PRMT5 markedly decreases phosphorylation of STAT1 and transcription of pro-inflammatory genes, including IL-17 and IFN-γ. Additionally, PRMT5 inhibition disrupts signaling transduction by regulating phosphorylation of ERK1/2, which leads to dysregulation of the cell cycle in activated T cells [34][46]. The data above indicate PRMT5 inhibitors as a novel method to treat T cell-dependent inflammatory disease.
5. PRMT6
Utilizing proteomics-based methods, a protein–protein interaction has been discerned between PRMT6 and interleukin-enhancer binding protein 2 (ILF2). Moreover, macrophage migration inhibitory factor has been shown to play a role in mediating alternative activation of tumor-associated macrophages. Avasarala et al. have identified the macrophage migration inhibitory factor as an important downstream molecule of PRMT6–ILF2 signaling [40][52]. HIV-1 Tat protein is a key player in HIV replication by increasing gene transcription efficiency. HIV-1 is a specific substrate of PRMT6 in vivo and in vitro that targets Tat R52 and R53 residues for arginine methylation [41][53]. The overexpression of PRMT6 decreases the level of Tat transactivation of HIV-1 long terminal repeat chloramphenicol acetyltransferase and luciferase reporter plasmids in a dose-dependent manner, while the knockdown of PRMT6 enhances HIV-1 production and the speed of viral replication [41][53]. Thus, PRMT6 disrupts the transcriptional activation of Tat and may represent an innate cellular immune form of HIV-1 replication.
PRMT6 also plays a role in immunity by targeting a series of signaling pathways. PRMT6 has been identified as an NF-κB coactivator because it can generate transgenic mice that express PRMT6 fused to the hormone-binding portion of the estrogen receptor [42][54]. PRMT6 engages in a direct interaction with RelA, whereby its overexpression amplifies the transcriptional activity of an ectopic NF-κB reporter and intrinsically regulates NF-κB target genes [42][54]. In response to TNF-α stimulation, RelA recruits PRMT6 to specific NF-κB target promoters. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is recognized as a tumor-suppressor gene, and its mutation has implications in the progression of various cancers [58][70]. PRMT6 interacts with PTEN and methylated PTEN R159, weakening the PI3K–AKT cascade [60][72]. G protein pathway suppressor 2 (GPS2) cytoplasmic actions and anti-inflammatory roles are linked with the regulation of JNK activation as well as TNF-α target genes in macrophages [61][73]. Interaction with the exchange factor TBL1 is helpful to protect GPS2 from degradation. The methylation of GPS2 by PRMT6 modulates the interaction with TBL1 and suppresses proteasome-dependent degradation [62][74]. PRMT6 also attenuates anti-viral innate immunity by blocking TBK1–IRF3 signaling [43][55]. In PRMT6-deficient mice, the TBK1–IRF3 interaction is enhanced and activates IRF3 as well as increases the production of type I IFN. A Viral infection not only upregulates PRMT6 protein levels, but also promotes the binding between PRMT6 and IRF3 and dampens the interaction between IRF3 and TBK1 [43][55].
