Doorknob accessories, wheelchair-mounted door-opening accessories, door-opening robots, and door-opening drones—were used to group the various technologies for manually opening doors. Drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with a wide range of applications, including product delivery, asset inspection, search and rescue, law enforcement and military services, disaster management, and emergency medical services. Drones are emerging as safe alternatives to humans in applications involving inaccessible environments or dangerous scenarios. In cases of medical emergencies, when a person is stuck in remote locations and an ambulance is unable to reach a patient in time, medical drones are being used for emergency medical services. Door-opening drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with the capability to open doors.
- door-opening
- drones
1. Introduction
2. Door-Opening Drones
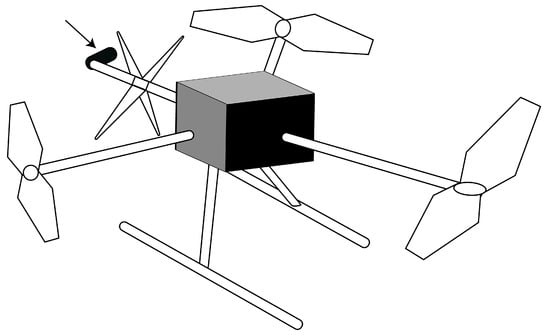
| Specification | Lemur-2 | BoomCopter | FlyCroTug | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 1.5 | 2.3–2.9 | 0.1 | ||||
| Drone can push doors already ajar | Yes | USD 10k–20k | Dimensions (L/W/H) (″) |
13/16/4 | 23.6/27.6/11.4 | 4/4/- | |
| Propeller design | |||||||
| Single drone | Attachment turns doorknobs and pulls or pushes door | No | – | Quadcopter | Tricopter with a horizontally mounted reversible propeller |
Quadcopter | |
| Swarm of tiny drones | One drone turns doorknob; Another drone pulls the door |
No | – | Payload (kg) | 0.45 | 1.86–1.2 | 0.02 (flight) ~4 (tugging) |
| Flight time (min) | 20 | 13–21.4 | 5 | ||||
| Flight range (km) | - | 8.8–14.4 | - | ||||
| Sensors | Forward and downward LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor; dual tracking cameras (daytime, night vision, thermal) | GPS module; force sensor; sonar sensor; camera; flight management unit (FMU) | Autopilot module (inertial measurement unit, barometer) |
| Door opening AT | Features | Commercial Availability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single drone | Attachment breaks glass; |
