Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Marizuana Mat daud and Version 2 by Wendy Huang.
The Internet of Everything (IoE) represents a paradigm shift in the world of connectivity. While the Internet of Things (IoT) initiated the era of interconnected devices, the IoE takes this concept to new heights by interlinking objects, individuals, data, and processes. Symmetry in IoE innovation and technology is essential for creating a harmonious and efficient ecosystem to ensure that the benefits are accessible to a broad spectrum of society while minimizing potential drawbacks.
- Internet of Everything
- Internet of Things
- objects
- individuals
- data
- processes
1. Introduction
The digital transformation of the 21st century has ushered in a new era of connectivity, where everyday objects, devices, and systems are becoming increasingly interconnected, intelligent, and data-driven. As a result of the exponential emergence of the Internet in interconnected networks, most technology must adhere to more rigorous standards. This transformative phenomenon is commonly referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT) [1][2][1,2]. However, beyond the IoT lies a more comprehensive and expansive concept known as the Internet of Everything (IoE), which expands the boundaries of network connectivity with intelligent devices and is forecasted to see even more rapid advancement in the future [3]. The IoE is an ecosystem where devices and things are connected to the Internet, and where people, processes, and data are seamlessly integrated, creating a web of interconnectedness that transcends traditional boundaries [4]. The Internet of Everything (IoE), as delineated by Cisco Systems Inc., encompasses an intricate network of interconnections involving individuals, processes, data, and IoT devices. According to Cisco’s estimations, the forthcoming 15 years are poised to yield substantial advantages from IoE implementation in the global public sector, amounting to an impressive USD 4.6 trillion. Simultaneously, the private sector is expected to generate a remarkable USD 14.4 trillion in economic value during this period [5].
In this digital realm, objects can communicate with each other, make autonomous decisions, and interact with humans in ways that were once the stuff of science fiction. The IoE concept not only encompasses smart devices and sensors but also leverages data analytics, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and advanced networking technologies to create a symbiotic relationship between the digital and physical worlds. It promises to revolutionize industries, enhance the quality of life, and address some of the most pressing global challenges, from healthcare and transportation to energy efficiency and sustainability. This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the IoE ecosystem, its key components and challenges, and the transformative impact it is poised to have on various domains of human activity.
The motivation to explore IoE technologies is driven by its capacity to solve complex challenges. The IoE has the potential to address global issues such as the integration of physical and digital realms, creating a landscape where devices, systems, and individuals converge, interoperate, and share data in real time. In conclusion, this exploration of IoE technologies and innovation sets the stage for a compelling journey into the interconnected world of the future. By understanding and leveraging IoE, itwe can pave the way for a more efficient, sustainable, and connected society that unlocks opportunities for growth and transformation across all sectors.
 The IoE plays a pivotal role in enabling the creation of innovative services, based on the Internet of Things (IoT), fog, and cloud computing paradigms. IoT-based sensors are poised to enhance data transmission for analysis, thus contributing to improved decision making and an overall increase in the quality of citizens’ lives [6]. The IoE is anticipated to receive significant amounts of attention in the coming years, especially with the emergence of new, exciting technologies in the sectors of networking, software, hardware, and luxury-oriented services for humans [5]. Several researchers have made significant contributions, with diverse objectives that collectively enhance the capabilities of the IoE. Antonios et al. conducted a systematic literature review on semantic technologies in smart cities, with objectives centered on identifying trends and challenges in adopting semantic interoperability solutions for sustainable, green, and resilient urban environments [7].
In the context of the Internet of Everything (IoE) environment, the incorporation of infrared communication into the smart home system emerges as a noteworthy development. Researchers [8] have effectively addressed the longstanding challenge wherein a significant portion of infrared-communication-based household appliances faced limitations in their integration into the smart home network. This innovative effort not only resolves this problem but also helps to lower the implementation costs of such a smart home system, making it more affordable and useful in the everyday lives of the general population.
Another study attempted to replicate a multitude of pragmatic Internet of Everything (IoE) scenarios, mirroring real-world applications. In this pursuit, this paper adeptly harnesses the capabilities of the Cisco Packet Tracer, an instrumental tool employed in the experimental setup [9]. This comprehensive exploration necessitates the interconnection of a substantial array of sensors and devices, effectively emulating the complexities that are inherent to IoE ecosystems. Moreover, this investigative work encompasses the deployment of a diverse range of network components, including routers, switches, and servers, with IoT devices thus culminating in the establishment of a fully operational network infrastructure, like the contributions such as [10].
Numerous researchers are eagerly contributing to holistic performance enhancement by adopting heuristic and metaheuristic algorithms that are used extensively for time–cost optimization in cloud computing [11]. Equally, in [12], the researchtudy focuses on elevating various performance aspects of quality management (QM) and bolstering consumer confidence within the Internet of Everything (IoE) framework. The researchstudy introduces a QM platform designed to prioritize swift responses and minimize latency in acquiring sensor data, while also ensuring authentication, data consistency, and transparency in the context of cold supply chain logistics. Additionally, an innovative adaptive data smoothing and compression (ADSC) mechanism is proposed to efficiently reduce the size of IoE data. This facilitates storage within edge gateways, even when they have limited computational and storage capacities. This research contributes significantly to optimizing cold supply chain logistics by harnessing IoE and blockchain technologies to enhance quality management and transparency in supply chain operations.
The IoE plays a pivotal role in enabling the creation of innovative services, based on the Internet of Things (IoT), fog, and cloud computing paradigms. IoT-based sensors are poised to enhance data transmission for analysis, thus contributing to improved decision making and an overall increase in the quality of citizens’ lives [6]. The IoE is anticipated to receive significant amounts of attention in the coming years, especially with the emergence of new, exciting technologies in the sectors of networking, software, hardware, and luxury-oriented services for humans [5]. Several researchers have made significant contributions, with diverse objectives that collectively enhance the capabilities of the IoE. Antonios et al. conducted a systematic literature review on semantic technologies in smart cities, with objectives centered on identifying trends and challenges in adopting semantic interoperability solutions for sustainable, green, and resilient urban environments [7].
In the context of the Internet of Everything (IoE) environment, the incorporation of infrared communication into the smart home system emerges as a noteworthy development. Researchers [8] have effectively addressed the longstanding challenge wherein a significant portion of infrared-communication-based household appliances faced limitations in their integration into the smart home network. This innovative effort not only resolves this problem but also helps to lower the implementation costs of such a smart home system, making it more affordable and useful in the everyday lives of the general population.
Another study attempted to replicate a multitude of pragmatic Internet of Everything (IoE) scenarios, mirroring real-world applications. In this pursuit, this paper adeptly harnesses the capabilities of the Cisco Packet Tracer, an instrumental tool employed in the experimental setup [9]. This comprehensive exploration necessitates the interconnection of a substantial array of sensors and devices, effectively emulating the complexities that are inherent to IoE ecosystems. Moreover, this investigative work encompasses the deployment of a diverse range of network components, including routers, switches, and servers, with IoT devices thus culminating in the establishment of a fully operational network infrastructure, like the contributions such as [10].
Numerous researchers are eagerly contributing to holistic performance enhancement by adopting heuristic and metaheuristic algorithms that are used extensively for time–cost optimization in cloud computing [11]. Equally, in [12], the researchtudy focuses on elevating various performance aspects of quality management (QM) and bolstering consumer confidence within the Internet of Everything (IoE) framework. The researchstudy introduces a QM platform designed to prioritize swift responses and minimize latency in acquiring sensor data, while also ensuring authentication, data consistency, and transparency in the context of cold supply chain logistics. Additionally, an innovative adaptive data smoothing and compression (ADSC) mechanism is proposed to efficiently reduce the size of IoE data. This facilitates storage within edge gateways, even when they have limited computational and storage capacities. This research contributes significantly to optimizing cold supply chain logistics by harnessing IoE and blockchain technologies to enhance quality management and transparency in supply chain operations.
2. Transformative Potential of the IoE in Diverse Domains
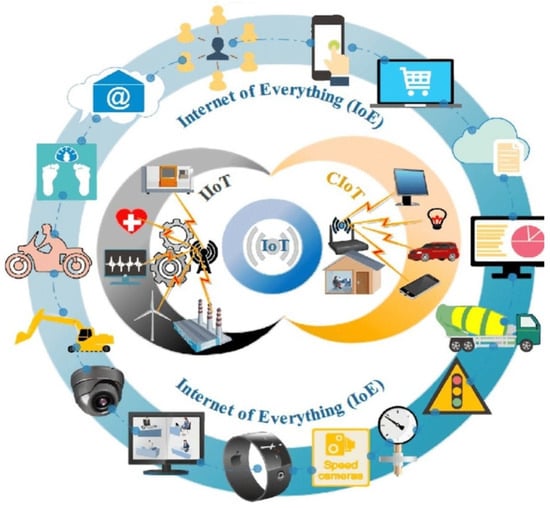
The evolution of the Internet of Everything (IoE) has been a subject of profound interest and investigation in recent years. Researchers and scholars alike have delved into various facets of the IoE, seeking to unravel its intricate web of connections between people, processes, data, and objects. A significant body of related works has emerged, shedding light on the transformative potential of the IoE in diverse domains, including industry IoT (IIoT) and cognitive IoT (CIoT), as shown in Figure 1. These studies have elucidated the critical role of the IoE in enhancing efficiency, enabling data-driven decision making, and ushering in the new era of connectivity.
Figure 1.
The Internet of Everything (IoE).
