Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Abolfazl Heydari and Version 2 by Jason Zhu.
Injectable bioadhesive hydrogels, known for their capacity to carry substances and adaptability in processing, offer great potential across various biomedical applications. They are especially promising in minimally invasive stem cell-based therapies for treating cartilage damage. This approach harnesses readily available mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to differentiate into chondrocytes for cartilage regeneration.
- bioadhesive
- injectable
- hydrogel
- stem cell
1. Introduction
Hydrogels, which are 3D cross-linked natural or synthetic polymer networks with high water-absorbing capacity and versatile fabrication characteristics, have wide-ranging applications, particularly in the fields of tissue engineering (TE) and regenerative medicine [1].
Injectable hydrogels specially offer potential advantages in minimally invasive local drug delivery, precise and site-specific implantation, as well as targeted delivery to hard-to-reach tissue sites and interface tissues. The phase transition in a polymer solution, from liquid to solid at a critical point, is known as the sol–gel transition state. Injectable hydrogels, including in situ forming and shear-thinning hydrogels, undergo a rapid sol–gel phase transition, which allows the matrix an easy taking of the shape of the cavity, providing a suitable fit and interface in tissues [2][3][4][2,3,4]. In this light, the adhesivity of applied hydrogel is one of the crucial properties for hydrogels in biomedicine.
Bioadhesive hydrogels have emerged as pivotal materials in the realm of cell therapy research, owing to their exceptional attributes. These attributes, including desired biocompatibility, biodegradability, tissue and cellular adhesion capabilities, as well as mechanical properties conducive to the emulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM), play a pivotal role in fostering critical cellular processes such as proliferation, wound healing, and tissue regeneration [5][6][7][5,6,7]. Drawing upon the information presented thus far and the observed experimental outcomes, it can be cautiously inferred that hydrogels exhibit favorable attributes as a potential material for biomedical applications, notably hinting at their potential suitability as a conducive environment for the proliferation of stem cells [8][9][8,9].
2. Bioadhesion
By definition, bioadhesion is the phenomenon in which natural and synthetic materials adhere to biological surfaces. This may or may not be associated with the use of adhesives to bond the material to the biological surface. Bioadhesion also refers to the incorporation of a biomaterial into the body, manifested by the formation of a biofilm on the biomaterial. Xiong at al. divided bioadhesion into three aspects: mucosal adhesion, cell adhesion and bioadhesives [7]. Mucoadhesion is a specific type of bioadhesion in which a layer of mucus gel forms on the surface of the biological surface during the adhesion process [10][12]. Cell adhesion is a complex phenomenon where aside from morphology, the chemical composition of the biomaterial surface interacts with surface molecules on cells [11][13]. Bioadhesives derived either from synthetic or biological source are highly biocompatible and biodegradable polymers, which are used to join two surfaces where at least one of them is a living tissue [12][14]. There are also other approaches to classify bioadhesion. Chopra et al. proposed three types: Type 1: adhesion between two biological phases; Type 2: adhesion of a biological phase to an artificial substrate; Type 3: adhesion of an artificial material to a biological substrate [13][15]. Overall, hydrogel adhesion involves a complex interplay of chemistry, topology, and mechanics, as various types of bonds are introduced (Figure 1). Hydrogels can manifest robust adhesion through the involvement of both covalent and noncovalent bonds. Covalent bonds contribute their inherent strength individually, while noncovalent bonds, through the synergistic interplay of polymer chains, collectively impart substantial adhesive properties [7][14][15][7,16,17]. The nature of bonds present within hydrogels significantly influences the process of cross-linking, which subsequently impacts their adhesive properties. Notably, heightened cross-linking levels tend to diminish the adhesive capacity of hydrogels. This reduction is attributed to the constrained mobility resulting from increased cross-linking, thereby impeding functional groups along polymer chains from accessing the hydrogel surface and establishing interactions with the substrate for adhesion [16][18].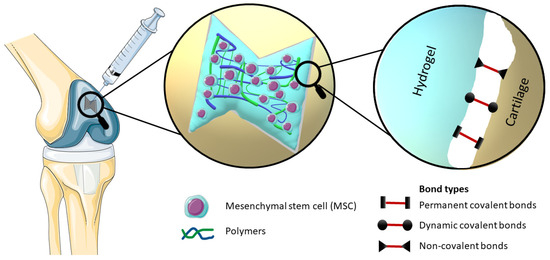
Figure 1. Elucidation of the mechanism of an injectable bioadhesive hydrogel with incorporated stem cells, which effectively occupies the defect in the cartilage structure, provides a visual representation of the different types of bonds involved in bioadhesion, namely Permanent covalent bonds, Dynamic covalent bonds and Non-covalent bonds.
-
the polymer and its degradation products must be non-toxic, biodegradable and non-absorbable;
-
it should have the ability to establish robust bonds with mucus or other biological surfaces;
-
rapid and strong adhesion to surfaces should be achievable;
-
it should offer ease of formulation with drugs without impacting drug release patterns.
3. Testing of Bioadhesion
Adhesion represents a multifaceted phenomenon governed by intricate interactions involving chemical, topological, and mechanical factors. The comprehensive evaluation of adhesion typically encompasses four distinct mechanical assessments. Notably, within this set of tests, the probe-pull and lap-shear methodologies serve to quantitatively assess adhesion strength by specifically gauging the maximum force per unit area. Meanwhile, the peel and bilayer-stretch tests are employed to assess adhesion toughness, quantifying the energy necessary for separation per unit area. These four tests serve to investigate and differentiate various facets of adhesion properties [14][18][16,53]. The majority of adhesion and bioadhesion tests are typically mechanical tests conducted usually ex vivo. Peel tests are a type of mechanical tests used to assess the strength of adhesive bonds, particularly for flexible adherents [19][54]. There are more variants based on the peeling angle, and all are standardized protocols; e.g., Wei at al. followed standard protocol for peeling adhesion test ASTM F2256-05 [20][21][55,56], sometimes minorly modified by research teams; e.g., Jeon et al. utilized a 90° peel test with a porcine skin substrate [22][57]. One of the most commonly employed assessments for evaluating the adhesive properties of bioadhesive hydrogels involves the utilization of the lap-shear test, also referred to as bulk adhesion testing. The test assesses shear strength, with cohesive failure occurring within the adhesive, while the adhesive failure depends on the adherend’s interface properties [23][58]. It is a standardized method (ASTM F2255:2005 [24][59]) that research teams modify [25][60]; usually, the test undergoes ex vivo utilizing porcine skin [26][27][20,61], and the test could be also performed in vitro [28][41]. The form of a bilayer stretch test methodology can be applied to assess extensional adhesion, wherein the adhesion energy is quantified when the hydrogels are either in their unextended or extended states [29][62]. Moreover, novel perspectives on adhesion measurement are emerging; e.g., Dehene et al. recently introduced a straightforward and replicable supplement method in viable tissues [30][63]. Ultimately, scientific teams frequently quantify adhesion in a straightforward manner by using weights and increasing tensile loading till adhesion failure [31][32][64,65]. In addition to mechanical tests, biocompatibility tests are an important part of hydrogel bioadhesiveness tests. One such test is the ISO-10993-11 [33][66] medical device rules and standards. Thanusha at al. evaluated biocompatibility for the developed hydrogel wound dressing [34][67]. The evaluation of bioadhesive hydrogels also includes clinical trials. For instance, as reported in the study by Øvrebø et al., the transition of hydrogels from laboratory development to clinical application necessitates adherence to an extensive array of protocols and regulatory standards, as well as the establishment of post-market surveillance measures [35][68].4. Application of Bioadhesive Injectable Hydrogels in Cartilage Regeneration
Bioadhesive injectable hydrogels have garnered substantial interest in recent years due to their remarkable properties. The diverse applications of these hydrogels, ranging from wound healing and tissue repair to cell adhesion and wearable sensors, are discussed, underscoring their promising role in biomedicine and offering valuable insights for future research [7]. As an illustration of the increasing prominence of bioadhesive injectable hydrogels in medicine, various studies stand out. These studies encompass adhesive hydrogels for delivering mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to treat spinal cord injuries [36][69], an innovative approach using hypoxia-stimulated exosomes within a peptide-modified adhesive hydrogel for spinal cord injury treatment [37][70], the GelMA–dopamine–EV hydrogel for enhanced MSC-EV function in diabetic wound healing [38][71], and an adhesive hydrogel integrated with placental mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium (CM) to prevent uterine adhesions and improve patient outcomes [39][72]. Additionally, a PEG-based hydrogel shows potential for muscle regeneration [40][73], and Col/APG hydrogels incorporating umbilical cord stem cell factor (SCF) offer effective therapeutic treatment for diabetic wounds [10][12] as well as for diabetic ulcer treatment [41][74]. The bioadhesive injectable hydrogel with a phenolic nanozyme (SAN) and a CpGODN adjuvant holds promise for localized immunomodulation and catalytic immunotherapy in the tumor microenvironment [42][31]. Inspired by mussel adhesive proteins, a dopamine-modified poly(α,β-aspartic acid) derivative (PDAEA) forms an injectable bioadhesive hydrogel with strong adhesion and drug delivery potential [43][75]. An innovative dynamic cross-linked photothermal hydrogel adhesive exhibits photothermal effects and on-demand removability, suitable for wound closure and healing, including MRSA-infected wounds [44][76]. A novel injectable acacia gum (AG) hydrogel with rapid gelation, self-healing, and effective bioadhesion holds promise for future biomedical applications as a wound-healing agent carrier [45][77]. Lastly, a composite hydrogel designed for bladder injuries shows potential for tissue engineering and bladder tissue regeneration [28][41], and a Tetra-PEG hydrogel bioadhesive (SS) offers sutureless repair of GI defects with controlled inflammation and tissue regeneration [46][78]. Articular cartilage has limited regenerative capacity. MSC-based approaches have emerged as a promising alternative in the treatment of cartilage defects and osteoarthritis. MSCs are a promising source of therapeutically relevant cells for hyaline cartilage regeneration due to their capacity to differentiate into the chondrogenic lineage. However, experimental evidence suggests that after a while, intra-articularly injected MSCs tend to differentiate into transient cartilage that is transformed into bone by the endochondral ossification rather than hyaline articular cartilage. This process leads to decreased effectiveness of the treatment. Similarly, the stratified ultrastructure and spatial organization of native hyaline cartilage disappear [47][79]. At the same time, the most MSCs injected intra-articularly fail to attach to the damaged cartilage layer, and it is possible that they quickly spread into systemic circulation due to the rapid turnover of synovial capillaries and lymphatic vessels [48][80]. Consequently, for the optimization of clinical strategies in the domain of cell-based cartilage engineering, it becomes imperative to establish a conducive 3D microenvironment. This microenvironment should comprise a tailored amalgamation of biomaterials and bioactive factors, aimed at further augmenting the differentiation of MSCs into chondrocytes. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) are a promising source of therapeutically relevant cells for hyaline cartilage regeneration due to their capacity to differentiate into the chondrogenic lineage. The aim of the targeted differentiation is to obtain an artificial cartilage tissue with biomechanical properties similar to that of native hyaline cartilage (hyperelastic and dissipative properties, smoothness, toughness, wear resistance, resistance to compressive, tensile, and shear forces). In addition to the MSC differentiation into chondrocytes, the enhancement of the synthesis of the proteins of the hyaline cartilage extracellular matrix including fibronectin, collagens, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, cytokines, and growth factors involved in the functioning of cartilage [49][50][81,82] is necessary. MSCs can be applied to a suitable scaffold without prior induction of differentiation. Then, the so-called indirect method of differentiation is carried out, and its success depends on the properties of the scaffold. Another method is the in vitro targeted direct differentiation of MSCs into the chondrocytes that are subsequently applied to the scaffold (Figure 2). Clinical trials with MSC therapies for the regeneration of hyaline cartilage are summarized by Carneiro et al. [51][83]. Most experimental methods of hyaline cartilage regeneration, which have already been introduced in clinical practice, use direct modification techniques.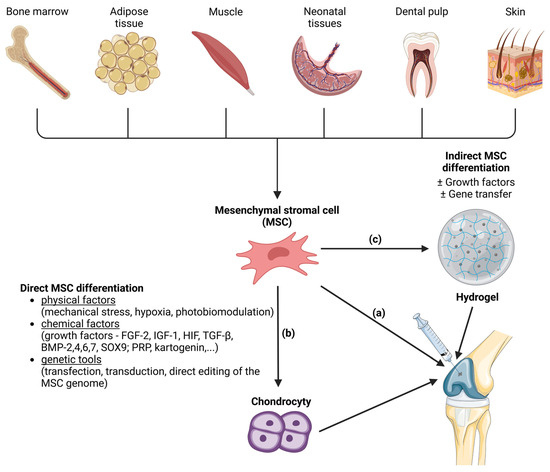
Figure 2. Methods of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) differentiation into the hyaline cartilage´s chondrocytes. MSCs are a source of the therapeutically relevant cells for cartilage regeneration. MSCs can be harvested from various tissues (bone marrow, adipose tissue, muscle, neonatal tissues, dental pulp and skin). MSCs can be injected directly into joint (a). Another approach is induction of MSC differentiation into chondrocytes before microinjection into the joint. Induction of differentiation can be direct (b) or indirect (c). Direct MSC differentiation can be induced by various physical, chemical and genetical factors. In the case of indirect MSC differentiation, the MSCs are applied to a suitable scaffold (like hydrogels) where the differentiation is induced with or without the presence of growth factors or gene transfer. After that, hydrogel with attached cells is microinjected into the joint. Created with BioRender.com.
