Lentil (Lens culinaris; Family: Fabaceae) is a potential functional dietary ingredient which has polyphenol-rich content. Several studies have demonstrated that the consumption of lentil is immensely connected to the reduction in the incidence of diseases such as diabetes, obesity, cancers and cardiovascular diseases due to its bioactive compounds. There has been increasing scientific interest in the study area of lentils as the functional food due to its high nutritive value, polyphenols, and other bioactive compounds. These polyphenols and the bioactive compounds found in lentil play an important role in the prevention of those degenerative diseases in humans. Besides that, it has health-promoting effects.
- polyphenols
- lentils
- antioxidants
- degenerative diseases
- health-promoting effects
1. Introduction
2. Nutritional Compositions of Edible Lentils
Nutritional compositions of raw, sprouted and cooked lentils are summarized in Table 1. Lentils are known to be an abundant source of protein storage, providing essential and non-essential amino acids to the human body. The predominant proteins in lentils are globulin (47% of the total seed proteins) and an adequate quantity of albumin [5]. Lentils play an important role in crop rotation and the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen. High quantities of these proteins and essential amino acids in lentils offer an important dietary source for low and middle-income countries [6]. Among 23 pulses, lentils yield the second highest starch percentage of 47.1% and a greater percentage of insoluble dietary fibers [7][8][7,8]. Lentils are known to be a good source of prebiotics [9] and have nutritionally important quantities of prebiotic carbohydrates (12.3–14.1 g/100 g of dry lentils) that help to keep up the gut microbial environment and prevent gut-associated diseases [10][11][10,11]. Furthermore, lentils are relatively low in fat and sodium, but high in potassium content (1:30 ratio of sodium and potassium) [12]. Given that, it is the best dietary food for patients with obesity and CVD. Lentil seeds are an excellent vegetable source of iron. Studies have shown that the consumption of cooked lentil in the diet prevents iron deficiency anemia [13], iron being a very important mineral, which is required daily, especially for adolescents and pregnant women. Several minerals (zinc, copper, manganese, molybdenum, selenium and boron) and vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, folate, α, β and γ tocopherols and phylloquinone) have been well documented in lentils [7][14][15][7,14,15]. Furthermore, lentils have an average quantity of vitamin K of 5 μg/100 g, as reported by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) [7]. However, the daily requirement of this vitamin in adults is about 80 μg. The low content of vitamin K renders lentils as safe for patients with CVD upon anticoagulant treatment. Overall, lentils are considered as one of the best dietary sources that has health-promoting effects on various illnesses.|
Nutrients |
Unit |
Raw |
Sprouted |
Cooked |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Water |
g |
8.26–9.65 |
||||||
|
Phytosterols |
β-sitosterol |
15.0–24.0 mg 51.85–67.34 |
Regulate the membrane fluid |
69.64–137.89 |
||||
[ |
Energy |
|||||||
|
campesterol |
kcal |
343–356 |
82–106 |
116–226 |
||||
15.0 mg |
Protein |
g | ||||||
|
stigmasterol |
20.0 mg 24.44–25.71 |
6.9–8.96 |
9.02–17.86 |
|||||
|
Total lipid (fat) |
||||||||
|
Active Proteins |
g |
0.92–1.06 |
0.42–0.55 |
0.38–0.75 |
||||
|
Carbohydrate |
g | |||||||
|
Trypsin/protease inhibitors |
Bowman–Birk trypsin inhibitors 60–64.44 |
3–8 trypsin inhibitor unit (TIU)/mg 17.05–22.14 |
20.13–38.69 |
|||||
Anti-nutritional components; decrease the digestibility of dietary proteins; inhibit the cell proliferation in cancer | [ |
Total dietary fiber |
g |
10.7–31.4 |
- |
|||
Hypoglycemic and antidiabetic potential | ||||||||
[ | ||||||||
] | ||||||||
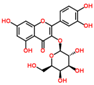
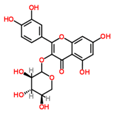
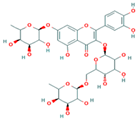
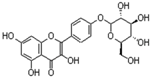
4. Polyphenols in Lentils
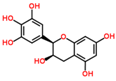
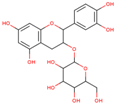
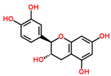
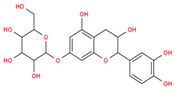
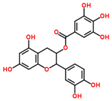
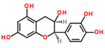
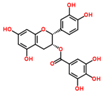
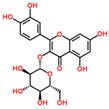
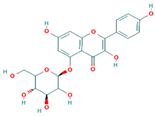
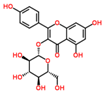
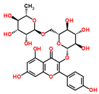
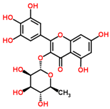
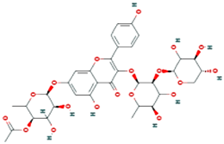
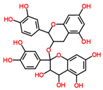
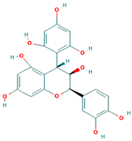
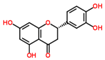
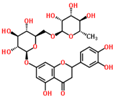
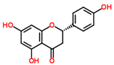
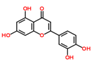
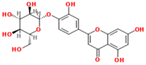
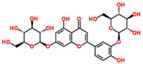
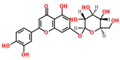
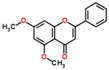
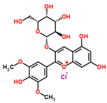
Lentils have the highest total phenolic content in comparison to six other common legumes, such as green pea, chickpea, cowpea, yellow pea, mung bean and peanut [3]. Polyphenols are generally a large group of compounds, classified into different classes, based on the presence of the number of phenolic rings and their structural elements or substituents [30][31][30,31]. Two main groups can be identified based on the aromatic rings, which are attached to the heterocyclic rings, known as the flavonoid groups (flavones, flavonols, flavanones, flavanonols, flavanols or catechins, anthocyanins, neoflavonoids and chalcones) and the non-flavonoid groups (simple phenols, phenolic acids, hydroxybenzoic acids, tannins, acetophenones and phenylacetic acids; hydroxycinnamic acids, coumarins, benzophenones, xanthones, stilbenes, lignans and secoiridoids) [31][32][31,32]. Various functional polyphenols in the lentils are described according to their classes, subclasses and chemical structures in Table 3.|
Polyphenol |
Classes |
Sub-Classes |
Compound Name |
Structure |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Flavonoids |
Flavonoids |
Flavanols |
(−)-Epigallocatechin |
|
||||||
|
(+)-Catechin-3-O-glucose |
|
|||||||||
|
Catechin |
|
|||||||||
|
Catechin-7-O-glucoside |
|
|||||||||
|
Catechin gallate |
|
|||||||||
7.9–15.6 | ||||||||||
|
Total sugars |
||||||||||
|
Lectins |
Lectins or hemagglutinins |
12.0 mg |
||||||||
|
Epicatechin |
| Ability to agglutinate red blood cells RBC and strong stimulators of murine B lymphocyte proliferation |
g |
2.03–2.86 |
- | |||||
|
Epicatechin gallate | 1.80–3.56 | |||||||||
|
Defensins |
Defensins |
8.0 mg |
Participate in the development of innate immunity |
[21] |
Minerals |
|||||
|
Dietary Fibers | Insoluble fibers (93–99.7 mg/g) and soluble fibers (<7 mg/g) |
Potential effect of hypocholesterolemic, anti-cancer, anti-tumor, antibacterial and hypoglycemic effects | ||||||||
8–16 | ||||||||||
|
Fibers |
[ | |||||||||
|
Flavonols | ] | [ |
Quercetin-3-O-glucoside |
|
Calcium |
|||||
|
Resistant starches |
mg |
35–57 |
19–25 |
19–38 |
||||||
25.4 g |
Significant contributor to gastrointestinal health and gut microbiota |
[23 | ||||||||
|
Quercetin-3-O | ] | -galactoside |
|
Iron |
mg | |||||
|
Polyphenols Flavonoids | ||||||||||
|
Quercetin-3-O |
Flavonols (e.g., quercetin and kaempferol) |
6.51–7.71 |
0.03 to 10.85 and 0.24 to 13.20 mg 2.47–3.21 |
-xyloside 3.33–6.59 |
||||||
Antioxidant potential |
|
Magnesium |
mg |
|||||||
|
Flavones, flavanones | ||||||||||
|
Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside 7-O-rhamnoside | 47–69 |
28–37 |
36–71 |
|||||||
Total phenolic content: 26 mg gallic acid equivalents (GAE/100 g fresh wt; total flavonoid content: 21 mg catechin equivalents/100 g, and the condensed tannin content of 870 mg catechin equivalents/100 g |
|
Antioxidant activity and potential effect on cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, osteoporosis and neurodegenerative diseases |
Phosphorus |
mg |
281–335 |
133–173 |
180–356 |
|||
] | ||||||||||
|
Kaempferol-4′-O-glucoside |
Potassium |
|||||||||
|
Proanthocyanidins or condensed tannins (e.g., prodelphinidins and procyanidins) |
|
|||||||||
|
Flavan-3-ols or flavanols (e.g., catechin and gallocatechin) |
759 mg (GAE)/100 g; glycosides of flavanones: 33.1–186.0 µg; glycosides of flavonols: 9.6–241 µg; dimers procyanidins: 619–1122 µg; trimer procyanidins: 441–498 µg; tetramer procyanidins: 18.5–59.5 µg; galloylated procyanidins 69.3–123 µg | |||||||||
|
Kaempferol-5-O-glucoside | 677–943 |
|
Antioxidant activity |
248–322 |
[3] |
369–731 |
||||
[ | ] |
Sodium |
||||||||
|
Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside |
mg |
3–6 |
8–11 |
123–471 |
||||||
|
Anthocyanidins (e.g., delphinidin and cyanidin) |
|
Zinc |
mg |
3.27–5.89 |
||||||
|
Polyphenols Non-flavonoids |
Hydroxybenzoic acids | 1.16–1.51 |
1.27–2.51 |
|||||||
Hydroxybenzoic acids: 4.5–28.4 µg |
Antioxidant activity and potential effect on diabetes, osteoporosis CVD and neurodegenerative diseases |
|||||||||
|
Kaempferol-3-O | ] | -rutinoside |
|
Vitamins |
||||||
|
Hydroxycinnamic acids (e.g., p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid and sinapic acid) |
Prodelphinidins 369–725 µg; condensed tannins: 870 mg catechins equivalent |
|||||||||
|
Myricetin-3-O-rhamnoside | Antioxidant activity |
Vitamin C |
||||||||
|
Stilbenoids, trans-resveratrol-3-O-glucoside mg |
||||||||||
|
4″″-Acetylsagittatin A | 3.4–4.5 |
Glycosides of trans-resveratrol: 5.5–9.3 µg; 12.7–16.5 |
Antioxidant activity and potential effect on diabetes and CVD |
[24] 1.5–3.0 |
||||||
[ | ] |
Thiamin |
||||||||
|
Phytoestrogens: isoflavones |
mg |
|||||||||
|
Proanthocyanidins | 0.756–0.873 |
Formononetin, daidzein, genistein, glycitein, matairesinol, biochanin A, coumestrol, lariciresinol, pinoresinol, secoisolariciresinol, coumestrol |
Procyanidin 0.176–0.228 |
0.169–0.335 |
||||||
Total isoflavones (9.5 μg), total lignans (26.6 μg) and total phytoestrogens (36.5 μg) |
Antioxidant potential |
[ |
26] |
Riboflavin |
||||||
|
Phytate |
mg |
Phytic acid 0.189–0.211 |
620 mg | |||||||
|
Prodelphinidin |
| 0.099–0.128 |
Inhibit the proliferation of colorectal cancer 0.073–0.0145 |
|||||||
[ | ] |
Niacin |
mg |
|||||||
|
Triterpenoids |
||||||||||
|
Flavanones |
Squalene |
Eriodictyol 2.605–3.459 |
0.7 mg 0.869–1.128 |
Chemopreventive potential against colorectal cancer 1.060–2.099 |
||||||
[ | ] |
Vitamin B6 |
mg |
0.540–0.698 |
||||||
|
Saponins |
||||||||||
|
Eriodictyol-7-O-rutinoside |
Saponins |
|
0.146–0.190 |
0.178–0.352 |
||||||
25 mg |
Folate |
µg |
||||||||
|
Naringenin | 479–555 |
77–100 |
181–358 |
|||||||
|
Vitamin B12 |
µg |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
||||||
|
Flavone |
Luteolin |
|
Vitamin A, RAE |
|||||||
|
Luteolin-4′-O-glucoside |
µg |
2.0–2.5 |
1.8–2.0 |
0 |
||||||
|
Vitamin A, IU |
IU |
32–39 |
||||||||
|
Luteolin-3′,7-diglucoside |
| 35–45 |
Vitamin E |
|||||||
|
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside |
mg |
0.49–0.55 |
0 |
0.11–0.22 |
||||||
|
Vitamin K |
µg |
4.2–5.0 |
0 |
1.7–3.4 |
|||||
|
5,7-dimethoxyflavone |
|
Lipids |
||||||||
|
Anthocyanins |
Malvidin-3-O-galactoside |
|
Total saturated fatty acids |
|||||||
|
g |
0.154–0.198 |
0.044–0.057 |
0.053–0.105 |
|||||||
Non-flavonoids |
Total monounsaturated fatty acids |
g |
0.0179–0.193 |
0.08–0.104 |
0.064–0.127 |
|||||
|
Total polyunsaturated fatty acids |
g |
0.469–0.526 |
0.169–0.219 |
0.175–0.346 |
||||||
3. Bioactive Compounds in Lentils
Various bioactive compounds or secondary metabolites are present in the lentil seed, which are categorized into different functional groups. The bioactive functional groups and their quantity in lentils are listed in Table 2.|
Bioactive Functional Groups |
Individual Components |
Quantity in 100 g of Lentils |
Biological Functions |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Phenolic acids | ||||
Hydroxybenzoic acids | ||||
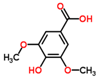
Syringic acid | ||||
| ||||
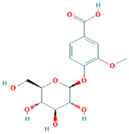
Vanillic acid 4-|A-D-glucoside | ||||
| ||||
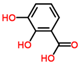
2,3-Dihydroxy benzoic acid | ||||
|
||||
|
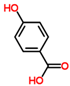
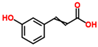
p-hydroxy benzoic acid |
|
|||
|
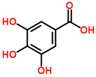
Gallic acid |
|
|||
|
Hydroxycinnamic acid |
3-hydroxy cinnamic acid |
|
||
|
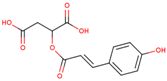
p-Coumaroyl malic acid |
|
|||
|
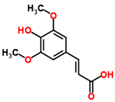
Sinapic acid |
|
|||
|
Other polyphenols |
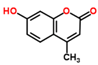
Hydroxycoumarin |
4-Hydroxy-6-methyl coumarin |
|