Postprandial plasma glucose and triglyceride concentrations are predictive of relative cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, and the pathogenesis of both insulin resistance and atherosclerosis has been attributed to acute states of hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Postprandial lipemia and hyperglycemia suppress vascular reactivity and induce endothelial dysfunction. Epidemiological studies suggest that chronically-high consumption of milk and milk products is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and CVD. The addition of dairy products to meals high in carbohydrates and fat may lessen these risks through reductions in postprandial glucose and triglyceride responses. Purported mechanisms include dairy proteins and bioactive compounds, which may explain the inverse relationship between dairy consumption and cardiometabolic diseases.
- milk
- dairy
- postprandial metabolism
- hyperglycemi
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Introduction
Traditionally, fasting plasma glucose and triglyceride concentrations have been used as clinical determinants of CVD (cardiovascular disease). However, as most individuals spend the majority of their awake and ambulatory time in a postprandial state, acute responses in plasma glucose and triglycerides following a meal have been shown to be better predictors of relative CVD risk than fasting measures [1][2][3][1–3]. Epidemiological data indicate that two-hour glucose concentration measured during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is an independent predictor of CVD risk while fasting glucose concentration is not [4]. Similarly, postprandial triglycerides are better predictors of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease (CAD) than fasting concentrations [5][6][5,6].
The pathogenesis of both insulin resistance and atherosclerosis has been attributed to acute states of hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Indeed, postprandial hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia are associated with increased risk of CVD and mortality [6][7][8][4,6–8]. Elevated postprandial plasma glucose or triglyceride concentrations following a high-carbohydrate or high-fat meal contribute to a pro-atherogenic metabolic state [9][10][11][9–11]. Moreover, both postprandial lipemia and hyperglycemia are associated with reduced vascular reactivity and impaired endothelial function [12][13][12,13].
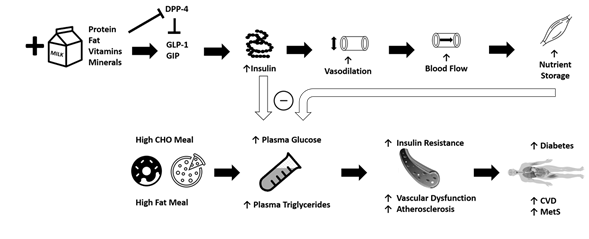
Epidemiological studies suggest that chronically-high consumption of milk and milk products is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes [14][15][16][14–16], metabolic syndrome[17] [17], and CVD [18]. The addition of dairy products to a meal high in carbohydrates or fat may potentially lessen the risk of cardiometabolic diseases through reductions in postprandial glucose and triglycerides [19][20][21][19–21] (Figure 1). Potential mechanisms driving this could include the proteins or bioactive compounds found in dairy. For instance, several of dairy’s bioactive compounds possess functional properties although the identification of the exact component responsible for reduced postprandial glycemia/lipemia is difficult to ascertain. Despite their low glycemic index, milk products, specifically milk proteins, are insulinotrophic, which may be a potential mechanism to explain, at least in part, the inverse relationship between dairy consumption and cardiometabolic diseases [22][19,22]. Insulin receptors are found on endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells, and binding initiates vasodilation [23]. When consumed with a meal, dairy proteins generate a hyperinsulinemic response that may aid in postprandial vasodilation [24], thereby increasing limb blood flow and capillary recruitment for nutrient disposal [25][26][25,26], and facilitate the clearance and storage of glucose and triglycerides after a meal [27][28][29][27–29]. The resultant increase in clearance of glucose and triglycerides may lead to an attenuated impairment of postprandial vascular dysfunction. The focus of the current review is to evaluate the available literature describing the relationships between metabolic dysfunction, postprandial metabolism, and vascular dysfunction, and to discuss the potential role of milk in attenuating these impairments.
Figure 1. The addition of milk and dairy products to a meal high in carbohydrates or fat may potentially lessen the risk of cardiometabolic diseases through reductions in postprandial reductions in blood glucose and triglycerides. Purported mechanisms include dairy proteins and bioactive compounds acting via vascular function. CHO = carbohydrate, CVD = cardiovascular disease, MetS = metabolic syndrome, GIP = glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, GLP-1 = glucagon-like-peptide-1, DPP-4 = dipeptidyl peptidase IV.
2. Postprandial Metabolism and Acute Vascular Dysfunction
In the past, clinical evaluation of hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia as a predictor of CVD and mortality has utilized fasting measures. In more recent years, it is becoming increasingly well accepted that atherosclerosis is a postprandial phenomenon [30]. Most humans eat every four to five hours but require upwards of eight hours for complete clearance of glucose and triglycerides from the blood stream [31]. This suggests that most humans spend the majority of their day in a postprandial state. Therefore, postprandial measures represent a more robust indication of daily plasma glucose and triglyceride exposure and are a truer reflection of the associated risks [1,4,6,11].
2.1. Hyperglycemia
Precise matching of glucose utilization with endogenous glucose production and dietary glucose delivery is required for maintenance of normal plasma glucose concentrations. In a fasting state, plasma glucose concentration is maintained relatively stable as a tightly-regulated physiological variable [32]. After a meal, plasma glucose concentrations increase rapidly as glucose absorption increases to more than twice the rate of endogenous glucose production. Postprandial hyperglycemia depends on a number of factors including timing, quantity, and composition of the meal, the total amount of carbohydrate, the rate and degree of glucose absorption, the secretion of insulin, and inhibition of glucagon [33]. Epidemiological studies have consistently shown that plasma glucose levels two hours after an oral glucose challenge are significant predictors of CVD risk [7].
An intervention study using participants with impaired glucose tolerance determined whether an intervention to limit postprandial hyperglycemia would reduce the risk of CVD [34]. Acarbose, an α-glucosidase inhibitor that specifically reduces glucose absorption and thus postprandial hyperglycemia, was associated with a 34% reduction in risk of developing new cases of hypertension and a 49% risk reduction in CV events [34]. In addition, acarbose treatment is associated with a reduction in intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes [35] and a significant reduction in cardiovascular events independent of other risk factors [36]. In the progression of atherosclerosis, an LDL molecule enters the sub-endothelial space and becomes oxidized. After a meal, LDL oxidation increases acutely and augments the degree of hyperglycemia [37][38][37,38]. Clearly, attenuating postprandial hyperglycemia may positively influence CVD development.
The response of insulin following a meal is highly variable and depends on a number of factors, including timing, quantity, and composition of the meal, as well as the rate and degree of glucose absorption. The postprandial insulin response is also attributed to the secretion of insulinotropic amino acids as well as enterogastric incretin hormones (e.g. glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide or GIP, and glucagon-like-peptide-1 or GLP-1). GLP-1 and GIP are secreted from enteroendocrine cells in a nutrient-dependent manner and their release stimulates glucose-dependent insulin secretion via binding to their distinct receptors on the pancreatic β-cells to stimulate insulin secretion. Both incretins promote expansion of β cell mass by stimulating β cell proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis [39]. GIP and GLP-1 are metabolized by dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4), which is thought to assist in the retention of incretin-related insulinotropic activity. In addition to incretins, recent in vitro data in preadipocytes have shown that certain proteases (e.g. membrane metallo-endopeptidase/neprislyin) favor insulin signaling and may enhance insulin sensitivity [40].
2.2. Hyperglycemia and Vasculature
Acute hyperglycemia, independent of insulin levels, significantly attenuates forearm endothelium-dependent, but not independent, vasodilation in healthy humans [13]. In both diabetic and healthy adults, hyperglycemic spikes have been shown to induce endothelial dysfunction [41][33,41]. It is purported that these effects are linked with a reduced bioavailability of nitric oxide (NO) since the hyperglycemia-induced endothelial dysfunction is counterbalanced by arginine [41]. One mechanism proposed is that hyperglycemia activates reactive oxygen species production that disrupts endothelial tight junctions, inducing endothelial permeability [42]. The rapid decrease in brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD), a measure of endothelium-dependent vasodilation, is inversely correlated with the magnitude of postprandial hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes [43].
There are a number of other ways that hyperglycemia could influence vasculature. Thrombin is a molecule involved in the coagulation cascade, alterations of which are linked to thrombosis [44]. Postprandial hyperglycemia causes an overproduction of thrombin, which has been shown to be strictly dependent on blood glucose levels [44]. Further, adhesion molecules regulate the interaction between endothelium and leukocytes, and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and/or vascular disease. Postprandial hyperglycemia has been shown to be a sufficient stimulus for increased circulating levels of ICAM-1, thus activating one of the first stages of atherosclerosis [45][46][45,46]. Finally, acute hyperglycemia has been shown to increase the production of inflammatory cytokines [47][48][47,48]. These increases in thrombin, intracellular adhesion molecules, and inflammatory cytokines in the postprandial state could contribute to the impaired vascular function observed during acute hyperglycemia.
2.3. Hypertriglyceridemia
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL), present on the luminal side of endothelial cells, is responsible for the hydrolysis of triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids. After consumption of a high-fat meal, chylomicrons carry triglyceride through the vasculature where fatty acids are liberated by lipoprotein lipase and taken up by surrounding adipose and muscle cells [49]. Triglyceride removal is dependent on LPL activity and the tissues’ need for lipids [50]. In a postprandial state, LPL availability becomes limited due to competition for binding sites and causes triglyceride-rich lipoproteins such as chylomicrons to accumulate [51][9,51].
The magnitude of postprandial plasma lipid increase is directly proportional to the fat content in meals [52][53][10,52,53]. After a high-fat meal, plasma triglycerides increase, peaking around four hours and returning to fasting levels around eight hours [31]. Because a fatty meal increases plasma lipids, multiple high-fat meals throughout the day results in prolonged presence of elevated plasma triglyceride. Increased plasma triglyceride results in reduced HDL cholesterol and increased small, dense LDL. This contributes to an increased susceptibility to oxidation and a perpetual cycle of hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis [54]. Postprandial triglyceride concentrations are associated with carotid artery wall thickness as measured by the intima-media thickness [55][56][57[55–57] and are better predictors of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease than fasting levels [58][2,58]. Every 1.1 mmol/L increase in postprandial triglyceride concentration is associated with a 1.4 increase in relative risk for a myocardial infarction [59]. The classification based on the magnitude of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia demonstrates a 68% accuracy in detecting the presence of CVD [6]. Importantly, different metabolic effects and risks are associated with various types of fat (saturated vs. unsaturated fat) as well as the specific fatty acids consumed [60].
2.4. Hypertriglyceridemia and Vasculature
Endothelial dysfunction is present in states of hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia and is attributed in large part to reduced bioavailability of NO [61]. Though the exact mechanism for the reduced NO bioavailability is unknown, it could involve any number of impairments to receptors, L-arginine use, concentration and activity of endothelial NO synthase, release and diffusion of NO, and oxidative inactivation of NO by superoxide [62]. High levels of postprandial plasma triglycerides after a high-fat meal are associated with endothelial dysfunction [63]. Indeed, a high-fat meal transiently impairs endothelial function, and mean triglyceride changes are proportionally associated with endothelial dysfunction [64]. Moreover, the infusion of a triglyceride emulsion induces a loss of vascular reactivity [65]. Even in young healthy adults, postprandial triglyceride levels are closely associated with impaired brachial artery FMD after a high-fat meal [66].
Acute hypertriglyceridemia induced by a high-fat meal correlates positively with changes in leukocyte production of reactive oxygen species. These changes are not seen with a low-fat meal, indicating that acute hypertriglyceridemia causes endothelial dysfunction via enhanced oxidative stress that reduces NO bioavailability [67]. Hypercholesterolemia impairs the L-arginine pathway, through which NO is produced, by activating the angiotensin-II receptors to cause vasoconstriction and neurohumoral activation. This facilitates the release of reactive oxygen species thereby further decreasing NO bioavailability and increasing vascular cell apoptosis and expression of adhesion molecules, chemotactic factors, and pro-inflammatory cytokines [68]. These cellular mechanisms likely contribute to vascular impairment observed during postprandial hypertriglyceridemic states.
3. Milk and Dairy
Considering that for most individuals in modern society, a majority of time is spent in a postprandial state, identification of treatments that moderate or attenuate postprandial hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia is critically needed. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary interventions, offer an affordable and easily implemented alternative to pharmacological interventions.
Bovine milk is comprised of approximately 87% water, 4–5% lactose, 3% protein, 3–4% fat and less than 1% of vitamins and minerals combined. Milk supplies 32 g of protein per liter. Of the milk protein fraction, 20% is whey, a soluble protein, and 80% is casein, an insoluble protein. Both are considered high-quality proteins because they provide essential amino acids, are readily digested, and have high bioavailability. These two protein fractions differ in their amino acid profile. Whey protein is rich in branched chain amino acids whereas casein is higher in histidine and phenylalanine. The fat fraction of milk, present as globules, is dependent on animal origin, stage of lactation, and feed-related factors. Typically, the fat found in milk is comprised of 98% triglycerides, of which 70% is saturated fatty acids (e.g. palmitic acid, myristic acid, stearic acid, butyric acid) and 30% is unsaturated fatty acids (e.g. oleic acid, linoleic acid, α-linoleic acid). Lactose, the carbohydrate found in milk, is a disaccharide sugar comprised of galactose and glucose. The glycemic index of lactose is 45 compared with the reference 100 for glucose. In addition to the primary macronutrient composition, dairy products have a specific micronutrient composition including calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D [69].
3.1. Epidemiological and Prospective Studies on Dairy Intake
Both epidemiological and prospective studies indicate that chronic consumption of dairy exhibits a protective effect in preclinical populations. A diet including high consumption of dairy products show lower chances of having prediabetes, undetected diabetes, or prevalent diabetes, compared with a Western diet [70]. For individuals with prediabetes, a diet that includes dairy decreases postprandial glucose, insulin, and triglyceride response compared with a red meat/refined carbohydrate diet [71]. Total dairy intake is associated with lower odds of hyperglycemia over a 9-year follow-up in a prospective study of individuals with metabolic syndrome [72]. Findings from the Framingham Heart Study show an inverse correlation between dairy consumption and risk of incident prediabetes [73]. Total, low-fat, and high-fat dairy intakes are associated with 39%, 32%, and 25% lower risks of prediabetes whereas neither cheese nor cream and butter is associated with prediabetes. Additionally, only high-fat dairy and cheese exhibit a dose–response inverse association with incident type 2 diabetes. These findings suggest that incident prediabetes may vary by dairy product and type and by baseline glycemic status [73].
Beyond preclinical states, chronic dairy consumption is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and CVD [74][14–16,74]. Specifically, for each daily serving of dairy consumed, there were 9% and 4% decreases in risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women 14-16. Additionally, milk consumption is inversely associated with the overall risk of CVD and stroke [75][76][75,76]. There is a 15% lower relative risk for all-cause mortality and an 8% lower overall relative risk of ischemic heart disease with high dairy consumption [74]. Similarly, there is an inverse association between dairy intake and metabolic syndrome development in healthy, overweight, and obese individuals [77][17,77]. Thus, the available evidence supports the benefits of dairy intake on cardiometabolic diseases.
4. Dairy and Glycemia
4.1. Dietary Intervention Studies
Dietary intervention studies investigating the effects of milk or dairy products and glucose response indicate a wide range of effects, likely due to the different types of dairy utilized. In a six-week randomized cross-over trial, participants replaced 13% of their daily energy intake with either butter or cheese of equivalent fat content [78]. Compared with the butter trial, fasting blood glucose concentration increased after the cheese intervention although insulin resistance values were not different between the trials [78]. An eight-week clinical trial investigating the effects of low-fat dairy intake (low-fat milk and yogurt) on overweight and obese men found no effect on fasting glucose concentration [79]. However, a six-week randomized control trial found decreased plasma glucose concentrations with high dairy consumption compared with a control food in obese women [80]. Fasting blood glucose concentration did not change within or between trials in patients with hypertension who consumed 4+ servings of low-fat dairy or eliminated all dairy for 4 weeks [81]. As all studies used low-fat dairy as an intervention, the discrepancies are likely attributed to metabolic health or, more specifically, glycemic states of the population studied.
4.2. Postprandial Intervention Studies
The effects of dairy on postprandial metabolism indicate that milk elicits favorable effects on glucose metabolism both alone or with a meal. In a well-designed randomized cross-over study [82], whole milk (a control), a beverage based on equivalent milk macronutrients, complete milk protein (16 g), lactose (24 g), or milk fat (16 g) were compared. Whole and simulated milk lowered blood glucose concentration more than predicted by the sum of individual dietary components 83. Low-fat milk reduced post-meal peak blood glucose concentration and post-meal glucose area under the curve (AUC) compared with water, soy beverage, 1% chocolate milk, orange juice, or a cow milk-based infant formula [83][84][83,84].
The majority of intervention studies examining postprandial metabolism and dairy employed milk-derived proteins, specifically whey protein. The incremental AUC for glucose decreased in a dose-dependent manner with the highest dose of whey protein supplement having a significantly greater effect than lower doses on postprandial hyperglycemia from a glucose drink [85]. Similarly, increasing doses of whey protein (10–40 g) pre-meal reduced post-meal blood glucose and insulin AUC in a dose-dependent manner [86]. The combination of whey protein and carbohydrate intake results in increased plasma insulin and reduced plasma glucose concentrations compared with those consuming carbohydrate alone [87]. The addition of whey protein to a high glycemic meal for breakfast and lunch increases plasma insulin concentration by 31% at breakfast and 57% at lunch compared with meals without whey. Further, the consumption of whey decreases postprandial plasma glucose concentration by 21% compared with the meal without whey [27]. A study on individuals with type 2 diabetes who consumed 50 g of whey or placebo with a high glycemic breakfast found that glucose levels were reduced 28% and insulin increased 105% after the protein preload [88]. Interestingly, while not compared in a head-to-head fashion, the decrease in glycemia was a larger reduction than that observed after different doses of a rapid-acting non-sulfonylurea insulin secretagogue [88][89][88,89]. Taken together, whey protein consumption both in healthy and diabetic individuals appears to attenuate the rise in postprandial glycemia when combined with a high-carbohydrate load.
Dairy products appear to have favorable effects on post-consumption glycemia independent of insulin [90]. Milk products give rise to insulinemic responses far exceeding expected insulin production independent of their lactose production, suggesting that some component of milk is responsible for stimulating insulin release [22]. Independent of a direct effect on insulin, dairy’s bioactive compounds, in particular whey amino acids, appear to act on incretin hormones via bioactive peptides and amino acids released during digestion. Several gut hormones are stimulated (e.g. cholecystokinin, peptide YY) that increase insulin secretion while others serve as endogenous inhibitors (e.g. dipeptidyl peptidase-4) preventing incretin degradation [88].
5. Dairy and Lipemia
The effects of regular dairy consumption on lipid profiles has been examined in the literature [91][92][93] [91–93]. While increased consumption of saturated fatty acids is associated with increased LDL cholesterol concentration, a number of intervention studies using whole milk and other whole fat dairy products have not shown significant increases in LDL cholesterol [91][92][93][91–93]. For lipid profiles, a higher proportion of small dense LDL (sdLDL) particles represents a greater atherogenic risk than larger, less dense LDL cholesterol molecules. In a cross-sectional study of healthy men, sdLDL particles were positively associated with plasma triglycerides and fasting insulin levels and inversely associated with HDL cholesterol concentrations. Individual fatty acids typically found in milk products (e.g. palmitic acid, myristic acid, butyric acid) are associated with fewer sdLDL particles, suggesting that milk’s fatty acids are associated with a more favorable lipid profile [94].
5.1. Dietary Intervention Studies
In a 10-year longitudinal study, a higher intake of dairy saturated fatty acids was associated with a lower CVD risk compared with a higher intake of saturated fat from meat products [60]. Interestingly, substitution of 2% of energy from saturated fat from meat with energy from dairy-derived saturated fat was associated with a 25% lower CVD risk. This attenuation has been attributed to other components of dairy such as calcium, magnesium, and/or bioactive peptides as well as to the relative proportions of different saturated fatty acids in meat and dairy [60]. However, a five-year prospective study of 300 women demonstrated that total dairy, milk, yogurt, cottage cheese, and calcium were positively related to triglycerides and negatively to HDL cholesterol at baseline, but no association was found for any five-year changes [95]. Moreover, healthy normocholesterolemic males who consumed 20% of dietary energy as butter for 21 days showed no significant change in blood lipid or apolipoprotein profile [93].
The available studies show conflicting results regarding milk protein’s effects on lipid profiles. Whey protein isolate supplementation over 3 months reduced fasting triglycerides, total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol concentrations in overweight and obese adults [96]. A similarly-designed study employing a malleable protein matrix (protein-enriched yogurt) reduced fasting triglycerides, with the effect more pronounced in those with elevated triglycerides at baseline [97]. In contrast, three-month supplementation with whey protein during a weight regain study showed no effect on plasma lipids[98] [98]. In a study examining the effects of lactotripeptide supplementation with or without physical exercise on vascular measures, there was no change in lipid panel including total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, or triglycerides in postmenopausal women after eight weeks of lactotripeptide supplementation [99]. Thus, the available evidence indicates that milk proteins may have a beneficial effect at least in some individuals (e.g. postmenopausal women).
5.2. Postprandial Intervention Studies
Postprandial triglyceridemia is strongly influenced by the composition of the meal, including the quality and quantity of fat. To date, there are few studies examining the role of complete dairy products on postprandial metabolism [100][20,21,100]. As such, the majority of dairy and lipemia studies have examined the effects of milk-derived proteins on postprandial metabolism. The postprandial appearance of triglycerides decreased by 21% and 27% when a meal was consumed with whey and casein, respectively [101]. There was no difference between four milk-derived proteins (α-lactalbumin, whey isolate, caseinoglycomacropeptide, and whey hydrolysate) on postprandial plasma triglycerides during an eight-hour high-fat test [102]. Postprandial apolipoprotein B-48 (apo B-48) response to a high-fat meal was significantly reduced when consumed with 60 g of whey protein compared with an equivalent dose of casein protein, independent of medium-chain saturated fatty acids. This reduced apo-B-48 is indicative of a reduced number of chylomicron particles within the blood stream, suggesting the potential of dairy to reduce the CVD risk associated with a high-fat meal[103]. [103]