The spleen plays numerous important roles in various diseases. There has been a growing interest in developing radiomic models for implementation in clinical practice, and spleen imaging has not been exempted from this trend.
1. Introduction
The spleen, though considered for many years the “forgotten organ”, is well visualized in imaging of the left hypochondriac region of the abdomen
[1]. The spleen has a wide range of functions, as it is the body’s larger filter of blood, produces white blood cells and antibodies, and removes microorganisms and inadequate red blood cells
[2]. This diverse range of functions of the spleen predisposes it to involvement in a variety of diseases, including immunological, infectious, hematopoietic, storage disorders, and, ultimately, also oncological diseases
[3][4][3,4]. These can lead to an overwork of the spleen that increases in size, i.e., splenomegaly
[3]. Splenomegaly and hypersplenism could also be consequences of chronic liver diseases, through the development of portal hypertension
[5]. Furthermore, the spleen can be affected by primary neoplasms, categorized as nonlymphoid and lymphoid, and can serve as a secondary target for metastases, particularly from melanoma, breast, and lung cancers
[6]. Imaging modalities such as ultrasound (US), computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) enable radiologists to visualize the spleen’s anatomy and detect gross abnormalities
[1]. However, these modalities fail when it comes to capturing the intricate and subtle variations occurring at the microscopic level, which may have the potential to deeply transform our understanding of spleen physiology and pathology.
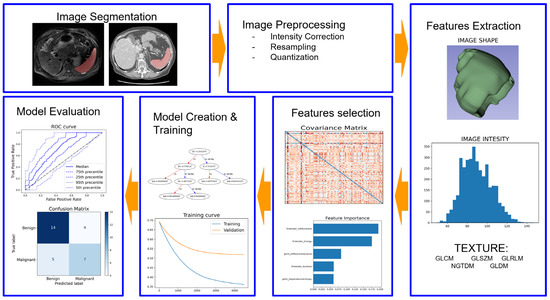
Radiomics, defined as the high-throughput extraction of a huge number of quantitative features from medical images, presents an innovative approach to capture these subtle variations and overcome the limitations of traditional imaging
[7][8][7,8]. The radiomic approach typically involves several key steps, including image segmentation, normalization, feature extraction, model creation, and validation (
Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Radiomics pipeline.
Image segmentation is the process of identifying and delineating regions of interest within the image, such as tumors or organs. A wide range of quantitative features is extracted from the segmented regions, which can include shape, texture, and intensity-based features
[9]. Finally, these features are used to create predictive models, which need rigorous validation using independent datasets to assess their performance and generalizability, ensuring the reliability of these applications in clinical practice
[9].
2. Radiomics Applications in Spleen Imaging
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in developing radiomic models for implementation in clinical practice, and spleen imaging has not been exempted from this trend. Radiomics has the potential to enhance spleen imaging by providing a quantitative and more objective perspective to the diagnostic process of primary splenic disorders. Enke et al. investigated the role of CT-based radiomics in differentiating malignant lymphoma of the spleen from non-lymphomatous lesions and found an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.86
[10][21]. In addition, the authors developed a classifier able to differentiate the lymphoma subtypes with AUCs ranging from 0.65 to 0.75.
However, what sets the spleen apart is its central role in immune function and regulation, which consequently leads to its involvement in systemic inflammatory diseases and even in the progression of primary tumors in other organs
[1][2][3][4][5][1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, the majority of the articles included herein did not focus on primary splenic disorders but examined the potential role of features extracted from the spleen in the diagnosis and prognosis of diseases affecting other regions or organs.
Yang et al. developed a radiomics score (Rad-score) to predict the 6-month survival of patients with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), a rare, life-threatening disorder of immune regulation that can potentially lead to end-organ damage and death
[11][35]. The authors extracted liver and spleen features from CT and PET images obtained from 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET/CT examinations and combined them with clinical parameters. This resulted in a Rad-score that demonstrated the ability to predict 6-month survival in adult HLH patients, with AUCs of 0.927 and 0.869 in the training and validation cohorts, respectively
[12][32].
The potential role of splenic features and characteristics was also investigated by Wang et al. with a different aim, namely the prediction of the survival rate of patients with early gastric cancer
[13][30]. The radiomic model achieved 80% accuracy in calculating the survival rate. Advanced gastric cancer has also been a subject of research; indeed, Lyu et al.
[14][34] combined gastric cancer and spleen features to predict varying differentiation status. Instead, Pan et al. enhanced the predictive capabilities of radiomics by developing a comprehensive model that combined radiomic spleen features with clinical factors, effectively determining the serosal invasion of gastric cancer
[15][27]. Similarly, the integration of features extracted from multiple organs proved advantageous. Li et al. successfully improved the model’s performance in predicting early and late recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection by integrating splenic and liver features
[16][23].
Another chronic condition where the spleen plays a significant role in the pathophysiology and complications is liver cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is the final endpoint of multiple liver diseases, such as viral infections and alcoholic or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and it has become one of the most common causes of death worldwide
[17][36]. Given the significance and healthcare burden associated with this condition, radiomics has been employed to enhance the diagnosis and staging of cirrhosis and liver diffuse diseases
[18][19][11,37]. However, cirrhosis is characterized by complex crosstalk between the spleen and liver, as the development of portal hypertension induces alterations in the splenic parenchyma, leading to hypersplenism and splenomegaly
[5]. Hence, radiomics of the spleen can potentially offer supplementary insights in liver fibrosis staging, cirrhosis detection and severity assessment, diagnosis of portal hypertension, and prediction of patients at high risk for esophagogastric variceal rebleeding.
Yin et al. found out that machine learning models incorporating CT splenic features outperformed models solely considering CT hepatic features when detecting the liver fibrosis stage
[20][33]. A similar approach was followed by Sack et al.
[21][28], who combined MRI liver and spleen radiomic features to detect cirrhosis, and by Nitsch et al.
[22][26], who developed a predictive model of disease severity for cirrhosis compared with the existing MELD (Model for End-Stage Liver Disease) score.
To assess portal hypertension, Tseng et al. proposed a noninvasive predictive model of portal venous pressure based on liver and spleen CT-extracted radiomic features
[23][29]. The same model was able to effectively predict variceal recurrence (AUC 0.86).
Esophagogastric variceal bleeding is the most fatal of the consequences of portal hypertension in cirrhotic patients, associated with a high mortality rate
[24][38]. Among the articles included here, 4 out of 14 focused on utilizing a radiomics-based model for the diagnosis of high-bleeding-risk esophageal varices in cirrhotic patients
[25][26][27][28][22,24,25,31]. To pursue this objective, the article of Yan et al. used the highest number of patients (796) and extracted liver, esophageal, and liver CT radiomic features
[28][31]. Lijuan Li et al. used the same organs and imaging method as Yan et al., but combined all these features and proposed a radiomics algorithm based on light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM). The LightGBM feature selection showed better performance compared to the other feature selection method used in their work (LASSO, Boruta, XGBoost)
[25][22]. Luo et al. combined radiomics (liver and spleen CT features) and clinical features to create a model to predict esophagogastric variceal bleeding risk with AUCs ranging from 0.925 to 0.912
[26][24]. Similarly, Meng et al. used liver and spleen CT radiomic features to create a radiomics score to predict the risk of esophageal variceal rebleeding and stratify patients according to the risk of rebleeding probability
[27][25].
Finally, another clinical scenario where radiomic features extracted from the spleen were helpful in clinical decision making is COVID-19. The value of lung parenchymal quantitative imaging biomarkers for COVID-19 diagnosis and severity assessment has been already widely proven in the literature
[29][30][31][39,40,41]. However, COVID-19 is known to also involve other organs
[32][42]. As highlighted by Batur et al., the spleen may be involved as well, with a decrease in the spleen size and a parenchymal microstructure change in a short follow-up time
[33][20]. However, the clinical relevance of these findings has yet to be demonstrated.