Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Sanjeev Kumar and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Blockchain technology has the potential to completely transform the hospitality sector by offering a safe, open, and effective method of payment. Increased customer utilisation efficiency may result from this.
- blockchain
- payment services
- hotel industry
1. Introduction
As reswearchers move through the industry 4.0 and digital transformation age, a significant digital revolution is happening worldwide. As a result, organisations need to evolve to survive. One method to achieve this is utilising cutting-edge technology like IoT, A.I., cloud computing, and blockchain. Blockchain technology has become increasingly important for many nations, entities, and organisations since it offers a novel solution to address the system’s inefficiencies. Numerous nations, including the United Arab Emirates [1], the United States [2], Australia [3], Estonia [4], Singapore [5], China [2], Georgia [6], and others, have begun experimenting with or implementing this technology at the production services level, with blockchain underpinning digital currencies. Also, countries like El Salvador have made bitcoin a legal tender [7][8][7,8].
Table 1 describes the characteristics of blockchain. The blockchain’s immutability results from the fact that new data can be attached but the chain’s old data is kept unchanged. Because everyone has access to the same data, blockchain can aid in establishing transparency in the processes. Its fundamental drawback continues to be the lack of flexibility and limited programmability. Decentralisation is one of the fundamental characteristics of the blockchain, which means that data (transactions) or code are kept identical on several computers, or “nodes”, throughout the network. The level of anonymity on a blockchain largely depends on its configuration (public vs. private) and is not a significant concern in many commercial applications with a well-defined group of participants. The process of reaching a consensus over the legitimacy of transactions and determining which entities are permitted to add data is another crucial component of a decentralised network.
Table 1. Characteristics of Blockchain.
| Characteristics | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Transparency | A limited number of users have access to the data on a blockchain. In particular, they all have the same perspective on facts. |
| Decentralisation | Blockchain technologies are decentralised and do not require a single point of control. Consensus protocols outline how scattered parties can agree on what information should be recorded on a blockchain and the current state of reality. |
| Immutability | Unless a specific portion of the network (for example, the majority of the hashing power in bitcoin) decides to do so, data in a blockchain cannot be changed. It is simple to detect whether data has been altered. |
| Anonymity | In a blockchain, the visibility of identifying information varies from complete anonymity to full identity. |
| Programmability | Blockchains that can be programmed allow for rules (commonly called “smart contracts”) that are automatically carried out when certain circumstances are met. |
| Consensus | An agreement component is applied to accomplish settlement on the condition of an organisation, including the legitimacy of exchanges and how choices can be made. |
Building customer-based value propositions has become possible thanks to technological advancement and digitisation in the travel sector. These ideas centre on decentralised autonomous value chains, information transparency, and flexible customisation. Therefore, a paradigm shift from conventional business models to customer-centric ones is required [8]. Preceding coronavirus, travel and the travel industry had formed into perhaps the main monetary area on the planet, supporting more than 320 million positions and giving 10% of the worldwide gross domestic product [6][9][10][6,9,10]. Worldwide the travel industry income is not supposed to arrive at 2019 levels until 2023. In this current year, until April 2023, travellers increased by more than 65%, as per new I.M.F. research on the travel industry in a post-pandemic world.
In contrast, following the financial crisis and the SARS outbreak, the increase was only 8 per cent and 17 per cent, respectively. In the first quarter of 2023, foreign arrivals were already around 80% of the pre-pandemic levels. Over twice as many visitors as in the same period in 2022 travelled abroad in the first three months, according to estimates of 235 million travellers. Nearly 7.8 billion passengers will travel by air by 2036. Like other industries, the hospitality sector had a market worth USD 500 trillion in 2018 and is expected to triple by 2030 [11] (vide Figure 1).
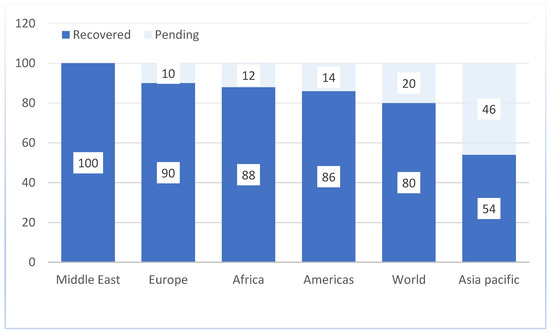
Figure 1. Arrivals of foreign tourists: Recovered percentage of 2019 levels in Q1 2023 (%) *.
Therefore, it is important to preserve trust between tourists and tourism and hospitality players and offer convenient services like ticket booking and payment while guaranteeing numerous travellers a good line of communication. Sadly, traditional centralised solutions cannot meet the above demanding requirements. Therefore, a decentralised method is required, which expands the potential in the service-based travel and hospitality industries. Blockchain satisfies tourism’s needs by incorporating transactions into an unchangeable distributed ledger [12], which fosters trust [13], transparency [14][15][14,15], security [16], and creditability [17]. The uses of blockchain technology are in healthcare [18][19][20][18,19,20], banking [21][22][21,22], education [23][24][23,24], IoT [25][26][25,26], and governance [27][28][27,28]. By enabling direct communication between clients and stakeholders, blockchain technology can replace third-party booking agencies in the tourism industry [9].
2. Blockchain Payment Services
Blockchain payment services are a brand-new payment processing system that uses blockchain technology to make payments easier [29][32]. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that makes transactions safe, transparent, and unalterable [30][33]. Due to its ability to lower costs, increase efficiency, and decrease fraud, it is the perfect choice for payment processing. Blockchain is a hard database with a [31][34] recurrent chain of blocks holding single data transactions transmitted among that specific network’s users using a decentralised mechanism [32][35]. Various sectors such as retail, financial services, supply chain, government and other sectors such as healthcare [33][36], education, and real estate are using blockchain to facilitate their payment services. Digital payments are transactions that take place using digital technology, such as near field communication (N.F.C.) interactions between an electronic wallet and a cash register or digital currency [34][37]. Digital platforms are, therefore, “a proprietary or open modular layered technological architecture that supports the efficient development of innovative derivatives, which are embedded in a business or social context” [35][38]. Blockchain is one example of this kind of platform (Figure 2).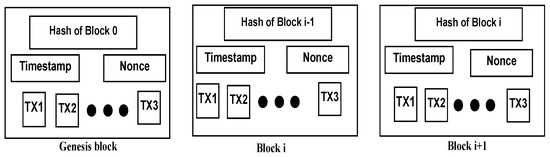
Figure 2. Example of a blockchain. Source: Authors’ Compilation.
