Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Lindsay Dong and Version 1 by Jitendra Pratap Singh.
The technology of wearable medical equipment has advanced to the point where it is now possible to monitor the electrocardiogram and electromyogram comfortably at home. The transition from wet Ag/AgCl electrodes to various types of gel-free dry electrodes has made it possible to continuously and accurately monitor the biopotential signals. Fabrics or textiles, which were once meant to protect the human body, have undergone significant development and are now employed as intelligent textile materials for healthcare monitoring. The conductive textile electrodes provide the benefit of being breathable and comfortable.
- wearable electronics
- textile electrode
- dry electrodes
- smart textiles
- electrocardiogram
- electromyogram
- biopotentials
1. Introduction
Wearable biopotential signal monitoring is a promising technology that has gained significant attention in recent years owing to its potential to revolutionize healthcare by enabling continuous and non-invasive monitoring of human physiological signals. Instead of the cumbersome healthcare systems used in hospitals, it is now possible to monitor patients’ health at home at their convenience and to improve healthcare facilities and treatment in separate locations due to the miniaturization of electronic devices [1,2][1][2]. Wearable electronics make it feasible to track patients’ health status and keep an eye on their medical issues over a prolonged length of time. Wearables can be used to treat neuromuscular ailments, fatal cardiovascular conditions, muscle-building for sports, and anomalies connected with the brain and at rehabilitation facilities [3,4,5][3][4][5]. Cardiovascular disease, the major cause of death across the globe, in which the ischemic disease, which is the leading cause of cardiovascular disease, alone was responsible for 9.44 million deaths in 2021 [6]. The early detection and management of CVD can significantly improve patient health and reduce the medical expenses. Hence, wearable biopotential signal monitoring are an an effective tool for early detection and monitoring of CVD as well as other health conditions, such as sleep disorders, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease [7,8,9][7][8][9].
Previously used only for clothing, textiles have transformed into smart textiles, which have a variety of applications, including temperature, pressure, strain, and motion sensing [10,11,12,13][10][11][12][13]. Due to the comfort that clothing offers, it may be simpler if the measuring device is incorporated into the clothing so that patients can wear it without any restrictions and without the need for special skin preparations [14]. Additionally, textile materials are freely accessible, which lowers manufacturing costs. Due to their distinctive qualities, including flexibility, breathability, and washability, textile electrodes are a promising technology for wearable biopotential signal monitoring [15,16][15][16]. Reusable electrodes will be more economically feasible for the long-term monitoring of biopotentials. Textile electrodes are therefore preferable to commercial wet electrodes made of Ag/AgCl that cannot be reused. Since the gel in commercial wet electrodes might get dehydrated and reduce the signal quality, they cannot be utilised for extended periods of time [17].

2. Biopotentials
Biopotentials are electrical signals produced by excitablecells like the neurons and cardiac cells and tissues as a result of the movement of charged particles like ions across cell membranes. The difference in electrical potential between the interior and the exterior of the cell as a result of ion transport across the cell membrane generates the electrical signals which are measurable in millivolts. These electrical potentials known as biopotentials travel towards the body’s surface, which serves as a conductor of volume [23,24][18][19]. Using electrodes positioned on the skin or directly on the tissue of interest, this electrical potential can be recorded. In disciplines such as cardiology, neurology, and sports science, biopotentials are frequently employed for diagnostic and research purposes since they can reveal important information about the physiological status of cells and tissues [25][20]. Collecting and analysing these signals help in understanding of the functioning of the body’s organs and abnormalities associated with them. The movement of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions across the voltage-gated channels are responsible for the propagation of action potentials through the heart and muscles. The resting membrane potential of −90 mV is raised to more positive values during depolarization, and the cell potential value is restored during repolarization [26][21]. The mechanism of voltage mediated ion transport across the cell membrane, resulting in the action potential curve in the depolarization–repolarization cycle, is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Action potential curve which illustrates the change in membrane potential during ion diffusion in cardiac myocytes.
2.1. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The human heart is a vital organ that pumps blood to the entire body. It is divided into four chambers, with the two upper chambers called atria and the two lower chambers called ventricles, as shown in
Figure 2. Blood flows from the atria to the ventricles through an atrioventricular septum, which separates them. The heart’s contraction is what moves blood throughout the body. The muscles surrounding the atria and ventricles contract, squeezing the blood down and out of the heart. The heart has valves that ensure blood flows in one direction. The tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle while the mitral valve regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle. Blood is received by the heart through two main veins, the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava, which bring in deoxygenated blood from the body. After the blood is pumped out of the right ventricle, it travels to the lungs through the pulmonary valve and artery. At the lungs, blood is oxygenated and returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein. The left ventricle then pumps the oxygenated blood throughout the body. The cardiac muscle in the left ventricle wall is thicker than the right ventricle wall because it needs to pump blood throughout the entire body [27].
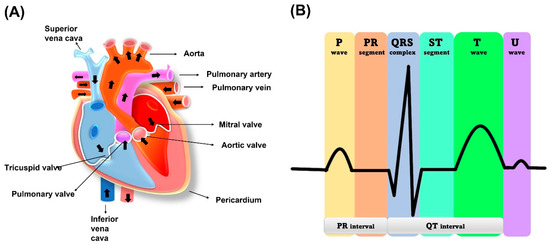
. Blood flows from the atria to the ventricles through an atrioventricular septum, which separates them. The heart’s contraction is what moves blood throughout the body. The muscles surrounding the atria and ventricles contract, squeezing the blood down and out of the heart. The heart has valves that ensure blood flows in one direction. The tricuspid valve is between the right atrium and right ventricle while the mitral valve regulates blood flow between the left atrium and left ventricle. Blood is received by the heart through two main veins, the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava, which bring in deoxygenated blood from the body. After the blood is pumped out of the right ventricle, it travels to the lungs through the pulmonary valve and artery. At the lungs, blood is oxygenated and returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein. The left ventricle then pumps the oxygenated blood throughout the body. The cardiac muscle in the left ventricle wall is thicker than the right ventricle wall because it needs to pump blood throughout the entire body [22].

Figure 2. (A) Human heart schematic representation. (B) ECG standard waveform from human heart.
The contraction of the heart is a crucial step in the circulation of blood throughout the body. This contraction process is controlled by the propagation of electrical signals induced by cation exchange through the heart cells [28].
The contraction of the heart is a crucial step in the circulation of blood throughout the body. This contraction process is controlled by the propagation of electrical signals induced by cation exchange through the heart cells [23].
The electrical activity of the heart that generates the ECG signal is produced by the depolarization and repolarization of cardiac muscle cells. When the heart muscle cells depolarize, they become more positively charged, creating a small electrical current that can be detected on the surface of the skin. The sinoatrial (SA) node is known as a natural pacemaker of the heart. The SA node is located in the wall of the right atrium, as shown in
Figure 2
.
The electrical activity of the heart can be described in terms of the principles of electrophysiology. This field of study examines the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues and how they relate to the function of the body. The principles of electrophysiology are based on the laws of physics, including Ohm’s law, which describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance, and the principles of electrical capacitance and inductance. By applying these principles, researchers can gain a better understanding of the electrical activity of the heart and how it can be measured and analysed to diagnose heart conditions [26].
The electrical activity of the heart can be described in terms of the principles of electrophysiology. This field of study examines the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues and how they relate to the function of the body. The principles of electrophysiology are based on the laws of physics, including Ohm’s law, which describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance, and the principles of electrical capacitance and inductance. By applying these principles, researchers can gain a better understanding of the electrical activity of the heart and how it can be measured and analysed to diagnose heart conditions [21].
2.2. Electromyogram (EMG)
The human body has both smooth and skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles are responsible for the movements of the body. The skeletal muscles are composed of numerous fibres. Each of these fibres are made of smaller subunits called myofibrils ranging from hundreds to thousands. Each myofibril is composed of many myosin filaments, which are large, polymerized protein molecules responsible for the actual muscle contraction. These nerve fibres innervate the skeletal muscle fibres, and the action potential is initiated in the muscle fibre by the nerves. A single motor nerve fibre and all the muscle fibres it innervates comprise a motor unit. The origin and execution of muscle contraction begins when the action potential travels along a motor nerve to its ending on the muscle fibres. Neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released at the nerve ending. This leads to the diffusion of large quantities of sodium ions into the interior of the muscle fibre membrane through the acetylcholine-gated channels. Depolarization occurs, leading to opening of voltage-gated sodium channels initiating action potential at the membrane. It depolarizes the muscle membrane, and action potential electricity flows through the centre of muscle fibre. Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which initiates attractive forces between the actin and myosin filaments, causing them to contract. After a fraction of a second, the calcium ions are pumped back and stored until a new muscle action potential is initiated. The removal of calcium ions causes the relaxation of the contracted muscles. This depolarization–repolarization cycle forms an electric dipole and travels through the surface of the muscle fibre. The movement of ions generates electrical potential in the muscle cells which travels along the surface of muscle fibre [26]. Electrodes placed on the surface of the skin records this electrical activity. The electrodes detect the superposition of all active motor units that can be detected under the bipolar electrode configuration site. Recording the electrical activity of the muscles and using it for clinical examination or for athletics training is called electromyography [25,30].The human body has both smooth and skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles are responsible for the movements of the body. The skeletal muscles are composed of numerous fibres. Each of these fibres are made of smaller subunits called myofibrils ranging from hundreds to thousands. Each myofibril is composed of many myosin filaments, which are large, polymerized protein molecules responsible for the actual muscle contraction. These nerve fibres innervate the skeletal muscle fibres, and the action potential is initiated in the muscle fibre by the nerves. A single motor nerve fibre and all the muscle fibres it innervates comprise a motor unit. The origin and execution of muscle contraction begins when the action potential travels along a motor nerve to its ending on the muscle fibres. Neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released at the nerve ending. This leads to the diffusion of large quantities of sodium ions into the interior of the muscle fibre membrane through the acetylcholine-gated channels. Depolarization occurs, leading to opening of voltage-gated sodium channels initiating action potential at the membrane. It depolarizes the muscle membrane, and action potential electricity flows through the centre of muscle fibre. Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which initiates attractive forces between the actin and myosin filaments, causing them to contract. After a fraction of a second, the calcium ions are pumped back and stored until a new muscle action potential is initiated. The removal of calcium ions causes the relaxation of the contracted muscles. This depolarization–repolarization cycle forms an electric dipole and travels through the surface of the muscle fibre. The movement of ions generates electrical potential in the muscle cells which travels along the surface of muscle fibre [21]. Electrodes placed on the surface of the skin records this electrical activity. The electrodes detect the superposition of all active motor units that can be detected under the bipolar electrode configuration site. Recording the electrical activity of the muscles and using it for clinical examination or for athletics training is called electromyography [20][24].
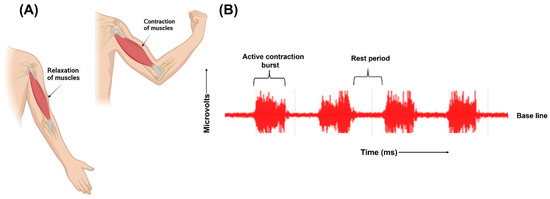
Figure 3 illustrates the contraction and relaxation of muscles and the recording of raw EMG signals.

Figure 3. (A) Representation of contraction and relaxation of muscles. (B) Graphical representation of raw EMG signals.
The signals recorded by the electrodes are raw, unfiltered EMG signals. Relaxed muscles are recorded as a less noise-free EMG baseline while on the contraction of the muscles, the signals are recorded as random non-reproducible amplitude spikes since motor units detected each time by the electrodes are not constant. Raw EMG signals range from −5 millivolts to 5 millivolts with a frequency range between 6 Hz to 500 Hz [30].
The signals recorded by the electrodes are raw, unfiltered EMG signals. Relaxed muscles are recorded as a less noise-free EMG baseline while on the contraction of the muscles, the signals are recorded as random non-reproducible amplitude spikes since motor units detected each time by the electrodes are not constant. Raw EMG signals range from −5 millivolts to 5 millivolts with a frequency range between 6 Hz to 500 Hz [24].
Recording EMG signals can help in understanding muscle fatigue, which is the decrease in the maximum contraction capability of specific muscles [31]. For a subject with muscle fatigue, there is a decrease in the fibre conduction velocity, with a diminishing number of fast contracting motor units. This results in shift of EMG power spectrum towards lower frequencies and the amplitude of the signals can increase because of the recruitment of additional motor units and their growing firing rates to sustain the required force. Textile electrodes are successful in monitoring EMG muscle fatigue monitoring. Graphene textile electrodes, which were fabricated with a dip–dye–reduce cycle on nylon fabric, were sewn onto elastic bands, which ensure sufficient pressure for skin electrode coupling. The textile electrodes placed on bicep brachii muscles successfully recorded the signals shifted to a lower frequency and increased amplitude, proving textile electrodes have the potential to be used in muscle fatigue monitoring, replacing the wet electrodes [32].
Recording EMG signals can help in understanding muscle fatigue, which is the decrease in the maximum contraction capability of specific muscles [25]. For a subject with muscle fatigue, there is a decrease in the fibre conduction velocity, with a diminishing number of fast contracting motor units. This results in shift of EMG power spectrum towards lower frequencies and the amplitude of the signals can increase because of the recruitment of additional motor units and their growing firing rates to sustain the required force. Textile electrodes are successful in monitoring EMG muscle fatigue monitoring. Graphene textile electrodes, which were fabricated with a dip–dye–reduce cycle on nylon fabric, were sewn onto elastic bands, which ensure sufficient pressure for skin electrode coupling. The textile electrodes placed on bicep brachii muscles successfully recorded the signals shifted to a lower frequency and increased amplitude, proving textile electrodes have the potential to be used in muscle fatigue monitoring, replacing the wet electrodes [26].
3. Biopotential Electrodes
3.1. Different Categories of Biopotential Electrodes
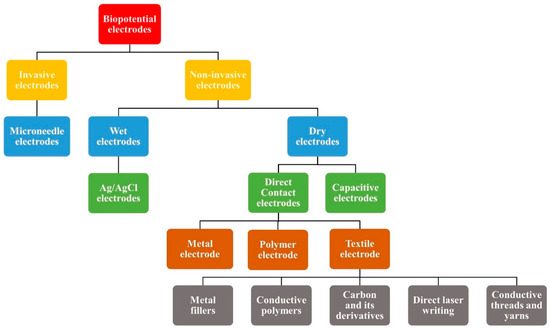
There are several types of biopotential electrodes depending upon the skin to electrode interaction, such as invasive and non-invasive electrodes. Invasive electrodes such as needle electrodes are typically used for deeper biopotential measurements such as intramuscular EMG. They penetrate the stratum corneum layer of the skin, which is the most resistive layer of the skin and hence the skin contact impedance is very low [39]. Different types of non-invasive electrodes are also used for ECG and EMG signal analysis. Surface electrodes used for non-invasive biopotential monitoring can be categorized into wet and dry electrodes, based on their charge transfer mechanism with the skin.There are several types of biopotential electrodes depending upon the skin to electrode interaction, such as invasive and non-invasive electrodes. Invasive electrodes such as needle electrodes are typically used for deeper biopotential measurements such as intramuscular EMG. They penetrate the stratum corneum layer of the skin, which is the most resistive layer of the skin and hence the skin contact impedance is very low [27]. Different types of non-invasive electrodes are also used for ECG and EMG signal analysis. Surface electrodes used for non-invasive biopotential monitoring can be categorized into wet and dry electrodes, based on their charge transfer mechanism with the skin.
Figure 4 represents the various kinds of biopotential electrodes.

Figure 4. Classification of different types of biopotential electrodes.
The above reactions represent the oxidation dominating at the electrode–electrolyte interface. The atoms of the metal can get oxidized, and they give up their electrons, which goes to the electrode while the atoms oxidized enter the solution as cations. In addition, the cations coming from the gel can become oxidized and then give their electrons to the electrode while depositing on the electrode as a neutral atom. Reverse reactions also occur at the interface. These oxidation and reduction reactions are responsible for the transduction of an ionic current to electronic current at the electrode skin interface [38].
Dry contact electrodes have direct contact with the skin surface. The absence of gel leads to a high skin contact impedance. Different kinds of direct contact dry electrodes are metal electrodes, contact penetrating electrodes, polymer electrodes, and textile electrodes [48][34]. Electrodes with microneedles can overcome the challenge of a high skin contact impedance since their microneedle array at the surface of the electrode can penetrate the stratum corneum, which is highly insulating in nature [49][35]. Metal electrodes have better conductivity, are durable, and can be reused, but they are rigid and do not have good conformance with the skin. This can lead to the movement of the electrodes when the patient moves and can result in distorted signals and low SNR [46][33]. Taking into consideration for the importance of the skin conformance of the electrode for a reduced motion artefact and good signal quality, flexible dry electrodes were investigated. Polymer and textile electrodes are good choices of the materials, which can give better skin conformance.
3.2. Wet Electrodes
Wet electrodes have a layer of gel between the electrode and skin interface. They are non-polarizable electrodes, where there is a charge transfer occurring in the electrolytic medium from chemical reactions [24,40]. The chemical reaction that occurs at the electrode–electrolyte interface for charges to cross the interface can be represented as follows:Wet electrodes have a layer of gel between the electrode and skin interface. They are non-polarizable electrodes, where there is a charge transfer occurring in the electrolytic medium from chemical reactions [19][28]. The chemical reaction that occurs at the electrode–electrolyte interface for charges to cross the interface can be represented as follows:
C ⇋ Cn+ + ne−
Am− ⇋ A + me−
3.3. Dry Electrodes
In the dry electrodes, there is no layer of gel between the electrode and skin interface. One of the advantages of the dry electrodes is that they can be used for long-term monitoring. This eliminates the problem of gel dehydration and loss is signal quality [43]. In addition, the problem of skin irritation can be avoided. Generally, when using textile-based dry electrodes, they have the advantage of being washable and reusable. Using textile- and polymer-based dry electrodes have the advantage of a better skin conformance due to their flexible nature [44,45], but one of the challenges of using dry electrodes is a higher skin contact impedance due to the absence of a gel layer. However, the presence of sweat accumulated between the electrode skin interface reduces the skin contact impedance [46]. There can be high signal-to-noise (SNR), and they are prone to motion artifacts [40].The above reactions represent the oxidation dominating at the electrode–electrolyte interface. The atoms of the metal can get oxidized, and they give up their electrons, which goes to the electrode while the atoms oxidized enter the solution as cations. In addition, the cations coming from the gel can become oxidized and then give their electrons to the electrode while depositing on the electrode as a neutral atom. Reverse reactions also occur at the interface. These oxidation and reduction reactions are responsible for the transduction of an ionic current to electronic current at the electrode skin interface [29].
3.3. Dry Electrodes
In the dry electrodes, there is no layer of gel between the electrode and skin interface. One of the advantages of the dry electrodes is that they can be used for long-term monitoring. This eliminates the problem of gel dehydration and loss is signal quality [30]. In addition, the problem of skin irritation can be avoided. Generally, when using textile-based dry electrodes, they have the advantage of being washable and reusable. Using textile- and polymer-based dry electrodes have the advantage of a better skin conformance due to their flexible nature [31][32], but one of the challenges of using dry electrodes is a higher skin contact impedance due to the absence of a gel layer. However, the presence of sweat accumulated between the electrode skin interface reduces the skin contact impedance [33]. There can be high signal-to-noise (SNR), and they are prone to motion artifacts [28].3.3.1. Direct Contact Electrodes
3.3. Dry Electrodes
In the dry electrodes, there is no layer of gel between the electrode and skin interface. One of the advantages of the dry electrodes is that they can be used for long-term monitoring. This eliminates the problem of gel dehydration and loss is signal quality [43][30]. In addition, the problem of skin irritation can be avoided. Generally, when using textile-based dry electrodes, they have the advantage of being washable and reusable. Using textile- and polymer-based dry electrodes have the advantage of a better skin conformance due to their flexible nature [44[31][32],45], but one of the challenges of using dry electrodes is a higher skin contact impedance due to the absence of a gel layer. However, the presence of sweat accumulated between the electrode skin interface reduces the skin contact impedance [46][33]. There can be high signal-to-noise (SNR), and they are prone to motion artifacts [40][28]. Wet electrodes typically require skin preparation.3.3.1. Direct Contact Electrodes
Dry contact electrodes have direct contact with the skin surface. The absence of gel leads to a high skin contact impedance. Different kinds of direct contact dry electrodes are metal electrodes, contact penetrating electrodes, polymer electrodes, and textile electrodes [48][34]. Electrodes with microneedles can overcome the challenge of a high skin contact impedance since their microneedle array at the surface of the electrode can penetrate the stratum corneum, which is highly insulating in nature [49][35]. Metal electrodes have better conductivity, are durable, and can be reused, but they are rigid and do not have good conformance with the skin. This can lead to the movement of the electrodes when the patient moves and can result in distorted signals and low SNR [46][33]. Taking into consideration for the importance of the skin conformance of the electrode for a reduced motion artefact and good signal quality, flexible dry electrodes were investigated. Polymer and textile electrodes are good choices of the materials, which can give better skin conformance. Various types of polymer materials, such as PDMS and polyurethane, which has good biocompatibility and Young’s modulus, comparable to skin and flexibility have been used for the fabrication of dry electrodes [50,51][36][37].3.3.2. Capacitive Electrodes
A capacitive electrode is a category of dry electrodes, which have an insulating material between the electrode and the surface of the skin. The conductive electrode and the surface of the skin separated by a dielectric or insulating material give rise to a capacitive component. These electrodes record the biopotential signals by capacitive coupling of the electric displacement current [54][38]. The main advantage of using a textile-based capacitive electrode is that there is not direct contact of the electrode with the skin. Therefore, this prevents problems like allergy, skin irritation, etc. that were observed in the contact electrode. In addition, this kind of electrode provides comfort to the user during long-term measurements [55][39]. Some of the disadvantages associated with capacitive electrodes are high skin contact impedance and high motion artefacts and noise in the signal. In addition, the skin contact impedance can vary according to the movement of the subject [56][40]. Therefore, a preamplifier can be used, and the electrode (except for the contact surface) can be shielded to reduce the noise [57][41]. There has been a successful usage of dry capacitive electrodes for biopotential signal measurements. Conductive electrodes can be embedded in objects used day-to-day to comfortably monitor ECG signals. The advantage of employing textile electrodes for ECG and EMG monitoring is the comfort the textile offers on the skin compared to other dry electrodes like metal or polymer varieties. Making them a part of daily attire makes it simpler to measure the signals. Even while sweat and moisture are needed to lower the skin contact impedance, excessive sweat that gets trapped between the skin and electrode might irritate the user and make the wearer uncomfortable. Additionally, it may cause the electrodes to acquire signals that are unstable and inaccurate [60][42]. The hydrophilic nature of textiles causes some perspiration to be retained in them. This may assist in lowering the skin contact impedance, a significant problem with dry electrodes. Extra sweat might drain thanks to the fabric’s porosity [61][43]. The electrode’s biocompatibility is also significantly influenced by the production process and the conductive materials employed. A hydrophilic and aqueous ink was created utilizing graphene and silk sericin to solve the water absorption issues brought on by the hydrophobic nature of graphene. This conductive ink was used to create a washable, breathable, and moisture-permeable textile electrode for the capture of human signals [62][44]. The conductive textile electrodes are mostly made of silver and other carbon-based materials, such as graphene, reduced graphene oxide, and conductive polymers. These substances induce neither allergic reactions nor irritation in human skin when exposed to it for an extended period of time [56,63][40][45].4. Different Conductive Coatings on Textile
4.1. Metallic Coating
Metals, such as copper, silver, and steel, are commonly used in smart textile applications to make conductive textiles due to their high electrical conductivity and biocompatibility. While there are many types of fabrics that can be combined with metal, the durability of metal-coated fabrics can be a concern when they are worn or washed because they may peel off easily from the areas that are exposed to air or water [70,71][46][47]. The conductive textile should withstand a certain number of washing cycles; the conductive layer should not be affected during bending, twisting, and stretching. If the conductive layer is weakly bonded to the surface of the fabric or is not properly adhered to the surface, there is chances of flaking off from the conductive layer, affecting its electrical conductivity. Among different methods to coat the metal layer on fabric, there had been many attempts to use a method called physical vapor deposition (PVD) to evaporate metals and make thin conductive films on different types of fabrics [72][48]. Silver and copper layers have been deposited on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) yarns and polyurethane (PU)-coated nylon fabrics using sputtering techniques [73,74][49][50]. Silver is most suitable for coating due to its antibacterial property and high conductivity, but due to the fact that the weak adhesion of silver in frequently used fabric washing can be an issue; it can reduce the durability of the electrode and lower the electrical conductivity. Therefore, the surface modification of the textile substrate can better adhere the conductive materials onto it. Thiol group modified polyester fabric can provide high washability to the fabricated conductive textile electrode. It provides sufficient adhesion to the silver coated on the fabric by electroless plating.4.2. Conductive Polymer Coating
There is a certain class of organic polymers, which are electrically conductive owning to their structure. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT: PSS), Polypyrrole (Ppy), and Polyaniline (PANI) belong to this category of intrinsically conductive polymers. These polymers have conjugated bonds with delocalized π-electrons giving them inherent property of electrical conductivity. The main limitation of the conductive polymers is their poor mechanical stability, stretchability, and flexibility [77][51]. This can be overcome by making composite of the conductive polymer with other elastic polymers and by using textiles as a substrate, which can result in high flexible conductive polymer composites [78,79][52][53]. PEDOT: PSS can be directly screen printed onto ready-made garments and used to obtain biopotential signals, such as EMG. To monitor the EMG signals from the leg, PEDOT: PSS can be screen printed onto stretched leg sleeves made of 100% polyester. Pre-stretching the fabric before screen printing mimics the stretching of the garment when the subject wears it during the signal monitoring. This can help in retaining the electrical conductivity of the coating on the fabric while stretching. The validation of textile electrodes was done by placing both the textile electrodes and the Ag/AgCl electrodes on the same muscle. The electrical conductivity of the electrode was 73 ± 11 mS/cm. Coating the textile electrode with multiple layers of the conductive material increased the robustness of the electrode to mechanical stress [80][54].4.3. Carbon and Its Derivatives
Due to their superior electrical and mechanical qualities, materials based on carbon have been extensively researched for use in sensing applications. They are desirable in the realm of biosensors and wearables due to their biocompatibility, flexibility, yield in higher quantities, and thermal and chemical stability [82,83][55][56]. Graphite, graphene, reduced graphene oxide, and carbon nanotubes are the mainly used carbon-based materials. Making textiles from these materials and using them go hand-in-hand. Because carbon materials can be produced in large quantities and are less expensive and because textile materials are readily available, therefore, there is a significant chance that commercialising the carbon-based textile electrode for electrophysiological signal monitoring will be possible if appropriate technologies are discovered that can generate a uniform stable coating of carbon on textile. Because of its biocompatibility and electrical conductivity, silver is one of the metals that is frequently used to create skin contact electrodes; however, due to its cost and tendency to oxidize, its potential use in greater quantities may be constrained. To create biocompatible skin contact electrodes, carbon materials, especially 2D materials such as graphene that are excellent conductors, can be a good choice [84][57]. Graphene can be used in a variety of ways to make textile materials conductible, including electrospinning, drop casting, and screen printing [85,86,87][58][59][60]. The simplest way to obtain a graphene-coated conductive textile is via dip coating or drop casting, which requires no special equipment. The graphene oxide dispersion, which was made using Hummers’ process, is applied to the nylon fibre. Hydrazine or hydrogen iodide can be used to reduce graphene oxide because it is less conductive. Nylon’s smooth surface, in contrast to materials such as cotton and Kevlar, makes it simpler for graphene to adhere to the fibre and create a good connection. After three iterations of dipping and drying, a sheet resistance of 13.96 kΩ/sq was attained. The manufactured electrode was incorporated into the calf band and utilised for monitoring EMG.4.4. Direct Laser Writing
Laser-induced graphene (LIG) is a process that uses a laser to create a conductive pattern on a polymer substrate, which can be used as a sensing electrode. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in laser-induced graphene (LIG) obtained from polymers since its discovery in 2014 [93][61]. The LIG has gained attention as a promising material for biopotential electrodes due to its low-cost, flexibility, and biocompatibility. Lin’s research group has effectively detected various electrophysiological activities, such as electroencephalograms (EEGs), electrocardiograms (ECGs), and electromyograms (EMGs), by attaching mechanical sensors based on laser-induced graphene (LIG) to different parts of the human body [94][62].4.5. Knitting, Weaving, and Embroidering with Conductive Threads, Yarns
In addition to techniques that involve adding a separate layer of conductive coatings to create e-textiles, there are techniques through which textiles themselves can be made inherent conductive. The textile electrode’s metallic or carbon coatings may delaminate and lose conductivity as conductive pathways lose connectivity from repeated use and washing [65][63]. Since conductivity is included into the cloth during the weaving, knitting, and embroidery processes, there is no requirement for adhesives to hold the electrodes in place. Threads can be made conductive by adding conductive elements, including silver, copper, nickel, and carbon [96][64]. The electrode material, electrode size, thread spacing, and the density are the key variables that affect the quality of the collected biopotential signals [66][65]. Using a high density knit to make textile electrodes increases the surface contact area and perspiration accumulation, which can diminish the skin contact impedance. Due to its biocompatibility and antibacterial qualities, silver-coated yarns and threads are one of the materials that are most frequently utilised to create textiles. The ECG data were monitored using weaving patterns made from silver plated nylon filaments. The wet electrodes produced comparable results to those of the dry electrodes when the ECG signals were analysed both at rest and during dynamic motions. Mass production of the wearable conductive textiles is essential since it less time consuming. Advanced technology like computerised embroidery can make this possible. However, this option is constrained by the unavailability of conductive thread that is compatible with the current conventional industrial textile mass manufacturing procedures. A new option for mass producing wearable electronic textiles has emerged with the use of a low-cost organic PEDOT: PSS-coated conductive thread with the mechanical robustness to be compatible with the current computerized embroidery technology. This technique was used to create a t-shirt that can track the ECG. The adherence of PEDOT: PSS to the OH-rich cotton fibre as well as the conductivity and mechanical strength of the conductive thread have all been improved by the combination of PEDOT: PSS, Ethylene Glycol (EG), and the crosslinker Divinyl Sulfone (DVS). The electrode’s capacity to be machine washed was examined. The electrical resistance was still stable after 15 washing cycles, and the ECG readings were on par with those generated by wet electrodes. During prolonged ECG monitoring, standard ECG waveforms were recognisable and stable.5. Fabrication Methods of Conductive Textiles
5.1. Electrospinning
Electrospinning is a technique that is used to produce nanofibers. In this method, a strong electric field is used to get nanosized fibres [100][66]. Several types of electrodes can be prepared using this method. Polymer-based conductive electrodes can be prepared with the electrospinning method, and then, these electrodes can be attached to the ready-made daily worn garments and used to monitor the electrical signals from the body [16,101][16][67]. Elastic polymers, such as polyurethane and PVDF can be used to make nanofibers with electrospinning. With electrospinning, ultrathin nanofibers with diameter ranging from few micrometres to several hundred nanometres can be prepared using high voltage power supply; this method is simple and low-cost. These nanofibers have good membrane strength and high specific area, large porosity, and good mechanical strength. Dipping these electrospun nanofibers into a silver- and carbon-based conductive solution gives highly conductive nanofiber-based electrodes. Stable signals were obtained during high load activities during EMG.5.2. Screen/Inkjet Printing
Printing techniques are simple, fast, and easy techniques to print conductive coatings on fabric in large scale [105][68]. It can be used in industries since it can be used for large scale manufacturing. Different kinds of conductive inks can be used for printing on the fabric. Inks made of metal nanoparticles, conductive polymers, and carbon materials can be used for printing. The inks used for printing should be viscous and should strongly bind to the surface of the fabric. It should not flake off or lose the conductivity when the fabrics undergo stretching, washing, and reusing [106][69]. Screen printed electrodes can be used for gesture controlling. First, conductive layers are printed with a silver polymer ink for conductive tracks. The final layer is a stencil printed conductive carbon rubber paste. Silicon rubber is also provided around the conductive layer to provide improved adhesion to the fabric. The electrodes are placed on the specific muscles. Three muscular groups were targeted, such as the brachioradialis, extensor group on the outer forearms, and the flexor group on the inner forearm [107][70]. The surface of the fabrics can also be modified using thermal transfer technology by coating it with a polymer layer to make the surface of the fabric rough and for better binding of the conductive materials to the fabric surface. Screen printing patterns were made on an untreated textile substrate and on top of modified textile. Viscous graphene ink is screen printed on the fabric, has comparable performance with wet electrodes during ECG acquisition, and has good stability after multiple washes, and its resistance increases with an increase in the number of washing cycles. This can be due to water absorption and small graphene nanoflake loss [108][71]. The use of three-layer printing with screen printing has been utilised to achieve a continuous conductive route and prevent any printing defect-related reduction in the performance of the textile electrode. It starts with printing a priming layer to smooth the surface, followed by printing the conductive layer and an encapsulating layer to protect the conductive tracks from electrical currents.5.3. Drop/Dye/Dip Coating
Dip coating, drop coating, and dye coating are very simple and low-cost techniques that can be used for the fabrication of conductive textiles for biosensing applications. Conductive polymers, conductive solutions, etc. can be coated on the textile surface by this method [111][72]. Conductive polymers like PEDOT: PSS mixed with DMSO to enhance the conductivity can be coated on top of cotton fabric with a simple drop coating method. ECG signals obtained from the conductive cotton electrodes were found to be stable [112][73]. These easy one-step methods can also be used to coat carbon-based materials on textile. Dyeing the fabric with graphene oxide and reducing it gives a conductive reduced graphene oxide-coated textile. Dip coating the fabric into conductive polymer PEDOT: PSS with a layer-by-layer technique enhances the conductivity of the already conductive fabric. There was decrease in sheet resistance from 2.5 MΩ to 120 Ω upon dip coating PEDOT: PSS to rGO-coated fabrics. The textile was stable under 20–30 washing cycles, and high-quality ECG signals were obtained in both wet and dry conditions [113][74].6. Essential Characteristics for a Wearable Textile Electrode
To make conductive textile electrodes for biopotential signal monitoring more effective than currently available gel electrodes in terms of signal quality and comfort as well as to enable their commercialization, research into their fabrication and modification is accelerating. Textile electrodes are increasingly being used for electrocardiogram (ECG) and electromyogram (EMG) monitoring due to their many advantages, such as improved comfort, reduced motion artifacts, and better adherence to the skin. The benefits that textile electrodes provide for comfortable long-term ECG signal monitoring at home or for tracking muscle activity during muscle training for athletes are unquestionably improvements in wearable technologies for the growth and advancement in the healthcare sectors [123,124][75][76]. To be employed as biopotential signal monitoring electrodes, textile electrodes must meet a number of qualitative and diagnostic requirements in order to be commercially viable and trusted by consumers. The choice of conductive materials should be significant since textiles act as insulation. Low surface resistance, homogeneous conductivity, and biocompatibility with human skin are all requirements for the conductive material [125,126][77][78]. The skin electrode contact may be unstable since there is no gel on the interface [46][33]. To reduce the skin’s contact impedance, a variety of techniques can be used, including contact pressure and ionic gels [19,126,127][78][79][80]. An impedance analyzer can be used to measure the electrodes’ average impedance.6.1. Electrode Design
The electrical performance of the conductive textile will vary depending on the manufacturing design of the fabric, such as woven or knitted. Brehm et al. used an iterative MATLAB optimizer in their work to investigate the effects of the woven fabric pattern, yarn type, and surface area on electrical conductivity. It was found that the more space there was, the more noise there was as well as larger signal amplitude waveforms. Although resistance varies depending on the type of conductive yarn, there was little variation in capacitance with the type of yarn [132][81]. Most of the previous studies have shown that the larger the electrode is in diameter, the better the signal quality and the lower the skin contact impedance [133][82].6.2. Effect of Pressure on the Electrode
Application of pressure on the electrodes has a strong influence in the signal quality. The optimum contact pressure is needed to reduce motion artefacts since the absence of a gel layer can make the contact between the electrode and the skin unstable [19][79]. In many textile-based electrode designs, the conductive electrodes are embedded onto tight fitting elastic garments, such as sports wears, or attached to elastic bands that can be wrapped around the chest, arms, or legs [133,135][82][83] Using elastic, tight-fitting garments ensures sufficient pressure is applied onto the garment, and the comfort of the subjects wearing them should also be taken into consideration since garments that are too tight can cause discomfort to the subjects, especially during long-term monitoring. The optimum clothing pressure comfortable to the wearer with comparable performance with wet electrodes was investigated in several studies [136][84].6.3. Effect of Noise and Motion Artifacts
The key benefit of employing textile electrodes built into T-shirts and other intelligent clothing is that they may be worn for longer periods of time to monitor the activity of the heart in circumstances like arrhythmias [34,35][85][86]. Commercially available equipment, such as the Holter ECG machine, can be used for conventional methods of long-term heart rate monitoring; however, because of its lengthy wires, it may restrict the patient’s movement. ECG signals can be measured without interfering with the patient’s everyday activities when employing smart clothing with electrodes and wireless modules integrated into it for heart rate monitoring. This provides the patient with a great deal of comfort, but the patient’s increased activity might also result in more noise and negative effects in quality of ECG signal. In a study by David et al., the performance of the Ag/AgCl electrode and electrodes constructed of silver yarn integrated into textiles was compared. Signals acquired using both approaches in the resting state were comparable while the ECG signals in both approaches during the dynamic period were of lesser quality. Both techniques had trouble distinguishing P waves. Thise study found that neither strategy outperformed the other in dynamic conditions [138][87]. During ECG and EMG measurements, several types of artifacts or interference can be observed, which may affect the quality and accuracy of the recorded signals. Some of the most common types of artifacts encountered in ECG and EMG measurements include motion artifacts, electrode motion artifacts, power line interference, and baseline drift [139,140][88][89]. The motion artifacts can arise from patient motion, poor electrode contact, electrical interference from other equipment, and various physiological factors. The level of artifacts should be kept as low as possible with proper electrode placement, subject at a relaxed position with minimum motion state, and other equipment kept off while ECG monitoring [141][90]. Motion artifacts in ECG can be monitored through various methods, including visual inspection, signal processing techniques, and machine learning algorithms.6.4. Effect of Washing and Stretching
The reusability and durability of textile electrodes are two major issues that must be resolved among the other requirements that textile electrodes must meet in order to be used for long-term ECG monitoring. Sweat can be a problem with them since they are being used during exercises and also in long-term monitoring. The electrodes should be washable, and washing them should not cause the conductive coatings on the textile’s surface to peel off, which would reduce the electrodes’ electrical capabilities [148][91]. Although stretching is likely to occur when utilising textile electrodes during exercise, this should not have an impact on the electrode’s electrical conductivity or capacity for signal acquisition.References
- Mshali, H.; Lemlouma, T.; Moloney, M.; Magoni, D. A Survey on Health Monitoring Systems for Health Smart Homes. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2018, 66, 26–56.
- Jeong, J.W.; Lee, W.; Kim, Y.J. A Real-time Wearable Physiological Monitoring System for Home-based Healthcare Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 104.
- Wongvibulsin, S.; Martin, S.S.; Steinhubl, S.R.; Muse, E.D. Connected Health Technology for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Management. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 21, 29.
- Düking, P.; Hotho, A.; Holmberg, H.C.; Fuss, F.K.; Sperlich, B. Comparison of Non-Invasive Individual Monitoring of the Training and Health of Athletes with Commercially Available Wearable Technologies. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 71.
- Byrom, B.; McCarthy, M.; Schueler, P.; Muehlhausen, W. Brain Monitoring Devices in Neuroscience Clinical Research: The Potential of Remote Monitoring Using Sensors, Wearables, and Mobile Devices. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 104, 59–71.
- IHME. New Report Tracks Latest Trends in Global Cardiovascular Health; IHME: Seattle, WA, USA, 2022.
- Robinson, T.; Condell, J.; Ramsey, E.; Leavey, G. Self-Management of Subclinical Common Mental Health Disorders (Anxiety, Depression and Sleep Disorders) Using Wearable Devices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2636.
- Munch Nielsen, J.; Zibrandtsen, I.C.; Masulli, P.; Lykke Sørensen, T.; Andersen, T.S.; Wesenberg Kjær, T. Towards a Wearable Multi-Modal Seizure Detection System in Epilepsy: A Pilot Study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 136, 40–48.
- Channa, A.; Popescu, N.; Ciobanu, V. Wearable Solutions for Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Neurocognitive Disorder: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2713.
- He, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J. An Ultralight Self-Powered Fire Alarm e-Textile Based on Conductive Aerogel Fiber with Repeatable Temperature Monitoring Performance Used in Firefighting Clothing. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 2953–2967.
- Gumus, C.; Ozlem, K.; Khalilbayli, F.; Erzurumluoglu, O.F.; Ince, G.; Atalay, O.; Atalay, A.T. Textile-Based Pressure Sensor Arrays: A Novel Scalable Manufacturing Technique. Micro. Nano Eng. 2022, 15, 100140.
- Alam, T.; Saidane, F.; Al Faisal, A.; Khan, A.; Hossain, G. Smart-Textile Strain Sensor for Human Joint Monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 341, 113587.
- Zhou, Y.; Myant, C.; Stewart, R. Multifunctional and Stretchable Graphene/Textile Composite Sensor for Human Motion Monitoring. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52755.
- Lee, S.Y.; Hung, Y.W.; Su, P.H.; Lee, I.P.; Chen, J.Y. Biosignal Monitoring Clothing System for the Acquisition of ECG and Respiratory Signals. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66083–66097.
- Heo, J.S.; Eom, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.K. Recent Progress of Textile-Based Wearable Electronics: A Comprehensive Review of Materials, Devices, and Applications. Small 2018, 14, 1703034.
- Ismar, E.; Kurşun Bahadir, S.; Kalaoglu, F.; Koncar, V. Futuristic Clothes: Electronic Textiles and Wearable Technologies. Glob. Chall. 2020, 4, 1900092.
- Xiao, X.; Pirbhulal, S.; Dong, K.; Wu, W.; Mei, X. Performance Evaluation of Plain Weave and Honeycomb Weave Electrodes for Human ECG Monitoring. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 7539840.
- Sverre, G.; Martinsen, Ø.G. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015.
- Webster, J.G. (Ed.) Measurement, Instrumentation, and Sensors Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014.
- Bandara, V.; Nanayakkara, A. A Low-Cost, Portable Biopotential Monitoring System to Study Electrical Activities of the Human Brain and Body. Eur. J. Phys. 2020, 41, 065801.
- Hall, J.E.; Hall, M.E. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020.
- Maithani, Y.; Choudhuri, B.; Mehta, B.R.; Singh, J.P. A Comprehensive Review of the Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of Dry Electrodes for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. In Modelling and Analysis of Active Biopotential Signals in Healthcare; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 2, pp. 8-1–8-32.
- Santana, L.F.; Cheng, E.P.; Lederer, W.J. How Does the Shape of the Cardiac Action Potential Control Calcium Signaling and Contraction in the Heart? J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010, 49, 901–903.
- Konrad, P. The ABC of EMG—A Practical Introduction to Kinesiological Electromyography; Noraxon USA, Inc.: Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2006.
- Yousif, H.A.; Zakaria, A.; Rahim, N.A.; Salleh, A.F.B.; Mahmood, M.; Alfarhan, K.A.; Kamarudin, L.M.; Mamduh, S.M.; Hasan, A.M.; Hussain, M.K. Assessment of Muscles Fatigue Based on Surface EMG Signals Using Machine Learning and Statistical Approaches: A Review. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan, China, 10–12 October 2019; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 705.
- Ozturk, O.; Golparvar, A.; Yapici, M.K. Smart Armband with Graphene Textile Electrodes for EMG-Based Muscle Fatigue Monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Sydney, Australia, 17 December 2021; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021.
- Kim, M.; Kim, T.; Kim, D.S.; Chung, W.K. Curved Microneedle Array-Based SEMG Electrode for Robust Long-Term Measurements and High Selectivity. Sensors 2015, 15, 16265–16280.
- Polachan, K.; Chatterjee, B.; Weigand, S.; Sen, S. Human Body–Electrode Interfaces for Wide-Frequency Sensing and Communication: A Review. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2152.
- Neuman, M.R. Biopotential Electrodes. In The Biomedical Engineering Handbook, 2nd ed.; Bronzino, J.D., Ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000.
- Gruetzmann, A.; Hansen, S.; Müller, J. Novel Dry Electrodes for ECG Monitoring. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 1375–1390.
- Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gou, L.; Zou, Y. A Novel Wearable Flexible Dry Electrode Based on Cowhide for ECG Measurement. Biosensors 2021, 11, 101.
- Nunes, T.; da Silva, H.P. Characterization and Validation of Flexible Dry Electrodes for Wearable Integration. Sensors 2023, 23, 1468.
- Fu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X. Dry Electrodes for Human Bioelectrical Signal Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 3651.
- Niu, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Surface Bioelectric Dry Electrodes: A Review. Measurement 2021, 183, 109774.
- Ren, L.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, K.; Chen, Z.; Pan, C.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of a Micro-Needle Array Electrode by Thermal Drawing for Bio-Signals Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 908.
- Jeong, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Hjort, K.; Hilborn, J.; Wu, Z.G. PDMS-Based Elastomer Tuned Soft, Stretchable, and Sticky for Epidermal Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5830–5836.
- Lee, E.; Cho, G. PU Nanoweb-Based Textile Electrode Treated with Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/Silver Nanowire and Its Application to ECG Monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 045004.
- Linz, T.; Gourmelon, L.; Langereis, G. Contactless EMG Sensors Embroidered onto Textile. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN 2007), Aachen, Germany, 26–28 March 2007; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007.
- Gao, Y.; Soman, V.V.; Lombardi, J.P.; Rajbhandari, P.P.; Dhakal, T.P.; Wilson, D.G.; Poliks, M.D.; Ghose, K.; Turner, J.N.; Jin, Z. Heart Monitor Using Flexible Capacitive ECG Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 4314–4323.
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-Enabled Dry Electrodes for Electrophysiological Sensing: A Review. J. Manag. 2016, 68, 1145–1155.
- Lim, Y.G.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, K.S. Capacitive Measurement of ECG for Ubiquitous Healthcare. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 2218–2227.
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Feng, S.; et al. All-Nanofiber-Based Janus Epidermal Electrode with Directional Sweat Permeability for Artifact-Free Biopotential Monitoring. Small 2022, 18, 2106477.
- Luo, D.; Sun, H.; Li, Q.; Niu, X.; He, Y.; Liu, H. Flexible Sweat Sensors: From Films to Textiles. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 465–481.
- Liang, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, H.; Dou, J.; Jian, M.; Xia, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Hydrophilic, Breathable, and Washable Graphene Decorated Textile Assisted by Silk Sericin for Integrated Multimodal Smart Wearables. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200162.
- Soroudi, A.; Hernández, N.; Wipenmyr, J.; Nierstrasz, V. Surface Modification of Textile Electrodes to Improve Electrocardiography Signals in Wearable Smart Garment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 16666–16675.
- Rayhan, G.S.; Khan, K.H.; Shoily, M.T.; Rahman, H.; Rahman, R.; Akon, T.; Hoque, M.; Khan, R.; Rifat, T.R.; Tisha, F.A.; et al. Conductive Textiles for Signal Sensing and Technical Applications. Signals 2022, 4, 1–39.
- Liu, W.; Shangguan, D.; Lee, J.C.B. Evaluation of Launderability of Electrically Conductive Fabrics for E-Textile Applications. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 10, 763–769.
- Pawlak, R.; Korzeniewska, E.; Koneczny, C.; Hałgas, B. Properties of Thin Metal Layers Deposited on Textile Composites by Using the PVD Method for Textronic Applications. Autex Res. J. 2017, 17, 229–237.
- Weder, M.; Hegemann, D.; Amberg, M.; Hess, M.; Boesel, L.F.; Abächerli, R.; Meyer, V.R.; Rossi, R.M. Embroidered Electrode with Silver/Titanium Coating for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 1750–1759.
- Jang, S.; Cho, J.; Jeong, K.; Cho, G. Exploring Possibilities of ECG Electrodes for Bio-Monitoring Smartwear with Cu Sputtered Fabrics. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 4551, pp. 1130–1137.
- Kaynak, A. Conductive Polymer Coatings. In Active Coatings for Smart Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Shaxton, UK, 2016.
- Jin Young, O.; Kim, S.; Baik, H.K.; Jeong, U. Conducting Polymer Dough for Deformable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4455–4461.
- Pradhan, S.; Yadavalli, V.K. Photolithographically Printed Flexible Silk/PEDOT:PSS Temperature Sensors. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 21–29.
- Spanu, A.; Botter, A.; Zedda, A.; Cerone, G.L.; Bonfiglio, A.; Pani, D. Dynamic Surface Electromyography Using Stretchable Screen-Printed Textile Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 1661–1668.
- Wang, C.; Xia, K.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Advanced Carbon for Flexible and Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801072.
- Mauter, M.S.; Elimelech, M. Environmental Applications of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5843–5859.
- Ilanchezhiyan, P.; Zakirov, A.S.; Kumar, G.M.; Yuldashev, S.U.; Cho, H.D.; Kang, T.W.; Mamadalimov, A.T. Highly Efficient CNT Functionalized Cotton Fabrics for Flexible/Wearable Heating Applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10697–10702.
- Mirjalili, M.; Zohoori, S. Review for Application of Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers Technology in Textile Industry. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2016, 6, 207–213.
- Ibanez Labiano, I.; Arslan, D.; Ozden Yenigun, E.; Asadi, A.; Cebeci, H.; Alomainy, A. Screen Printing Carbon Nanotubes Textiles Antennas for Smart Wearables. Sensors 2021, 21, 4934.
- Sadi, M.S.; Pan, J.; Xu, A.; Cheng, D.; Cai, G.; Wang, X. Direct Dip-Coating of Carbon Nanotubes onto Polydopamine-Templated Cotton Fabrics for Wearable Applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7569–7579.
- Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Ye, R.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Yacaman, M.J.; Yakobson, B.I.; Tour, J.M. Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Films from Commercial Polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5714.
- Sun, B.; McCay, R.N.; Goswami, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ling, Y.; Lin, J.; Yan, Z. Gas-Permeable, Multifunctional On-Skin Electronics Based on Laser-Induced Porous Graphene and Sugar-Templated Elastomer Sponges. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804327.
- Alshabouna, F.; Lee, H.S.; Barandun, G.; Tan, E.; Cotur, Y.; Asfour, T.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Coatsworth, P.; Núnez-Bajo, E.; Kim, J.S.; et al. PEDOT:PSS-Modified Cotton Conductive Thread for Mass Manufacturing of Textile-Based Electrical Wearable Sensors by Computerized Embroidery. Mater. Today 2022, 59, 56–67.
- An, X.; Stylios, G.K. A Hybrid Textile Electrode for Electrocardiogram (ECG) Measurement and Motion Tracking. Materials 2018, 11, 1887.
- Pitou, S.; Michael, B.; Thompson, K.; Howard, M. Hand-Made Embroidered Electromyography: Towards a Solution for Low-Income Countries. Sensors 2020, 20, 3347.
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, H.; Li, G.; Cho, H.; Jiang, M.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Developments of Advanced Electrospinning Techniques: A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100410.
- Luo, G.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; et al. Highly Conductive, Stretchable, Durable, Breathable Electrodes Based on Electrospun Polyurethane Mats Superficially Decorated with Carbon Nanotubes for Multifunctional Wearable Electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138549.
- Karim, N.; Afroj, S.; Tan, S.; Novoselov, K.S.; Yeates, S.G. All Inkjet-Printed Graphene-Silver Composite Ink on Textiles for Highly Conductive Wearable Electronics Applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8035.
- Marra, F.; Minutillo, S.; Tamburrano, A.; Sarto, M.S. Production and Characterization of Graphene Nanoplatelet-Based Ink for Smart Textile Strain Sensors via Screen Printing Technique. Mater. Des. 2021, 198, 109306.
- Court, D.; Torah, R. Development of a Printed E-Textile for the Measurement of Muscle Activation via EMG for the Purpose of Gesture Control. Proceedings 2021, 68, 8.
- Xu, X.; Luo, M.; He, P.; Yang, J. Washable and Flexible Screen Printed Graphene Electrode on Textiles for Wearable Healthcare Monitoring. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 125402.
- Ojstršek, A.; Jug, L.; Plohl, O. A Review of Electro Conductive Textiles Utilizing the Dip-Coating Technique: Their Functionality, Durability and Sustainability. Polymers 2022, 14, 4713.
- Maithani, Y.; Singh, A.; Mehta, B.R.; Singh, J.P. PEDOT: PSS Treated Cotton-Based Textile Dry Electrode for ECG Sensing. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 4052–4057.
- Akter Shathi, M.; Minzhi, C.; Khoso, N.A.; Deb, H.; Ahmed, A.; Sai Sai, W. All Organic Graphene Oxide and Poly (3,4-Ethylene Dioxythiophene)—Poly (Styrene Sulfonate) Coated Knitted Textile Fabrics for Wearable Electrocardiography (ECG) Monitoring. Synth. Met. 2020, 263, 116329.
- Alizadeh-Meghrazi, M.; Ying, B.; Schlums, A.; Lam, E.; Eskandarian, L.; Abbas, F.; Sidhu, G.; Mahnam, A.; Moineau, B.; Popovic, M.R. Evaluation of Dry Textile Electrodes for Long-Term Electrocardiographic Monitoring. BioMed. Eng. Online 2021, 20, 68.
- Chun, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J. Human Arm Workout Classification by Arm Sleeve Device Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2023, 23, 3106.
- Hakansson, E.; Kaynak, A.; Lin, T.; Nahavandi, S.; Jones, T.; Hu, E. Characterization of Conducting Polymer Coated Synthetic Fabrics for Heat Generation. Synth. Met. 2004, 144, 21–28.
- Kolanowska, A.; Kuziel, A.W.; Herman, A.P.; Jędrysiak, R.G.; Giżewski, T.; Boncel, S. Electroconductive Textile Coatings from Pastes Based on Individualized Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes—Synergy of Surfactant and Nanotube Aspect Ratio. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 130, 260–269.
- Cömert, A.; Honkala, M.; Hyttinen, J. Effect of Pressure and Padding on Motion Artifact of Textile Electrodes. BioMed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 26.
- Bihar, E.; Roberts, T.; Ismailova, E.; Saadaoui, M.; Isik, M.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Mecerreyes, D.; Hervé, T.; De Graaf, J.B.; Malliaras, G.G. Fully Printed Electrodes on Stretchable Textiles for Long-Term Electrophysiology. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600251.
- Brehm, P.J.; Anderson, A.P. Modeling the Design Characteristics of Woven Textile Electrodes for Long−Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 598.
- Kubicek, J.; Fiedorova, K.; Vilimek, D.; Cerny, M.; Penhaker, M.; Janura, M.; Rosicky, J. Recent Trends, Construction, and Applications of Smart Textiles and Clothing for Monitoring of Health Activity: A Comprehensive Multidisciplinary Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 15, 36–60.
- Belbasis, A.; Fuss, F.K. Muscle Performance Investigated with a Novel Smart Compression Garment Based on Pressure Sensor Force Myography and Its Validation against EMG. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 408.
- Beckmann, L.; Neuhaus, C.; Medrano, G.; Jungbecker, N.; Walter, M.; Gries, T.; Leonhardt, S. Characterization of Textile Electrodes and Conductors Using Standardized Measurement Setups. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 233–247.
- Can, Y.; Coimbra, M.T.; Vijaya Kumar, B.V.K. Arrhythmia Detection and Classification Using Morphological and Dynamic Features of ECG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; IEEE: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2010; pp. 1918–1921.
- Reddy, K. Recent Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Myocardial Infarction. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 243.
- Fouassier, D.; Roy, X.; Blanchard, A.; Hulot, J.S. Assessment of Signal Quality Measured with a Smart 12-Lead ECG Acquisition T-Shirt. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020, 25, e12682.
- Pérez-Riera, A.R.; Barbosa-Barros, R.; Daminello-Raimundo, R.; de Abreu, L.C. Main Artifacts in Electrocardiography. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2018, 23, e12494.
- De Luca, C.J.; Donald Gilmore, L.; Kuznetsov, M.; Roy, S.H. Filtering the Surface EMG Signal: Movement Artifact and Baseline Noise Contamination. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1573–1579.
- Hamilton, P.S.; Curley, M.G.; Aimi, R.M.; Sae-Hau, C.; Limited, E.P. Comparison of Methods for Adaptive Removal of Motion Artifact. In Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2000; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2000.
- Lee, J.C.B.; Liu, W.; Lo, C.H.; Chen, C.C. Laundering Reliability of Electrically Conductive Fabrics for E-Textile Applications. In Proceedings of the Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 28–31 May 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1826–1832.
More
