The current era is influenced by using modern digital technologies, which are meant to make people’s personal and work lives easier. Technologies bring positives such as speeding up and facilitating work and business processes, reducing the risk of accidents at the workplace, or increasing the competitiveness of economic entities on the market and increasing the quality of services and products provided. On the other hand, it is possible to register risks that consist of higher initial costs for purchasing modern digital technology and the need to employ highly qualified personnel, which will lead to retraining or layoffs.
Due to the changes brought about by digital technologies, it will be necessary to pay more attention to people and their HC, e.g., their knowledge, skills, and competencies. Economic entities should avoid mass layoffs and preferably, if possible, invest in the education of their employees.
2. Digitalization as an Industry 4.0 Element
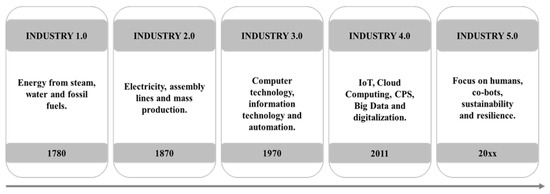
The fourth industrial revolution is built on several pillars (
Figure 1), such as digitalization, the Internet of Things, additive manufacturing, Big Data analysis, autonomous robots, simulations, horizontal and vertical system integrations, additive manufacturing (3D printing), cloud systems, augmented reality, cyber data protection, sensors, artificial intelligence, or Business Intelligence
[3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26].
Figure 1. Development of industrial revolutions (Source: own processing according to [16][17][18]. Development of industrial revolutions (Source: own processing according to [27,28,29].
Digitalization is one of the pillars and tools of the fourth industrial revolution, which is very important for entities operating in various business areas and several spheres of the national economy. It is about the possibility of optimizing several business parameters, such as performance, efficiency, or competitiveness
[19][20][30,31]. If economic entities want to be competitive, managers must respond effectively and quickly to changes brought about by the advent of digital technologies
[21][22][23][24][25][32,33,34,35,36]. The term digitalization is also associated with the term digital transformation
[26][37]. According to Lachvajderová et al. (2021), digital transformation represents a process in which modern technologies are used given the rapidly changing environment while expanding the innovative potential of the entity.
A distinction is made between the terms “digitization” and “digitalization”. The term digitization means digitalization in the process of converting human-readable analog signals into digital form and finally into binary numbers that digital technologies can understand. The second term, digitalization, represents the introduction of digital technologies into the enterprise and various socio-technical phenomena and processes related to this introduction and use
[27][28][29][30][31][38,39,40,41,42].
This technology also has the elements that characterize it. According to Porter and Heppelmann (2014)
[32][43], Pfeiffer and Jarke (2017)
[33][44], and Friedrich et al. (2013)
[34][45], these are sensors, devices forming an intelligent system, and finally, the integrating connectivity from devices to a digitalized platform. Digitalization brings changes in the business environment at the process, organizational, business domain, and company levels
[26][37].
Economic entities can use the digitalization of analog data, e.g., the personnel information system (HRIS), which transfers analog data into digital form. HRIS is an information system that collects, analyses, and stores information about employees
[35][46]. It captures the entire life cycle of an employee in an economic entity
[36][47]. HRIS is also positively evaluated by employees when they have the necessary knowledge and skills to use it
[37][48]. Large companies use HRIS the most, but nowadays, information systems for smaller companies are available
[38][49].
The digitalization of biometric data consists of using modern digital technologies to collect, process, and store the physical characteristics of a person, such as a face, eyes, voice, and fingerprints to verify the identity or identify a person
[39][50]. Economic entities use this type of digitalization for access rights for their employees
[40][41][42][51,52,53].
The use of digital platforms, including social networks, significantly affects not only the social and cultural life of people but also brings companies new opportunities for recruiting employees. It is a connection between the intrinsic world and the virtual one, with their gradual overlap, thanks to modern technologies in the field of virtual and augmented reality
[39][43][44][50,54,55].
Big data analytics are used to analyze employee motivation. It represents the collection of a large amount of diverse data characterized by its large volume (volume), the speed of generating new data (velocity), and, finally, the diversity of the type of data (variety), which must be further processed
[45][46][47][48][56,57,58,59].
As part of digitalization, predictive analytics is also used in the process of managing the employee’s work performance. It is an extensive set of different Business Intelligence (BI) technologies, thanks to which it examines the relationships between large volumes of data and uses them to predict events
[49][60].
Social networks (Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn) are a platform where people can exchange text messages, send pictures and videos, and make phone calls and video calls. Currently, social networks are used in the search and selection of employees
[50][61].
The European Parliament issued Regulation 2016/679 in April 2016, which concerns the protection of personal data and the free movement of data of this type (General Data Protection Regulation, GDPR)
[51][62]. In particular, the COVID-19 disease and the resulting measures and regulations contributed to digitalization in the field of GDPR in economic entities—activities were gradually transferred from paper to digital
[52][63].
Digitalization took place in several waves. The first wave of digitalization represented the replacement of office paper with computers, which also led to higher automation of business processes. In the second wave, there was a boom on the Internet, through which communication began not only in companies but also between them (the emergence of electronic commerce). The third wave consists of using smart technologies (SMAC—social, mobile, analytics, cloud computing), constant increase in computing power, higher storage capacity, or in the bandwidth of communication
[28][53][39,64].
Markovitch and Willmott (2014)
[54][65], Baršić et al. (2019)
[55][9], Akoyo and Muathe (2017)
[56][66], and De Silva and Da Silva Lima (2017)
[57][67] state that the use of ICT makes HCM processes more efficient and supports the fulfillment of the company’s business strategy. They see HRIS as linking complex HCM processes with ICT. A summary of the benefits of HRIS for companies was given by Beckers and Bsat (2002)
[58][68] and Kovach et al. (2002)
[59][69], who consider the pluses to be the increase in competitiveness caused by the improvement of HCM processes, the implementation of more diverse processes in the field of HCM, the transfer of HCM from a transactional perception to a strategic one, the involvement of employees in HCM processes and, finally, the reengineering of the entire HCM. It also has a positive effect on various fields in the company
[26][60][61][62][63][64][37,70,71,72,73,74].
The reason why it is necessary to pay attention to digitalization is also confirmed by the results of the digital economy and society index (DESI). In 2022, the Slovak Republic received a score of 43.40 points (23rd out of 27 places), while the average of the European Union was 52.30 points. Only four countries were ranked behind Slovakia—Poland, Greece, Bulgaria, and Romania
[65][75].
3. Human Capital Management
Human capital management (HCM) represents a set of activities for managing the human capital (HC) of an organization. It encompasses planning, recruitment and selection, placement, development, and training, maintaining employee satisfaction, engagement, and collaborative activities to manage individual and organizational competencies
[66][67][68][69][70][71][72][73][76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. The mentioned idea is also complemented by the European Partnership for Public Strategies (2022)
[74][84] and Kianto et al. (2017)
[75][85], who argue that HCM aims to manage people in such a way as to ensure greater efficiency and productivity in the enterprise. It is not only related to the development of HC but also its maximum use in the company; therefore, the emphasis should be placed on the education of employees.
Some say that digitalization is necessary if an economic entity wants to improve its processes, increase competitiveness, and increase work productivity and employee motivation. The introduction of elements, such as automation, digitalization, or robotization will cause employees to work much more efficiently than when the company did not use such elements
[76][77][78][4,86,87]. Managers in companies should motivate employees to take a proactive approach to education
[73][79][80][81][82][83][84][83,88,89,90,91,92,93].
The irreplaceability and great importance of HC have also been confirmed in the context of digital progress, which is related to the introduction of digital technologies in enterprises, and HC plays a relevant role. People are becoming the principal part of the enterprise, not only because of their work but also because of their knowledge, skills, and competencies, also within digital technologies
[85][86][87][94,95,96].
In the field of employment and working with people, digitalization will cause a change in the habits of workers, but also a change in work. Employees may be afraid of new technologies and their impact on their jobs. In addition, to avoid possible discrimination, it is necessary to still innovate the recruitment process. The number of HR personnel who recruit new employees for companies will decrease, as their work will be able to be performed by modern technologies. Digitalization will also cause the disappearance of some jobs, especially in administration and production
[88][89][90][91][97,98,99,100].
The DESI Index examines the link between digitalization and HC. Within the “Human capital” dimension, Slovakia’s most significant drop is within the indicator, which tells what percentage of companies provide their employees with vocational training in the field of ICT. In 2021 and 2022, only 16% of businesses did so, while the EU average was 20%
[65][75].