You're using an outdated browser. Please upgrade to a modern browser for the best experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Camila Xu and Version 1 by Jorge Washington Cárdenas.
Project-Based Learning (PBL), or Problem-Based Learning, is a pedagogical strategy that has cultivated an interest in reading and enhancing English language comprehension. This approach is founded on the premise that students acquire knowledge and skills most effectively when engaged in meaningful and practical projects, as opposed to mere rote memorization.
- Project-Based Learning
- active methodology
- teaching strategies
1. Introduction
Reading plays a vital role in the teaching-learning process, which is why promoting reading habits from the early years of schooling is necessary not only in the native language but also in learning English, which allows for a comprehensive education of the student [1,2][1][2] Educational institutions must provide instruction in English as a foreign language to ensure a complete and meaningful learning experience. Various strategies, such as educational projects, are encouraged for this purpose [3,4][3][4]. Additionally, appropriate techniques are being researched to develop English reading skills.
Generally, reading is not done for entertainment or personal improvement, which is a disadvantage in schools and colleges. Teachers find low reading attitudes and shared interest in reading, making it challenging to foster interest in reading and learning English in children and young people, especially texts in a different language. In addition, academic texts differ entirely from other types of literature.
Within the social framework, conducting research is relevant since it contributes to the student’s education, fostering a culture of study where the student has a leading role in their education, actively participating in the English learning process, both in reading and comprehension, as mentioned in [5,6][5][6].
Therefore, incorporating language skills in the teaching of English as a foreign language contributes to increasing students’ interest and involvement in the course through the application of didactic activities, allowing students to take advantage and benefit from their education fully while also promoting their ability to acquire a foreign language [7].
From the perspective of [8[8][9],9], PBL allows student motivation, collaborative learning, research, problem-solving through different technological media, and spontaneous communication and expression. In this teaching and learning process, students take on the central role while teachers guide them through each proposed step to achieve effective project outcomes [10,11,12][10][11][12].
PBL, or Problem-Based Learning, is a pedagogical strategy that has cultivated an interest in reading and enhancing English language comprehension [13,14][13][14]. This approach is founded on the premise that students acquire knowledge and skills most effectively when engaged in meaningful and practical projects, as opposed to mere rote memorization [13,14][13][14]. In the context of PBL, students are responsible for planning, researching, developing, and presenting projects aligned with their areas of interest [15,16,17][15][16][17].
Therefore, PBL is a methodology that contributes significantly to the educational field, both for teaching work and for the comprehensive development of students. It proposes different active methods to motivate students to practice reading effectively, developing their cognitive skills and attitudinal and procedural capacities. Moreover, it encourages future professionals in their work [18,19,20][18][19][20].
Figure 1 shows that PBL as an innovative methodology enables an effective dynamic of teaching and learning English, where the student acquires an efficient level of knowledge that allows them to assimilate and put into practice what they have learned in any sphere of life, whether personal, social, or academic. It proposes interdisciplinary and integrative tasks to real situations so the student can successfully face any challenge and develop the necessary skills for compelling English reading. This methodology incorporates various elements, such as student participation in their learning, collaboration among peers, training in self-reflection strategies, generating new ideas, and motivation [21,22][21][22].
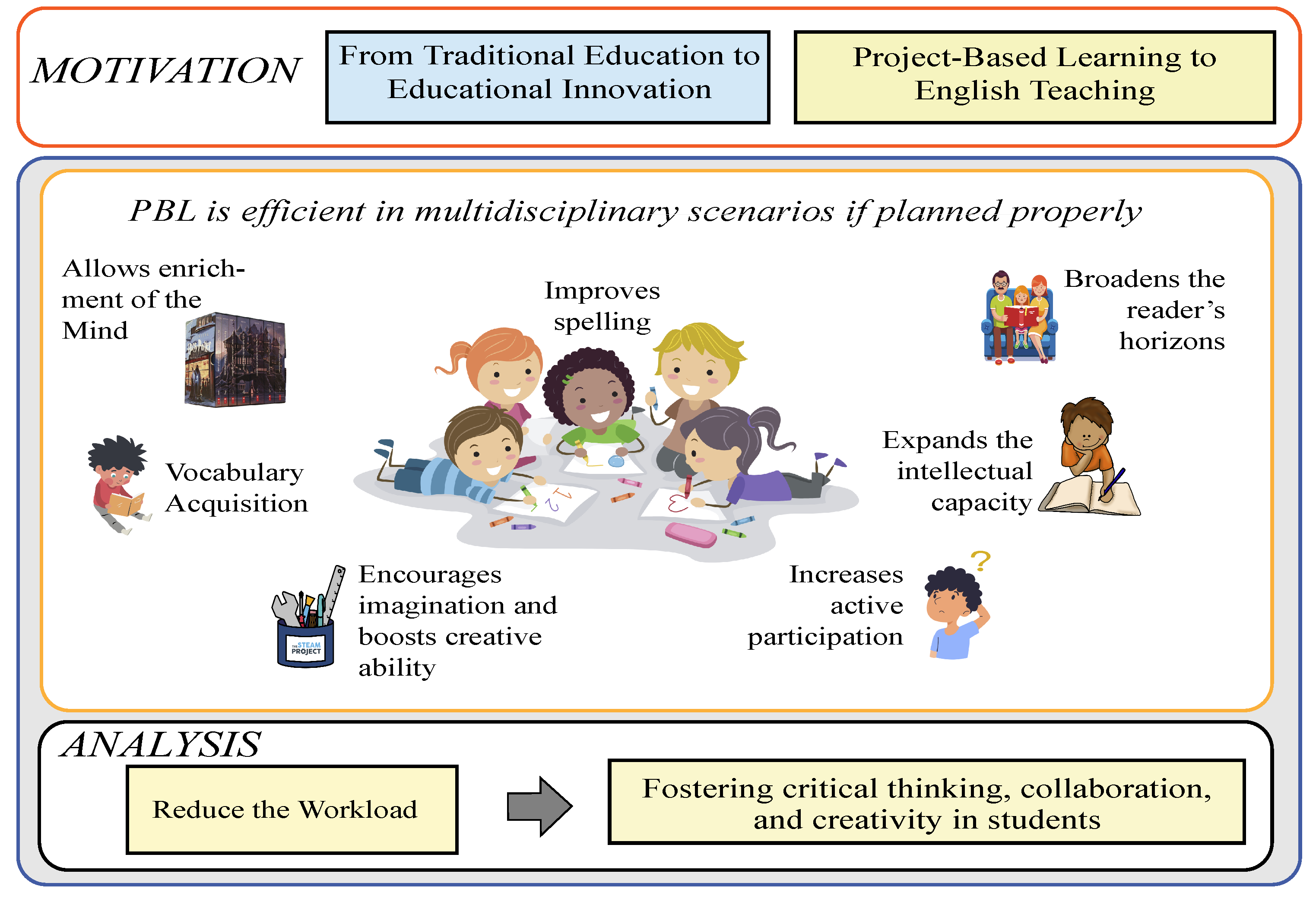
Figure 1.
Project Based Learning Multidisciplinary Strategy. Source: Authors.
2. Project-Based Learning as a Methodology to Improve Reading and Comprehension Skills in the English Language
According to [23], reading should not be described simply as an activity but as a tool enabling academic formation. Through reading, individuals can promote intellectual abilities, understand and contrast information, actively participate, provide clear responses, facilitate expression, learn and use new vocabulary, provide solid opinions, and imagine and create [24].
Reading requires understanding the ideas presented in the text, relating them to what the reader already knows, drawing conclusions, and using this information according to the stated purpose of the text, whether it be to investigate, study, collect data, or entertain. Teaching this process is essential, as the lack of guidance may be one reason students obtain low scores on reading comprehension tests [25].
As stated by [26], it is essential to prioritize fundamental learning methods that can be enhanced through active approaches, such as project-based learning, problem-solving, and questioning, to improve students’ competencies, such as the ability to create, imagine, and solve problems, as well as the development of skills in oral communication, reading comprehension, writing, and mathematical calculation. Ref. [27], also refers to the effectiveness of using diverse, active methodologies in the educational field.
According to [28], a study previously conducted by the National Institute of Statistics and Census (INEC) showed that 26.5% of Ecuadorians do not have the habit of reading, and the reasons mentioned include lack of interest, not necessary, lack of time, difficulties in concentration, among others. Regarding reading time, 50.3% read books for 1 to 2 h and 13.5% for 3 to 4 h per week. By age groups, young people aged 16 to 24 read more books at 83%, while those over 65 read less, which represents 62%. It should be noted that 33% of respondents mentioned that they must fulfill academic obligations, while a lower percentage do so to learn more about a specific topic.
Worldwide reading rates reveal that, in general, there are countries where reading ability is promoted since limited reading is an obstacle to the progress of society. Ecuador is no exception. The statistics are clearly below the indicators of other countries.
The habit of reading in English among primary school students is a critical factor for their academic and linguistic development. Reading in English allows them to develop their vocabulary, comprehension, and ability to communicate in this language, fundamental skills for their future academic and professional success, as stated by [29].
Technological media currently provide activities that can propose tasks [27,30,31][27][30][31] where students engage and enjoy being part of a reading community. However, many primary school students face difficulties in developing reading habits. Factors that may influence this include a lack of access to English books, a lack of interest or motivation, or problems understanding the language.
Ref. [32] argues that presenting texts in physical and digital formats using various virtual media and using the available technology for reading comprehension students is essential. It creates a meaningful learning environment, as students are more interested when texts are projected through virtual media public in the classroom [33].
In their work, Ref. [34] mentions that reading comprehension is a cognitive process in which the reader can read various texts with different levels of complexity using appropriate fluency, tone of voice, and intonation. It is more than just reading a certain number of words in a given time.
In addition, Ref. [35] argue in their study that reading ability is a procedure that involves relating, extracting, and constructing the reader’s experiences and knowledge. From an educational perspective, these elements must be considered as they are beneficial for interpreting, evaluating, and managing information [36].
Therefore, it is essential to clearly understand the characteristics of texts to achieve quality comprehension as part of a cognitive process [37,38][37][38].
The bibliometric analysis uses the Vosviewer software tool, which made it possible to analyze the countries where research is being conducted on PBL and its relationships with other countries through scientific documents published in Web of Science and Scopus.
Looking at Figure 2a, the data from Scopus reveals that the United States is still the country with the most research publications on PBL, with 408 documents and 589 citations. Australia has a considerably high number of publications, with 60,124 papers, but a relatively low number of sources, with only 135. Spain follows the United States and has many publications with 198 documents and 393 citations. China has 153 compositions and 177 citations, while Indonesia has 182 papers and 173 medals. The United Kingdom has a moderate number of publications, with 63 documents and 111 sources. Germany, Portugal, and Taiwan have lower numbers of publications, with 49, 47, and 55 papers, but still have a significant number of citations, with 77, 123, and 180, respectively. Malaysia, Brazil, Norway, Hong Kong, and Sweden have even fewer publications and sources, with 53, 59, 25, 25, and 23 documents, respectively.
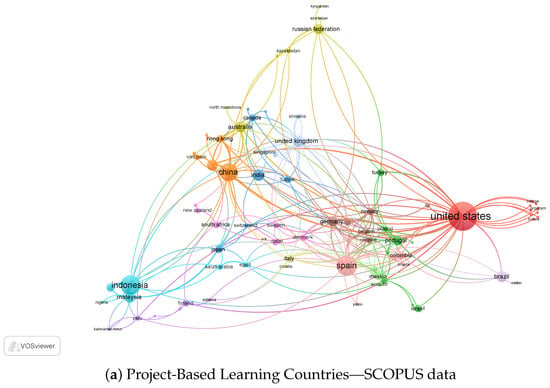
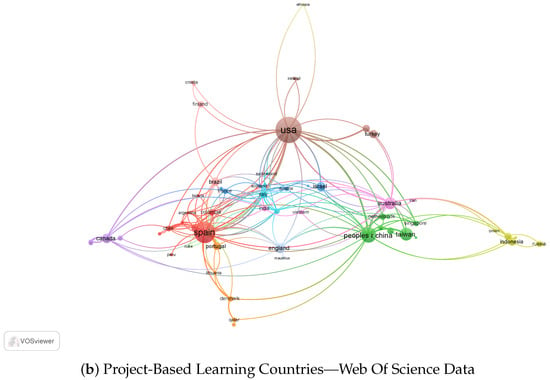
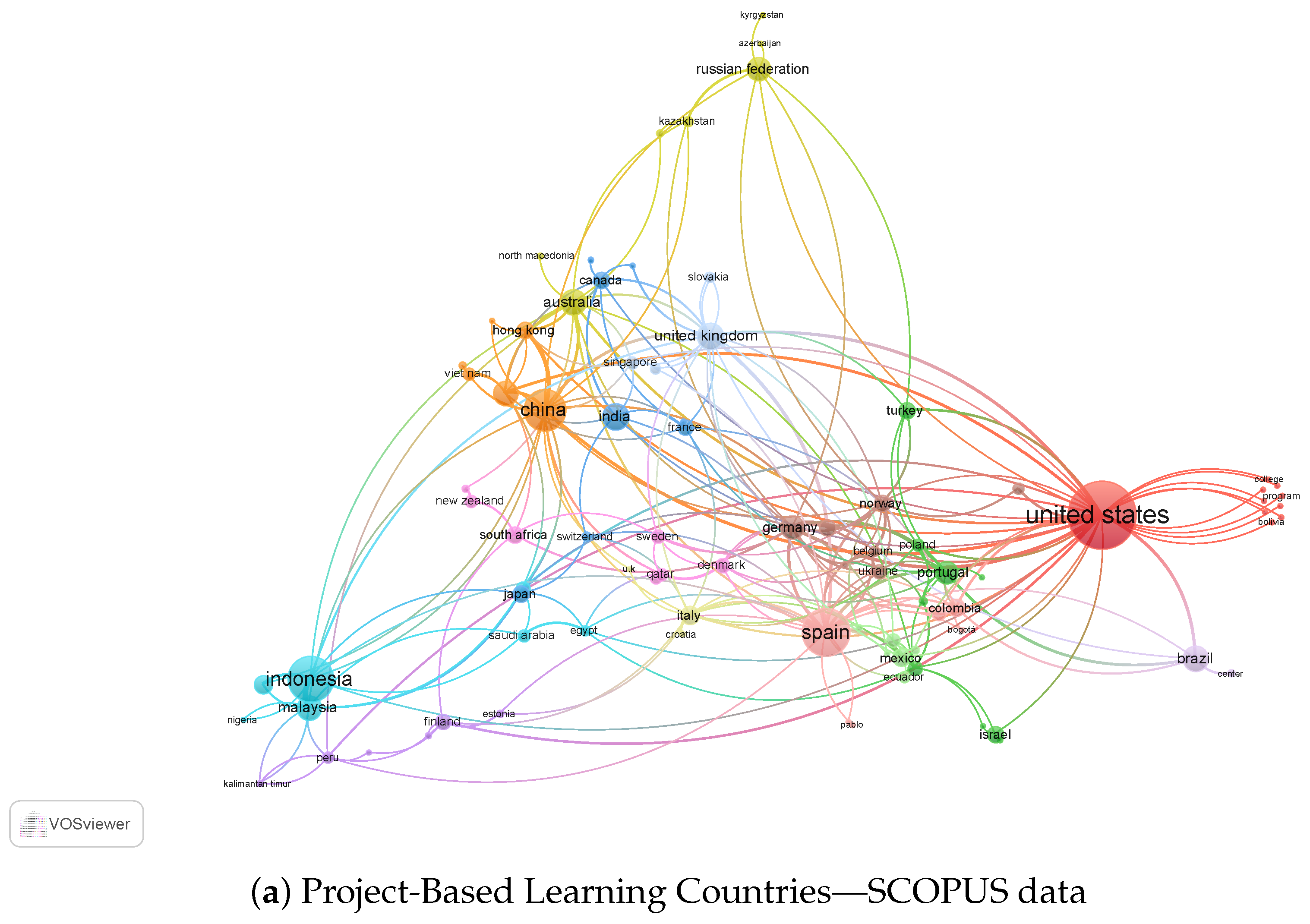
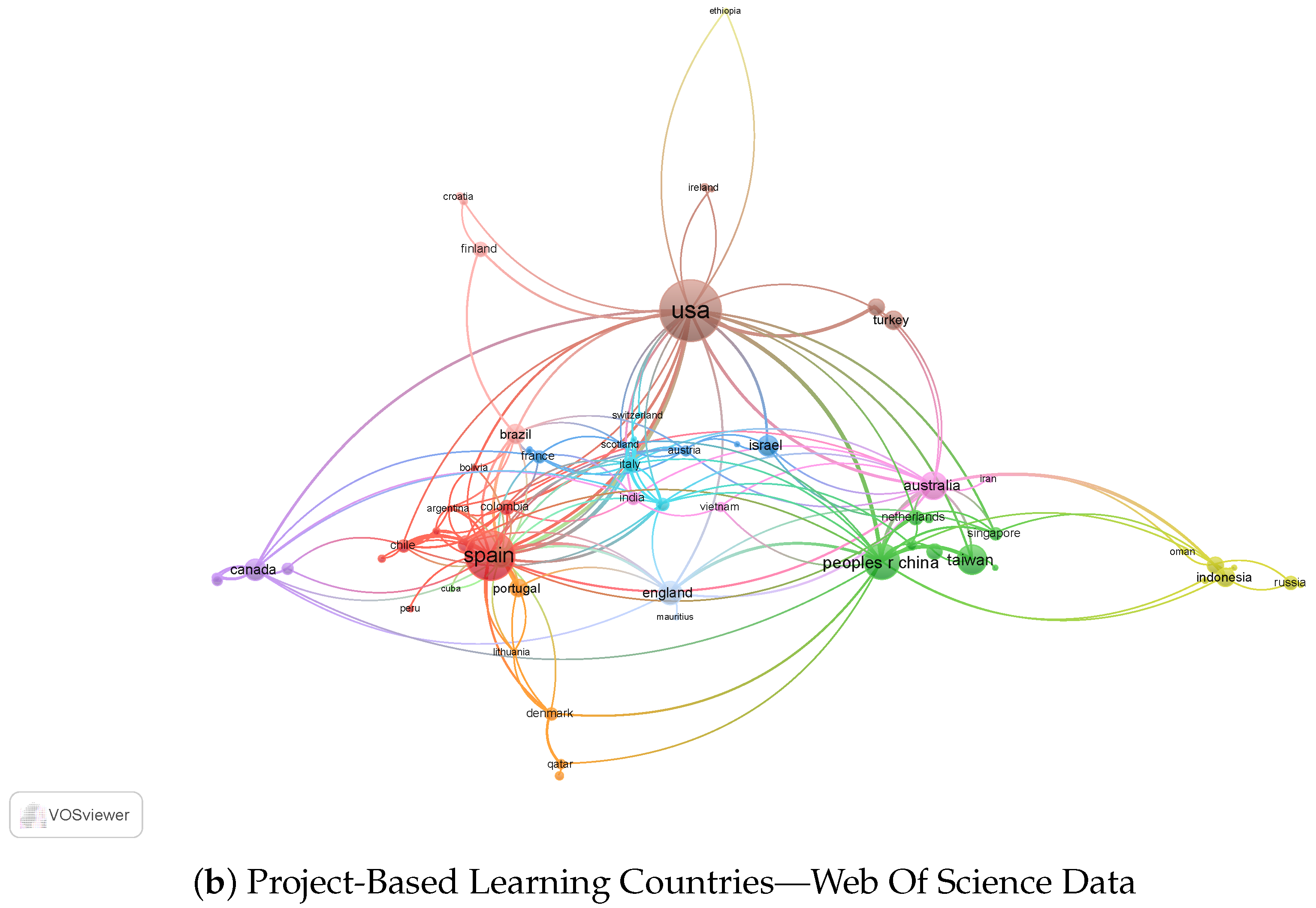
Figure 2.
Bibliometric Analysis—(
a
) Scopus (
b
) Web of Science. Source: Authors.
As shown in Figure 2b, the data from the Web of Science reveals that the United States has the most research publications on PBL, with 178 documents and 6277 citations. China follows this with 124 papers and 1491 citations, and Canada with 54 records and 1093 citations. Australia, Denmark, and England also have many publications on this topic, with 63, 55, and 55 documents, respectively.
The Netherlands has fewer publications, with 47 papers, but has many citations, with 2869. Germany and Sweden have lower numbers of publications, with 18 and 23 documents, respectively, but still have a significant number of sources, with 283 and 440, respectively. Qatar has minor publications and citations, with only 16 documents and 71 medals.
The data from both databases indicate that PBL is a popular research topic in the United States, China, Canada, Australia, and Europe. The United States has the highest number of publications and citations in both databases, indicating its leading position in PBL research. Australia has an increased number of publications, but a relatively low number of sources, meaning their study may not be as impactful as those from the United States or Europe. China also has many publications, but its citations are lower than the United States and European countries.
Moreover, the data from Scopus reveals that Spain is a significant player in PBL research, with many publications and citations [39,40][39][40]. Indonesia also has many journals and sources, indicating that it is an emerging country in PBL research [41,42][41][42]. On the other hand, countries such as Brazil, Norway, Hong Kong, and Sweden have a small number of publications and citations, indicating their relatively minor role in PBL research.
The United States is the dominant country in PBL research, with the most publications and citations in both databases. Australia has an increased number of publications but a relatively low number of sources. In contrast, China has many magazines, but its citations are lower than in the United States and European countries. Europe, particularly Spain and Portugal, is significant in PBL research.
About Table 1, The list of universities researching the PBL is quite diverse, with some universities leading regarding the number of documents published and citations received. The University of California, Berkeley, and Stanford University stands out with 5 and 7 papers published and 1518 and 1454 citations, respectively. It indicates a high level of research activity and the impact of their research on the academic community.
Table 1.
Most influential Universities Searching PBL Strategies.
| Bibliometric Analysis Using VosViewer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web of Science | Scopus | ||||
| Universities | Documents | Citations | Universities | ||
Table 2 presents the most relevant studies on the subject, which justifies the relevance of this research supported by authors whose works are related to peer instruction and PBL, which were investigated through scientific literature from various databases. The pieces were analyzed based on three critical aspects: problem, constraint, and proposal. The authors aimed to contrast the results obtained from each type of instruction based on the proposed aspects.
Table 2.
Summary of works related to Peer Instruction and Learning Engineering.
| Work | Problem | Constraint | Proposal | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author | Enthusiasm in Reading | Language Comprehension | Application of learning strategies | Project-oriented approaches | |||||||||||
| Documents | Citations | ||||||||||||||
| Wu, 2023 [21] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | Univ Calif Berkeley | 5 | 1518 | Qatar University | 3 | 94 | ||
| Yu, 2023 [29] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | Stanford Univ | 7 | 1454 | Michigan State University | 8 | 50 | |||||
| Univ Michigan | 11 | 574 | Universitas Negeri Malang | 3 | Mirza, 2023 12 | ||||||||||
| [7] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | Technion Israel Inst Technol | 12 | 363 | North Carolina State University | 3 | 11 | ||||||
| Natl Taiwan Univ Sci | 10 | 350 | Beijing Normal University | 3 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Univ Hong Kong | 14 | 316 | Georgia Institute of Technology | 3 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Arizona State Univ | 9 | 213 | National Taiwan University of Science and Technology | 4 | 8 | ||||||||||
| Michigan State Univ | 16 | 167 | Johannes Kepler University | 4 | 7 | ||||||||||
| Indiana Univ | 5 | 156 | Purdue University | 6 | 13 | ||||||||||
| Univ Autonoma Barcelona | 6 | 140 | Universitat de València | 4 | 5 | ||||||||||
Other notable universities include Michigan University, with 11 documents published and 574 citations; the Technion Israel Institute of Technology, with 12 papers published and 363 citations; and the National Taiwan University of Science, with 10 published and 350 sources. These universities have a significant research output and actively contribute to advancing knowledge in the PBL field.
It is interesting to note that some universities with fewer documents published, such as Hong Kong University, with 14 papers published and 316 citations, have a similar or even more significant impact than other universities with more documents. The quality of research, rather than the quantity, plays a crucial role in the effects of research in the PBL field.
Additionally, it is essential to highlight that universities from different regions are researching PBL. For instance, universities from Spain, Indonesia, and Qatar are represented in the list. It indicates that the PBL approach is gaining popularity and recognition globally.
However, some universities in the list have a low number of documents published and citations, such as Universitas Negeri Malang, with only 3 and 12 sources, and National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, with four papers published and eight citations. It suggests that these universities have a lower research output and impact in the PBL field.
The analysis of the most influential universities researching PBL strategies is relevant to the study project because this study aims to improve reading and comprehension skills in the English language through PBL methodology. The universities named demonstrate a high level of research activity and impact on the academic community, indicating that PBL is a well-studied and practical approach. Additionally, the global representation of universities researching PBL highlights its growing popularity and recognition, emphasizing the need to explore its potential for further advancements in diverse educational contexts.
| Integrated projects | Restricted reading resources | Instruction in reading techniques | Availability of reading resources | Training on PBL | |||||
| Liao, 2023 [10] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | ||||
| 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | |||||||
| Chigbu, 2023 [25] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | |||
| Santos, 2023 [23] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | |||||
| Rivadeneira, 2023 [27] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | |||
| Velasco, 2023 [17] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | ||||||
| Perez, 2023 [12] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | ||
| Castro, 2023 [18] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | ||||
| Lozano, 2023 [16] | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | ||
| Proposal Authors | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 | 🗸 |
Of the ten works, eight identified the problem of traditional teaching methods, characterized by teachers’ need for more motivation and interest in reading to develop students’ soft skills. In contrast, PBL was proposed as a solution to address this problem. Additionally, the works identified various constraints, such as limited appropriate reading materials, commitment and accessibility to reading materials, and training on reading strategies, which may affect the implementation of PBL methodology.
The proposals presented in the works as solutions included training on PBL. Some results suggested that learning strategies should be adopted to ensure the success of PBL. Other works suggested implementing a motivation for project-based practices and student participation.
References
- Cárdenas, J.; Inga, E. Methodological Experience in the Teaching-Learning of the English Language for Students with Visual Impairment. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 515.
- Ripoll, J.; Tapia, M.; Aguado, G. Reading rate in Spanish-speaking students: A meta-analysis. Rev. Psicodidáct. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 25, 158–165.
- Viramontes, A.; Núñez, L.; Amparán, A.; Flores, P. Comprensión lectora y el rendimiento académico en Educación Primaria. Investig. Sobre Lect. 2019, 12, 65–98.
- Gutiérrez, R.; Planelles, M. Effects of the development of reading comprehension questions on learning improvement. Rev. Lenguas Para Fines Específicosíficos 2022, 28, 61–74.
- Lopez, J.; Pina, V.; Ballesta, S.; Bordoy, S. Proyecto Petit UBinding: Método de adquisición y mejora de la lectura en primero de primaria. Estudio de eficaci. Logop. Foniatría Audiol. 2020, 40, 12–22.
- Vásconez Paredes, C.D.; Inga Ortega, E.M. El modelo de aprendizaje TPACK y su impacto en la innovación educativa desde un análisis bibliométrico. INNOVA Res. J. 2021, 6, 79–97.
- Mirza, A.; Gottardo, A. The Role of Context in Learning to Read Languages That Use Different Writing Systems and Scripts: Urdu and English. Languages 2023, 8, 86.
- Zambrano, M.; Bravo, M. El aprendizaje basado en proyectos como estrategia didáctica. Conrado-Rev. PedagóGica Univ. Cienfuegos 2022, 18, 1–12.
- Yangari, M.; Inga, E. Educational innovation in the evaluation processes within the flipped and blended learning models. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 487.
- Liao, Y.; Chen, M. The Project-Based Learning Study of Insurance Information Courses to Simulate the Application of Online Analytical Processing. Appl. Sist. Innov. 2023, 6, 47.
- Martinez, D. Project-Based Learning (PBL), an Interdisciplinary Methodological Strategy. Nomadas 2022, 56, 295–304.
- Pérez, R.; González, W.; Sarasola, M. Implementación del aprendizaje basado en proyectos en centros de educación media uruguayos. Pensam. Educ. Rev. Investig. Educ. Latinoam. 2022, 59, 1–17.
- Mantilla-Cabrera, L.F.; Larrea-Vejar, M.L.; Tapia-Salinas, J.A. Aprendizaje basado en proyectos y destreza oral en inglés de estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Arbitr. Interdiscip. Koin. 2020, 5, 544.
- Cueva, A.; Inga, E. Information and Communication Technologies for Education Considering the Flipped Learning Model. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 207.
- Caeiro-Rodríguez, M. Creation-based learning and artistic education: Projects classroom between metacognition and metaemotion. Arte Individuo Soc. 2018, 30, 159–177.
- Lozano, A.; López, R.; Pereira, F.J.; Blanco Fontao, C. Impact of Cooperative Learning and Project-Based Learning through Emotional Intelligence: A Comparison of Methodologies for Implementing SDGs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16977.
- Velasco Moreno, M.I. on Project Based Learning Approach and Future Foreign Language Teachers. Hum. Rev. Int. Humanit. Rev. Rev. Int. Humanidades 2023, 17, 1–8.
- Castro, L. Aprendizaje basado en proyectos para fortalecer el proceso de enseñanza aprendizaje Project-based learning to strengthen the teaching-learning process Aprendizagem baseada em projetos para fortalecer o processo de ensino-aprendizagem Ciencias de la Educac. Polo Del Conoc. 2022, 7, 2294–2309.
- Li, H.; Majumdar, R.; Chen, M.R.A.; Ogata, H. Goal-oriented active learning (GOAL) system to promote reading engagement, self-directed learning behavior, and motivation in extensive reading. Comput. Educ. 2021, 171, 104239.
- Inga, E.; Inga, J.; Cárdenas, J. Planning and Strategic Management of Higher Education Considering the Vision of Latin America. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 188.
- Wu, L.; Valcke, M.; Van Keer, H. Differential effects of reading strategy intervention for three levels of comprehenders: Focus on text comprehension and autonomous reading motivation. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 104, 102290.
- Ramirez, A. Educational Innovation in Adult Learning Considering Digital Transformation for Social Inclusion. Educ. Sci. 2022, 12, 882.
- Santos, C.; Rybska, E.; Klichowski, M.; Jankowiak, B. ScienceDirect Science education through project-based learning: A case study. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 1713–1720.
- Otárola, J.; Díaz, C.; Cuitiño, J. Historias digitales mediante Windows Movie Maker: Una herramienta para mejorar la escritura en inglés. Entramado 2019, 16, 122–136.
- Chigbu, U.E.; Atiku, S.O.; Du Plessis, C.C. The Science of Literature Reviews: Searching, Identifying, Selecting, and Synthesising. Publications 2023, 11, 2.
- Bunting, L.; af Segerstad, Y.H.; Barendregt, W. Swedish teachers’ views on the use of personalised learning technologies for teaching children reading in the English classroom. Int. J. Child-Comput. Interact. 2021, 27, 100236.
- Rivadeneira, J.; Inga, E. Interactive Peer Instruction Method Applied to Classroom Environments Considering a Learning Engineering Approach to Innovate the Teaching–Learning Process. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 301.
- Ripalda, V.; Macías, J.; Sánchez Mata, M. Rincón de lectura, estrategia en el desarrollo del lenguaje. Horizontes Rev. Investig. Cienc. Educ. 2020, 4, 127–138.
- Yu, L.; Yu, J.J.; Tong, X. Social–Emotional Skills Correlate with Reading Ability among Typically Developing Readers: A Meta-Analysis. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 220.
- Arenas, A.; Roa, L.; Centeno, J.; Téllez, K. La enseñanza de la lectura y la mediación cognitiva en estudiantes de media académica: Estudio de correlación. Rev. Electrón. Educ. 2021, 25, 664–689.
- Garach-Gómez, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, A.; García-Lara, G.M.; Jiménez-Castillo, I.; Ibáñez-Godoy, I.; Expósito-Ruiz, M. Promoting early reading in a social exclusion district in primary care. An. Pediatr. 2021, 94, 230–237.
- Stole, H.; Mangen, A.; Schwippert, K. Assessing children’s reading comprehension on paper and screen: A mode-effect study. Comput. Educ. 2020, 151, 103861.
- Chen, Y.L.; Hsu, C.C. Self-regulated mobile game-based English learning in a virtual reality environment. Comput. Educ. 2020, 154, 103910.
- Rocha, J. Metodologías activas, la clave para el cambio de la escuela y su aplicación en épocas de pandemia. INNOVA Res. J. 2020, 5, 33–46.
- Tarchi, C.; Zaccoletti, S.; Mason, L. Learning from text, video, or subtitles: A comparative analysis. Comput. Educ. 2021, 160, 104034.
- Inga, E.; Hincapié, R. Creación de artículos académicos basados en minería de datos y Web 2.0 para incrementar la producción científica en ingeniería. Rev. Educ. Ing. 2015, 10, 65–74.
- Krepel, A.; de Bree, E.H.; Mulder, E.; van de Ven, M.; Segers, E.; Verhoeven, L.; de Jong, P.F. Predicting EFL vocabulary, reading, and spelling in English as a foreign language using paired-associate learning. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2021, 89, 102021.
- Rodriguez-Segura, D. A closer look at reading comprehension: Experimental evidence from Guatemala. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2022, 93, 102630.
- Vaca Torres, A.M.; Gómez Rodríguez, L.F. Increasing EFL Learners’ Oral Production at a Public School Through Project-Based Learning. Profile Issues Teach. Prof. Dev. 2017, 19, 57–71.
- Belda-Medina, J. ICTs and Project-Based Learning (PBL) in EFL: Pre-service Teachers’ Attitudes and Digital Skills. Int. J. Appl. Linguist. Engl. Lit. 2021, 10, 63.
- Salam, S.; Firman, F.; Mirnawati, M. How to Improve Learning Outcomes of the Indonesian Language in Elementary Schools through the Implementation of Problem-Based Learning Methods. Pedagog. J. Islam. Elem. Sch. 2022, 5, 131–144.
- Pitrianti, S. The Implementation of Problem-Based Learning in Writing Discussion Text on Indonesian Language Learning. IJAEDU—Int.-J. Adv. Educ. 2017, III, 620–627.
More
