Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Camila Xu and Version 1 by Sheetal Kishor Parakh.
Among the available renewable resources, microalgae biomass, a third-generation feedstock, is promising for energy production due to its rich biochemical composition, metabolic elasticity, and ability to produce numerous bioenergy products, including biomethane, biohydrogen, and bioethanol.
- anaerobic digestion
- biomethane
- biohydrogen
- biophotolysis
1. Introduction
Energy has played a crucial role in economic and social development [1]. However, over 80% of our energy demand is fulfilled by non-renewable and less environment-friendly fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil [2]. These fuels are the primary source of carbon dioxide emissions, responsible for over 90% of global carbon emissions [3]. This dependency on fossil fuels has created two crises: fossil fuel depletion and global climate change. Despite this, energy demand continues to rise and is projected to increase by 47% in the next 30 years, particularly in developing countries [4]. It is, thus, imperative to find alternative renewable and clean energy sources to ensure a sustainable future. Bioenergy, the oldest known form of energy derived from biomass, is a promising option for meeting growing energy demand sustainably [5]. Biomass can be replenished in a relatively shorter time when compared with fossil fuels, making bioenergy a renewable energy source [6]. Bioenergy is carbon-neutral, releasing only the carbon dioxide that biomass consumes during its growth. Compared to bioenergy, fossil fuels release new carbon dioxide into the atmosphere that was sequestered and stored under the earth’s crust for millions of years [7]. Another advantage of bioenergy is its local production, reducing the need for long-distance energy transportation [8]. Local bioenergy production reduces the environmental impact of energy production and stimulates the local economy by providing energy security and economic opportunities [9].
Bioenergy is a broad term that refers to energy derived from various biomass sources, including food/non-food crops, agricultural/forest residue, and even algae [10]. Biomass can be divided into three generations based on its type. First-generation biomass includes traditional food and energy crops, such as corn, sugarcane, maize, soybean, and palm. Second-generation biomass comprises non-food crops and waste, such as woody/grassy plants and forest product residues [11]. Currently, a majority of biofuel is derived from first-generation biomasses, such as sugar (36.3 billion liters/year), maize (61.8 billion liters/year), palm oil (18.3 billion liters/year), and soybean oil (13.6 billion liters/year) [12]. However, using first-generation feedstocks for bioenergy production presents a food vs. fuel dilemma and challenges the food security [13]. Although second-generation feedstocks do not include food crops, these still compete with food production systems for resources such as arable land, freshwater, and fertilizers [14], making them unsustainable for fuel production. Third-generation feedstock, algae, has the potential to meet future bioenergy demands without compromising resources used for food production [15].
Microalgae are highly efficient photosynthetic organisms that rapidly grow throughout the year in various habitats, including aquatic (fresh or marine) and terrestrial ecosystems [16]. Microalgae exhibit relatively higher growth rates than terrestrial plants, completing an entire growth cycle in just a few days [17]. Moreover, microalgae can be cultivated on non-arable land using wastewater or seawater as a source of nutrients [18]. High biomass yield, minimal resource requirements, and a consistent biomass supply make microalgae a leading candidate for bioenergy production. Initially, the interest in using microalgae for bioenergy production was primarily due to its high lipid content (up to 60–70%), which could be converted into biodiesel using transesterification processes [19]. However, microalgae biomass can also be converted into other forms of bioenergy using biochemical and thermochemical processes. Biochemical conversion mainly includes anaerobic digestion [20], alcoholic fermentation [21], and fermentation/biophotolysis [22] processes for biomethane, bioethanol, and biohydrogen production, respectively. Thermochemical conversion includes pyrolysis [23], gasification [24], and hydrothermal processes [25] for bio-oil/biochar/syngas, syngas, and bio-oil/hydrochar/biogas production, respectively. Both biochemical and thermochemical processes are efficient pathways to recover energy from microalgae biomass since these methods utilize the whole biomass and do not depend on extracting specific macromolecules [26]. However, biochemical processes have a competitive advantage over thermochemical processes due to their ability to process wet biomass, operate at ambient processing conditions (temperature and pressure), and exhibit high selectivity toward the desired product, making them more sustainable and environment-friendly in the long run [27].
2. Microalgae Biomass and Its Components
Algae are efficient, sunlight-driven green cell factories that convert carbon dioxide into various biomolecules, including lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins [31][28]. The cellular content of these biomolecules varies significantly between different algae species [32][29]. Algae can be classified into two broad categories: microalgae and macroalgae. Microalgae are unicellular and smaller (up to a few millimeters), whereas macroalgae are large (up to a few meters) and multicellular. There are more than 50,000 microalgae species in nature, of which 4000 species have been identified, and only a few species (<50) have been commercialized [33][30]. Therefore, microalgae biomass has immense untapped and unexplored potential. Table 1 displays the biochemical composition of commonly used microalgae species.Table 1.
Biochemical composition of some microalgae species (%
w
/
w
, on a dry mass basis).
| Microalgae Species | Lipid | Protein | Carbohydrate | References |
|---|
Table 2. Different approaches to enhance lipid and carbohydrate content in the microalgae biomass as well as biomass yield and their outcomes (↑: increase, ↓: decrease, and -: not available).
| Approach | Outcomes | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid | Carbohydrate | Biomass | |||||||
| Botryococcus braunii | 25–75 | 1.5 | 4–55 | [16] | |||||
| Chlorella emersonii | 23–63 | ||||||||
| Nutrient stress | |||||||||
| 36 | 41 | [ | 19 | ] | |||||
| Nitrogen deprivation/starvation | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | [19,[1945]][42] | Chlorella protothecoides | 40–60 | 10–28 | 11–15 | [19] |
| Phosphorus deprivation/starvation | ↑/↓ | -/↓ | ↓ | [19,45][19][42] | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii | 15–18 | 9.2 | 59.7 | [16] |
| Chlorella sorokiniana | 26.2 | ||||||||
| Trace metal availability | ↑/↓ | ↑ | ↑/↓ | [19,46][19][43] | 45.5 | 23.7 | [34][31] | ||
| Chlorella vulgaris | 41–58 | 51–58 | 12–17 | [19] | |||||
| Carbon availability | Dunaliella salina | 6–25 | 57 | 32 | [16] | ||||
| Euglena gracilis | 4–20 | 39–61 | 14–18 | [16] | |||||
| ↑ | - | Isochrysis galbana | 11 | 27 | 34 | [35][32] | |||
| Nannochloropsis gaditana | 23.3 | 48.3 | 9.3 | [20] | |||||
| Nannochloropsis granulata | 24–28 | 27–36 | 18–34 | [35][32] | |||||
| Neochloris oleoabundans | 35–65 | 10–27 | 17–27 | [19] | |||||
| Porphyridium cruentum | 9–14 | 28–39 | 40–57 | [20] | |||||
| Scenedesmus dimorphus | 16–40 | 8–18 | 21–52 | [19] | |||||
| Scenedesmus obliquus | 30–50 | 10–45 | 20–40 | [19] | |||||
| Tetraselmis chuii | 12 | 31–46 | 12 | [35][32] |
| ↑ | ||||
| [ | ||||
| 19 | ||||
| , | ||||
| 47 | ] | [ | 19 | ][44] |
| pH stress | ||||
| Acidic | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | [19,[1948]][45] |
| Alkaline | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | [19,48][19][45] |
| Temperature stress | ||||
| High temperature | ↑/↓ | - | ↑/↓ | [49][46] |
| Low temperature | ↑/↓ | - | ↑/↓ | [49][46] |
| Light stress | ||||
| Low Light | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | ↓ | [50][47] |
| High Light | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | ↑/↓ | [50][47] |
| Saline stress | ↑ | ↑ | ↑/↓ | [19,51][19][48] |
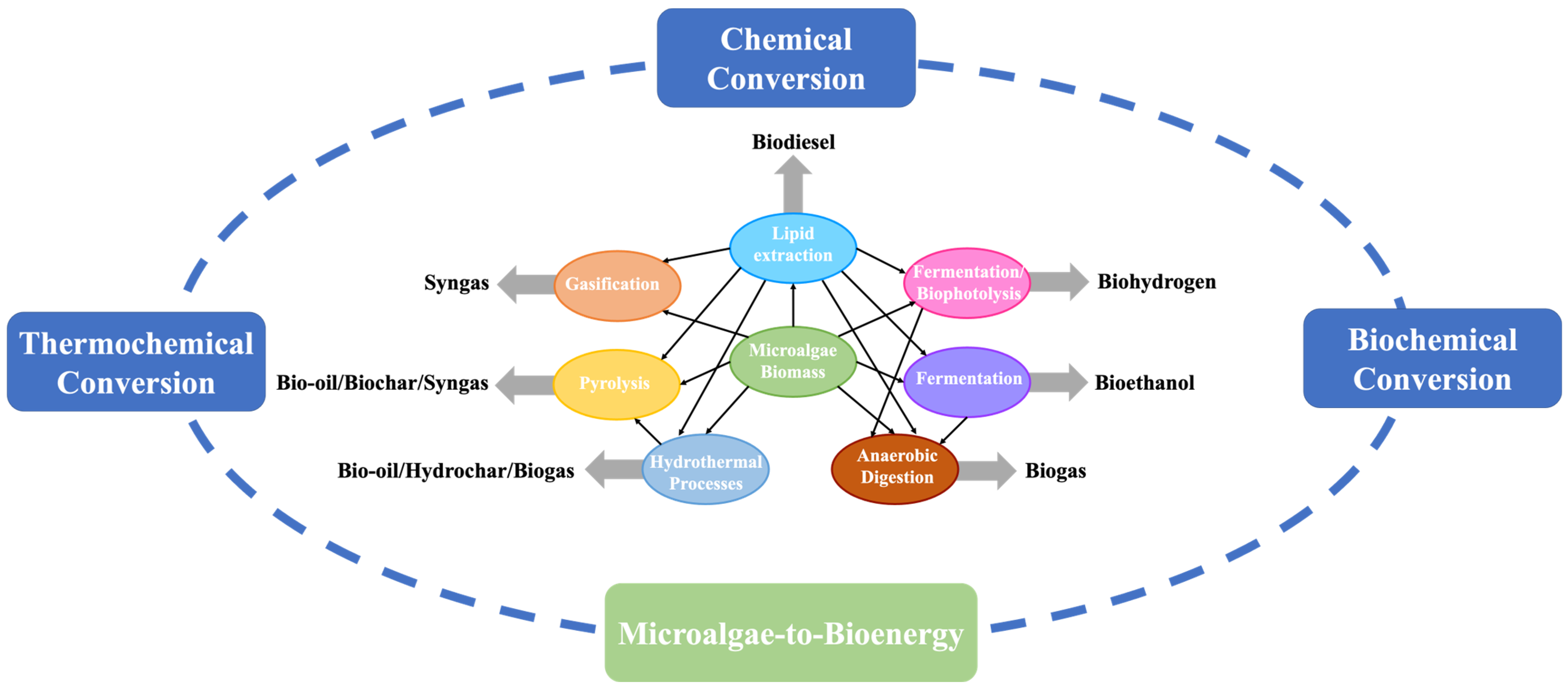
Figure 1.
Different biomass conversion pathways to produce bioenergy from microalgae.
3. Biochemical Conversion
The essential part of the biochemical conversion process is to use microorganisms or enzymes to convert biomass into bioenergy [27]. Biochemical conversion technologies can handle biomass with high water content (>50%) [57][54], making it suitable for processing wet algae biomass. Since drying microalgae biomass is an energy-intensive step [58][55], biochemical conversion technologies are promising for transforming microalgae into bioenergy. The classical biochemical conversion processes include anaerobic digestion for biomethane production, alcoholic fermentation for bioethanol production, and biological hydrogen production.3.1. Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a complex process in which microorganisms degrade organic biomass under anaerobic conditions and convert it into biogas, majorly comprising methane and other products, such as carbon dioxide, trace amounts of hydrogen, and ammonia [59][56]. Biogas produced from the AD process can be directly combusted in gas boilers to generate heat or electricity or upgraded into natural gas-quality biomethane and injected into gas grids [60][57]. AD process consists of four steps, hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis, where each step is led by a unique functional group of microorganisms [61][58]. In the first stage of AD (hydrolysis), existing macromolecules in the biomass, such as proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates, are broken down into simpler molecules, such as amino acids, long-chain fatty acids, and simple sugars, respectively. Hydrolysis is achieved by hydrolytic bacteria, mainly belonging to the phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, secreting a mixture of hydrolytic enzymes comprising cellulase, xylanase, pectinase, amylase, lipase, and protease [62][59]. In the second stage of AD (acidogenesis), hydrolyzed products obtained at the end of the hydrolysis stage are converted into volatile fatty acids, such as acetates, propionate, butyrate, valerate, and isobutyrate, using facultative and obligate anaerobic bacteria species, majorly belonging to the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Chloroflexi, Proteobacteria, and Atribacteria. Alcohol and other inorganic compounds, such as hydrogen, carbon dioxide, ammonia, and hydrogen sulfide, are also produced during the acidogenesis stage [63][60]. During the third stage of AD (acetogenesis), the acidogenesis products, such as propionate, butyrate, isobutyrate, valerate, and isovalerate, are further broken down into acetate as well as hydrogen and carbon dioxide using obligate anaerobic bacteria species, majorly belonging to phyla Firmicutes, Synergistota, and Myxococcota [64][61]. In the final step of AD (methanogenesis), methanogens (a specialized group of archaea belonging to the phyla Euryarchaeota, Bathyarchaeota, and Verstaraeteachaeota) convert acetic acid and hydrogen into methane and carbon dioxide [65][62]. Tuning these four metabolic stages in the AD process can influence final product yields [61][58]. AD is a well-established commercial technology that is currently being applied to a wide range of organic substrates (sewage waste [66][63], food waste [67][64], high-strength organic wastewater [68][65], and agricultural or forest residue [69][66]). Research on anaerobic digestion (AD) of microalgal biomass began in 1957 when microalgae (Chlorella and Scenedesmus) were cultivated for wastewater treatment and subjected to AD for biomethane production [70][67]. However, the resulting biomethane yields were significantly lower due to two main factors: the rigidity of microalgae cell walls and the low carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratio in microalgae biomass. Most microalgae cell walls are rigid, which limits anaerobic microorganisms’ access to biodegradable microalgal organic matter [28][68]. The rigidity of microalgae cell walls can be attributed to components such as hemicellulose, cellulose, glycoprotein structures, and certain carbohydrates (e.g., glucose, xylose, rhamnose, and galactose) [71][69]. Some types of microalgae species also contain algaenan in their outer cell walls. Algaenan is a heteropolymer compound, highly resistant to acidic and basic environments [72][70]. Several studies have reported intact microalgae cells in the AD effluent after a hydraulic retention time of 30–180 days [73[71][72],74], highlighting the recalcitrant nature of microalgal cell walls and their resistance to bacterial degradation during the AD process. Since insufficient biodegradation leads to lower biomethane production, a pretreatment step is necessary to disrupt the microalgae cell walls. Secondly, a C/N ratio of 20–30 (especially 25) is recommended for the optimal functioning of the AD process [75][73]. If the ratio falls below 20, high amounts of ammonia-nitrogen are released in the anaerobic digester due to the imbalance between microbial carbon and nitrogen requirements. Ammonia buildup can inhibit methanogen growth, leading to volatile fatty acid (VFA) accumulation and process failure [76][74]. However, the C/N ratio in microalgae biomass is usually between 4–8 [33][30]. To address the low C/N ratio in microalgae, several researchers have suggested co-digesting microalgae biomass with other biomass streams with a high C/N content [77][75]. Various biomass pretreatment and co-digestion technologies have been developed in the past decade to improve biomethane production from microalgae biomass.3.2. Biohydrogen Production
Biohydrogen is considered the fuel of the future due to its higher heating value (142 kJ/g) and ability to produce energy without emitting carbon dioxide [124][76]. It can be used in fuel cells to generate electricity and as a fuel for automobiles, providing a carbon-neutral solution to current energy crises [125][77]. To tap into the potential of biohydrogen as a future fuel, microalgae have emerged as a promising source for its production. Microalgae can produce biohydrogen through two different pathways: bio-photolysis and fermentation. During biophotolysis, microalgae cells act as a biocatalyst to directly produce biohydrogen, whereas in fermentation, microalgae biomass serves as a feedstock for biohydrogen-producing microorganisms [126][78].3.3. Alcoholic Fermentation
Bioethanol is the most extensively used renewable fuel for transportation and can be produced from microalgae using three pathways: dark fermentation (DF), photo fermentation (PF), and traditional fermentation (TF) [181][79]. Although DF and PF are similar process terminologies used to depict alcoholic fermentation and biohydrogen production pathways, the mechanisms involved in these pathways are different. Some examples of DF, PF, and TF for bioethanol production are listed in Table 83 and Table 94. In the DF process, microalgae species, such as Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlamydomonas moewusii, Chlorococcum littorale, Chlorogonium elongatum, and Chlorella fusca, ferment intracellular polysaccharides into bioethanol under dark and anaerobic conditions [182,183,184][80][81][82]. Pyruvate, an intermediate compound, is generated through hydrolysis and glycolysis of intracellular polysaccharides (starch). Subsequently, pyruvate is converted into various end products, including acetate, ethanol, formate, glycerol, lactate, biohydrogen, and carbon dioxide, depending on the type of microalgae species and surrounding environmental conditions [185][83]. Studies on microalgae DF for bioethanol production reported low bioethanol yields of less than 2% w/w, as shown in Table 83. This could be attributed to the complex network of metabolic pathways involved in microalgal DF and difficulties associated with understanding and selectively manipulating those metabolic pathways to enhance bioethanol production. Therefore, the practical application of the DF pathway for bioethanol production has not received much attention. Compared to the DF pathway, the PF pathway results in a more specific and efficient bioethanol production [186][84]. The PF pathway comprises two steps: photosynthesis and fermentation. During the first step of photosynthesis, inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide) is fixed into organic carbon (phosphoglycerate) through the Calvin cycle and later converted to pyruvate. In the second step, pyruvate is fermented into ethanol with the help of two key enzymes, pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase II (adhII). pdc catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate into acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide through a nonoxidative decarboxylation reaction, whereas adhII oxidizes the resulting acetaldehyde into ethanol [187][85]. However, these enzymes are naturally missing or expressed in insufficient quantities in microalgae. Therefore, genetic engineering is used to heterologously express pdc and adhII genes in microalgae, preferably cyanobacteria, to enable direct bioethanol production [188][86]. Cyanobacteria have relatively well-characterized genetic backgrounds, demonstrate a high tolerance to foreign gene introduction, and exhibit amenability to genetic modifications [189][87]. Foreign DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) can be introduced into cyanobacteria under controlled conditions through shuttle vectors or by directly integrating it into the chromosome via targeted homologous recombination. A research study by Deng and Coleman [190][88] was the first to report the cyanobacteria Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942 strain as the platform of bioethanol production. The authors constructed a new S. elongatus strain using a shuttle vector pCB4, cloned from the coding sequences of pdc and adhII genes obtained from the bacterium Zymomonas mobilis. Following four weeks of culture, the transformed S. elongatus strain produced a bioethanol titer of 0.23 g/L. Later, Dexter and Fu [191][89] used the same two genes from Z. mobilis and integrated them into the chromosome of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 using a double homologous recombination system and produced a bioethanol titer of 0.46 g/L in six days of cultivation. Since then, several genetic engineering efforts have been made to improve the bioethanol yield from cyanobacteria while maintaining cell growth (Table 83). However, PF pathways produce much lower bioethanol yields (<6 g/L), making the ethanol separation process (distillation) too costly for large-scale applications. Poor bioethanol yields could be attributed to co-factor imbalance [192][90], low ethanol tolerance levels [193][91], competition for carbon usage between biomass synthesis and target product formation [194][92], and inefficient carbon fixation mechanisms [195,196][93][94]. However, there is still room for optimizing the bioethanol yield from cyanobacteria through alternate gene expression approaches.Table 83.
Dark fermentation and photo fermentation for microalgae-based bioethanol production.
| Dark Fermentation | |||||
| Microalgae Species |
Operating Conditions |
Starch Content (% of Dry Cell Weight) |
% Starch Decomposed |
Bioethanol Yield (% of Dry Cell Weight) |
References |
| Chlamydomonas reinhardtii UTEX 2247 | Incubation under dark and anaerobic conditions at 25 °C for 46 h Slurry concentration: 15% w/w |
45 | NA | 1 | [182][80] |
| Chlamydomonas sp. YA-SH-1 | Incubation under dark and anaerobic conditions at 30–35 °C for 44 h Slurry concentration: 15–25% w/w |
30 | NA | 1.3 | [183][81] |
| Chlorococcum littorale | Incubation under dark and anaerobic conditions at 30 °C for 24 h Slurry concentration: 1.4% w/w |
15 | 46 | 1.6 | [184][82] |
| Photo Fermentation | |||||
| Cyanobacteria | Genes expressed (source of genes) and their expression mechanism | Promotor used | Gene deletion (Effect) |
Bioethanol titer (g/L) and days of cultivation (d) |
Reference |
| Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942 | pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adhII (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector |
rbcLS | NA | 0.23 in 28 d | [190][88] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 |
pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Homologous recombination; adhII (Zymomonas mobilis), Homologous recombination |
psbA2 | NA | 0.46 in 6 d | [191][89] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 |
pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Homologous recombination; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous overexpression), Homologous recombination |
Prbc | phaA and phaB (Disrupting PHB biosynthesis pathway) |
5.5 in 26 d | [197][95] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 |
pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Homologous recombination; adhII (Zymomonas mobilis), Homologous recombination |
nblA | glgC (Disrupting glycogen biosynthesis pathway) and phaC + phaE (Disrupting PHB biosynthesis pathway) |
3 in 3 d | [194][92] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 |
zwf (Endogenous overexpression to enhance NADPH production) Homologous recombination; pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Homologous recombination; yqhD, NADPH-dependent adh (Escherichia coli), Homologous recombination |
Pcpc560 | NA | 0.59 in 14 d | [192][90] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 |
pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous), Shuttle vector |
PnrsB | NA | 0.45 in 7 d | [196][94] |
| pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous), Shuttle vector; rbcSC, slr0009-slr0011-slr0012-FLAG with RuBisCO-encoding genes (Endogenous), Shuttle vector |
PnrsB (for pdc and adh) and psbA2 (for rbcSC, 70glpX, tktA, and fbaA) | 0.7 in 7 d | |||
| pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous), Shuttle vector; 70glpX with FBP/SBPase-encoding genes (Synechococcus PCC 7002), Shuttle vector |
0.75 in 7 d | ||||
| pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous), Shuttle vector; tktA, sll1070 with TK-encoding genes (Endogenous), Shuttle vector |
0.6 in 7 d | ||||
| pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous), Shuttle vector; fbaA, sll0018 with FBA-encoding genes (Endogenous), Shuttle vector |
0.75 in 7 d | ||||
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 |
pdc (Zymomonas mobilis), Shuttle vector; adh, slr1192 (Endogenous), Shuttle vector; fbaA, sll0018 with FBA-encoding genes (Endogenous), Shuttle vector; tktA, sll1070 with TK-encoding genes (Endogenous), Shuttle vector |
PnrsB (for pdc and adh) and psbA2 (for tktA and fbaA) | NA | 1.2 in 20 d | [195][93] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 (Fe2O3-treated culture) |
pdc (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), Shuttle vector; adh (Endogenous), Shuttle vector |
psbA1 | NA | 4.9 in 25 d | [198][96] |
| Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 (MgO-treated culture) | 5.1 in 25 d | ||||
Note: NA—not applicable, NADPH—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, pdc—pyruvate decarboxylase, adh—alcohol dehydrogenase, phaA—polyhydroxyalkanoate-specific β-ketothiolase, phaB—polyhydroxyalkanoate-specific acetoacetyl-CoA reductase, PHB—polyhydroxybutyrate, glgC—glucose-1-phosphate adenylyltransferase, phaC—polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, phaE—polyhydroxyalkanoate polymerase subunit, zwf—glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase, RuBisCO (rbcSC)—ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, FBA (fbaA)—Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase, FBP/SBPase (70glpX)—fructose-1,6-/sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase, TK (tktA)—transketolase.
Traditional fermentation has been the most widely studied method of bioethanol production, as it typically yields higher bioethanol quantities (21–88% w/w (% of dry cell weight) and 5–43 g/L (based on the working volume)) compared to DF (<2% w/w) and PF (<6 g/L) (Table 83 and Table 94). In the traditional fermentation process, the carbohydrate content of microalgae biomass is used as a feedstock by ethanologenic microorganisms, such as yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and bacteria (Zymomonas mobilis). However, S. cerevisiae is more commonly used for bioethanol fermentation due to its tolerance towards low pH and high ethanol concentrations [199][97]. As described earlier in Section 3.1, microalgae biomass pretreatment is crucial before fermentation for easy access to intracellular microalgal compounds. Various biomass pretreatment methods are discussed in detail in Section 3.1.1Section 3.1.1 of original paper, and the effects on bioethanol production have been summarized in Table 94. Shokrkar et al. [200][98] compared the effect of acidic and enzymatic pretreatments on the bioethanol production performance of a mixed microalgae culture and reported a 1.3 times higher bioethanol production when microalgae culture was pretreated with enzymes. De Farias Silva et al. [201][99] observed no significant variations between the acidic and enzymatic pretreatments for Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus obliquus biomass. Another study demonstrated an alternate approach for bioethanol production without any acidic or enzymatic pretreatments [202][100]. The authors combined the extraction and fermentation process in which a lysozyme and calcium chloride mixture was used to extract glycogen from Arthrospira platensis. Extracted glycogen was simultaneously degraded to glucose with the help of a recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae culture, which produced alpha-amylase and glucoamylase. However, such an approach can only work for cyanobacteria, which lack robust cell wall structure. The examples listed in Table 94 confirm that the effectiveness of microalgae pretreatment varies depending on the species.
The traditional fermentation process can be divided into two groups: separate hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) [203][101]. During SHF, hydrolysis and fermentation processes are conducted separately in different reactors, whereas, during SSF, hydrolysis and fermentation processes proceed simultaneously in the same reactor. The main advantage of the SHF process is the possibility to separately optimize the operating conditions of the hydrolysis and fermentation processes. El-Mekkawi et al. [21] used the response surface method (RSM) during SHF to optimize the process variables, such as algal biomass, yeast loading, and fermentation time, achieving a higher bioethanol concentration of 19 g/L. Other advantages of the SHF process are the potential use of cheaper chemicals, shorter residence time, and easy operation. However, its high capital cost is moving the research direction toward SSF. Kim et al. [204][102] compared the effect of SHF and SSF on bioethanol production from Phorphydium cruentum and observed that SSF produced slightly better bioethanol yields (74–80%) over SHF (70–78%). Similarly, Megawati et al. [205][103] observed a slightly better bioethanol production result with SSF (48.5%) compared to SHF (46%). Although most of the bioethanol production studies have used a single strain of yeast to study the fermentation process, some studies have applied a co-fermentation approach in which two or more different strains of yeast are used with a capacity to simultaneously degrade pentose and hexose sugar [201][99]. However, using a combination of different yeast strains would still require careful and thorough investigation.
Table 94.
Pretreatment of microalgae biomass for bioethanol production through traditional fermentation.
| Microalgae Species |
Pretreatment | Fermentation Microorganisms |
Fermentation Operating Conditions |
Bioethanol Concentration (g/L) and Yield (% of Dry Cell Weight) |
References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Separate hydrolysis and fermentation | |||||
| Carotenoid-free Chromochloris zofingiensis SAG 211-14 | Autoclave (120 °C for 0.34 h) followed by two-stage enzymatic pretreatment with α-Amylase (90 °C, 2 h, 4.5 pH) and glucoamylase (60 °C, 22 h, 6.5 pH) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCUG 53310 | Initial pH: 4.8 Inoculum size: NA Temperature: 37 °C Time: |
25 ± 2% | [206][104] |
| Autoclave (120 °C for 0.34 h) followed by three-stage enzymatic pretreatment with Cellic Ctec2 and Cellic Htec2 (45 °C, 48 h, 5 pH), α-Amylase (90 °C, 2 h, 5 pH) and glucoamylase (60 °C, 22 h, 5 pH) | 62 ± 2% | ||||
| Carotenoid-free Haematococcus pluvialis SAG 192.80 |
Autoclave (120 °C for 0.34 h) followed by two-stage enzymatic pretreatment with α-Amylase (90 °C, 2 h, 4.5 pH) and glucoamylase (60 °C, 22 h, 6.5 pH) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCUG 53310 | Initial pH: 4.8 Inoculum size: NA Temperature: 37 °C Time: |
35 ± 0.3% | [207][105] |
| Autoclave (120 °C for 0.34 h) followed by three-stage enzymatic pretreatment with Cellic Ctec2 and Cellic Htec2 (45 °C, 49 h, 5 pH), α-Amylase (90 °C, 2 h, 5 pH) and glucoamylase (60 °C, 22 h, 5 pH) | 88.1 ± 0.5% | ||||
| Chlorella vulgaris | 1 N HCl, 90 °C, 1 h | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Initial pH: 5 Inoculum size: 3% v/v Temperature: 30 °C Time: |
46% | [205][103] |
| Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E | 2% H2SO4, 121 °C, 0.34 h | Saccharomyces cerevisiae FAY-1 |
Initial pH: NA Inoculum size: NA Temperature: 30 °C |
21% (43 g/L) | [208][106] |
| Mixed microalgae consortium | 0.5 M H2SO4 and 2.5% (w/v) MgSO4 at 121 °C, 0.67 h | Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC 7921 |
Initial pH: 6.5 Inoculum size: 3% v/v Temperature: 30 °C |
5 g/L | [200][98] |
| Three-stage enzymatic pretreatment with β-glucosidase/cellulase (65 °C, 3 h), α-amylase (95 °C, 3 h) and amyloglucosidase (55 °C, 3 h) | 6.4 g/L | ||||
| Arthrospira platensis NIES-39 | 1 g/L lysozyme and 100 mM CaCl2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain BY4741 AASS/GASS |
Initial pH: 5.2–5.4 Inoculum size: 5% v/v Temperature: 38–40 °C |
32% | [202][100] |
| Wastewater-grown microalgae biomass dominated by Microcystis | 0.5 N H2SO4, 120 °C, 4 h | Immobilized Saccharomyces cereviciae ATCC 4126 |
Initial pH: 4.5 Inoculum size: 15% v/v Temperature: 30 °C |
19 g/L | [21] |
| Porphyridium cruentum KMMCC-1061 | One-stage enzymatic hydrolysis with pectinase and cellulase (37 °C, 7 h, 4.8 pH) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae KCTC 7906 | Initial pH: 4.5 Inoculum size: 0.1% w/v Temperature: 37 °C |
70–78% (based on initial glucose content) | [204][102] |
| Simultaneous Saccharification and Fermentation | |||||
| Chlorella vulgaris | Two-stage enzymatic pretreatment with α-Amylase (90 °C, 6 pH) and glucoamylase (80 °C, 5 h, 6 pH) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Initial pH: 5 Inoculum size: 3% v/v Temperature: 30 °C |
49% | [205][103] |
| Porphyridium cruentum KMMCC-1061 | One-stage enzymatic hydrolysis with pectinase and cellulase (37 °C, 10 h, 4.8 pH) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae KCTC 7906 | Initial pH: 4.5 Inoculum size: 0.1% w/v Temperature: 37 °C |
74–80% (based on initial glucose content) | [204][102] |
| Co-fermentation | |||||
| Dried and milled Chlorella vulgaris biomass powder Neoalgae® (Micro seaweed products B-52501749). | 3% H2SO4, 120 °C, 0.5 h | 75% Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cameo S.p.A. and 25% Pichia stipitis ATCC 58, 785 | Initial pH: 5–6 Inoculum size: 7.5 g/L Temperature: 30 °C |
49 ± 5% | [201][99] |
| One-stage enzymatic hydrolysis with Viscozyme® L, AMG 300 L, and Pectinex Ultra SP-L (50 °C, 4 h, 5 pH) | 49 ± 0.5% | ||||
| Scenedesmus obliquus SAG 276.7 |
3% H2SO4, 120 °C, 0.5 h | 87 ± 6% | |||
| Ultrasonication followed by One-stage enzymatic hydrolysis with Viscozyme® L, AMG 300 L, and Pectinex Ultra SP-L (50 °C, 8 h, 5 pH) | 41 ± 1.5% | ||||
Note: NA—Not available.
References
- Yilanci, V.; Haouas, I.; Ozgur, O.; Sarkodie, S.A. Energy diversification and economic development in emergent countries: Evidence from fourier function-driven bootstrap panel causality test. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 632712.
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2022; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022.
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Gregor, L.; Hauck, J.; Le Quéré, C.; Luijkx, I.T.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2022. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4811–4900.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). International Energy Outlook 2021 Narrative; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2021.
- Al-Bawwat, A.a.K.; Jurado, F.; Gomaa, M.R.; Cano, A. Availability and the possibility of employing wastes and biomass materials energy in Jordan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5879.
- Yadav, K.K.; Krishnan, S.; Gupta, N.; Prasad, S.; Amin, M.A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Sharma, G.K.; Marzouki, R.; Jeon, B.-H.; Kumar, S.; et al. Review on evaluation of renewable bioenergy potential for sustainable development: Bright future in energy practice in India. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 16007–16030.
- Wang, Y.; Guan, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, X. Biomass energy consumption and carbon neutrality in OECD countries: Testing pollution haven hypothesis and environmental Kuznets curve. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1691.
- Duarah, P.; Haldar, D.; Patel, A.K.; Dong, C.-D.; Singhania, R.R.; Purkait, M.K. A review on global perspectives of sustainable development in bioenergy generation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 348, 126791.
- Al-Bawwat, A.a.K.; Cano, A.; Gomaa, M.R.; Jurado, F. Availability of biomass and potential of nanotechnologies for bioenergy production in Jordan. Processes 2023, 11, 992.
- Maliha, A.; Abu-Hijleh, B. A review on the current status and post-pandemic prospects of third-generation biofuels. Energy Syst. 2022, 1–32.
- Malode, S.J.; Prabhu, K.K.; Mascarenhas, R.J.; Shetti, N.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances and viability in biofuel production. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 10, 100070.
- International Energy Agency. Renewables 2022: Analysis and Forecast to 2027; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022.
- Ahmed, S.; Warne, T.; Smith, E.; Goemann, H.; Linse, G.; Greenwood, M.; Kedziora, J.; Sapp, M.; Kraner, D.; Roemer, K.; et al. Systematic review on effects of bioenergy from edible versus inedible feedstocks on food security. NPJ. Sci. Food 2021, 5, 9.
- Jeswani, H.K.; Chilvers, A.; Azapagic, A. Environmental sustainability of biofuels: A review. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 476, 20200351.
- Olabi, A.G.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Rodriguez, C.; Anyanwu, R.C.; Russell, C.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Role of microalgae in achieving sustainable development goals and circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158689.
- Elalami, D.; Oukarroum, A.; Barakat, A. Anaerobic digestion and agronomic applications of microalgae for its sustainable valorization. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26444–26462.
- Sharma, P.K.; Saharia, M.; Srivstava, R.; Kumar, S.; Sahoo, L. Tailoring microalgae for efficient biofuel production. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 382.
- Parakh, S.K.; Praveen, P.; Loh, K.C.; Tong, Y.W. Integrating gravity settler with an algal membrane photobioreactor for in situ biomass concentration and harvesting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123822.
- Sajjadi, B.; Chen, W.-Y.; Raman, A.A.A.; Ibrahim, S. Microalgae lipid and biomass for biofuel production: A comprehensive review on lipid enhancement strategies and their effects on fatty acid composition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 200–232.
- Zabed, H.M.; Akter, S.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, X. Biogas from microalgae: Technologies, challenges and opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 117, 109503.
- El-Mekkawi, S.A.; Abdo, S.M.; Samhan, F.A.; Ali, G.H. Optimization of some fermentation conditions for bioethanol production from microalgae using response surface method. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 164.
- Ahmed, S.F.; Rafa, N.; Mofijur, M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Inayat, A.; Ali, M.S.; Farrok, O.; Yunus Khan, T.M. Biohydrogen production from biomass sources: Metabolic pathways and economic analysis. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 753878.
- Mustapha, S.I.; Mohammed, U.A.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F.; Isa, Y.M. Production of high-quality pyrolytic bio-oils from nutrient-stressed Scenedesmus obliquus microalgae. Fuel 2023, 332, 126299.
- Raheem, A.; Abbasi, S.A.; Mangi, F.H.; Ahmed, S.; He, Q.; Ding, L.; Memon, A.A.; Zhao, M.; Yu, G. Gasification of algal residue for synthesis gas production. Algal. Res. 2021, 58, 102411.
- Shahi, T.; Beheshti, B.; Zenouzi, A.; Almasi, M. Bio-oil production from residual biomass of microalgae after lipid extraction: The case of Dunaliella sp. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101494.
- Gomaa, M.R.; Mustafa, R.J.; Al-Dmour, N. Solar thermochemical conversion of carbonaceous materials into syngas by Co-Gasification. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 248, 119185.
- Hossain, S.M.Z. Biochemical conversion of microalgae biomass into biofuel. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 2594–2607.
- Parakh, S.K.; Praveen, P.; Loh, K.-C.; Tong, Y.W. Wastewater treatment and microbial community dynamics in a sequencing batch reactor operating under photosynthetic aeration. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 893–903.
- Niccolai, A.; Chini Zittelli, G.; Rodolfi, L.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R. Microalgae of interest as food source: Biochemical composition and digestibility. Algal. Res. 2019, 42, 101617.
- Parakh, S.K. Enhancing the Sustainability of Microalgae Production through Novel Photobioreactor Engineering and Harvesting Strategies; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2019.
- Córdova, O.; Passos, F.; Chamy, R. Physical pretreatment methods for improving microalgae anaerobic biodegradability. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 114–126.
- Barkia, I.; Saari, N.; Manning, S.R. Microalgae for high-value products towards human health and nutrition. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 304.
- Alishah Aratboni, H.; Rafiei, N.; Garcia-Granados, R.; Alemzadeh, A.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Biomass and lipid induction strategies in microalgae for biofuel production and other applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 178.
- Arif, M.; Bai, Y.; Usman, M.; Jalalah, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Al-Assiri, M.S.; Li, X.; Salama, E.-S.; Zhang, C. Highest accumulated microalgal lipids (polar and non-polar) for biodiesel production with advanced wastewater treatment: Role of lipidomics. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122299.
- Mimouni, V.; Couzinet-Mossion, A.; Ulmann, L.; Wielgosz-Collin, G. Chapter 5-Lipids from microalgae. In Microalgae in Health and Disease Prevention; Levine, I.A., Fleurence, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 109–131.
- Chhandama, M.V.L.; Satyan, K.B.; Changmai, B.; Vanlalveni, C.; Rokhum, S.L. Microalgae as a feedstock for the production of biodiesel: A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100771.
- Bligh, M.; Nguyen, N.; Buck-Wiese, H.; Vidal-Melgosa, S.; Hehemann, J.-H. Structures and functions of algal glycans shape their capacity to sequester carbon in the ocean. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2022, 71, 102204.
- Udayan, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Sirohi, R.; Sreekumar, N.; Sang, B.-I.; Sim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Pandey, A. Production of microalgae with high lipid content and their potential as sources of nutraceuticals. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 1–28.
- de Carvalho Silvello, M.A.; Severo Gonçalves, I.; Patrícia Held Azambuja, S.; Silva Costa, S.; Garcia Pereira Silva, P.; Oliveira Santos, L.; Goldbeck, R. Microalgae-based carbohydrates: A green innovative source of bioenergy. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126304.
- Bruce, A.; Heald, R.; Johnson, A.; Morgan, D.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 7th ed.; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- de Oliveira, M.C.; Bassin, I.D.; Cammarota, M.C. Microalgae and cyanobacteria biomass pretreatment methods: A comparative analysis of chemical and thermochemical pretreatment methods aimed at methane production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 497.
- Shokravi, Z.; Shokravi, H.; Chyuan, O.H.; Lau, W.J.; Koloor, S.S.R.; Petrů, M.; Ismail, A.F. Improving ‘lipid productivity’ in microalgae by bilateral enhancement of biomass and lipid contents: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9083.
- Zaparoli, M.; Ziemniczak, F.G.; Mantovani, L.; Costa, J.A.V.; Colla, L.M. Cellular stress conditions as a strategy to increase carbohydrate productivity in Spirulina platensis. BioEnergy Res. 2020, 13, 1221–1234.
- Ghosh, A.; Sarkar, S.; Gayen, K.; Bhowmick, T.K. Effects of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus supplements on growth and biochemical composition of Podohedriella sp. (MCC44) isolated from northeast India. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, e13378.
- Bibi, F.; Yasmin, H.; Jamal, A.; Al-Harbi, M.S.; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Ahmad, B.; Samra, B.N.; Ahmed, A.F.; Ali, M.I. Deciphering role of technical bioprocess parameters for bioethanol production using microalgae. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7595–7606.
- Jaiswal, K.K.; Banerjee, I.; Singh, D.; Sajwan, P.; Chhetri, V. Ecological stress stimulus to improve microalgae biofuel generation: A review. Octa. J. Biosci. 2020, 8, 48–54.
- Nzayisenga, J.C.; Farge, X.; Groll, S.L.; Sellstedt, A. Effects of light intensity on growth and lipid production in microalgae grown in wastewater. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 4.
- Yun, C.-J.; Hwang, K.-O.; Han, S.-S.; Ri, H.-G. The effect of salinity stress on the biofuel production potential of freshwater microalgae Chlorella vulgaris YH703. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 127, 105277.
- Choudhary, S.; Tripathi, S.; Poluri, K.M. Microalgal-based bioenergy: Strategies, prospects, and sustainability. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 14584–14612.
- Shin, Y.S.; Jeong, J.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; Kim, J.Y.H.; Jin, E.; Sim, S.J. Targeted knockout of phospholipase A2 to increase lipid productivity in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 368–374.
- Muñoz, C.F.; Weusthuis, R.A.; D’Adamo, S.; Wijffels, R.H. Effect of single and combined expression of lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, and diacylglycerol acyltransferase on lipid accumulation and composition in Neochloris oleoabundans. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1573.
- Brar, A.; Kumar, M.; Soni, T.; Vivekanand, V.; Pareek, N. Insights into the genetic and metabolic engineering approaches to enhance the competence of microalgae as biofuel resource: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125597.
- Olguín, E.J.; Sánchez-Galván, G.; Arias-Olguín, I.I.; Melo, F.J.; González-Portela, R.E.; Cruz, L.; De Philippis, R.; Adessi, A. Microalgae-based biorefineries: Challenges and future trends to produce carbohydrate enriched biomass, high-added value products and bioactive compounds. Biology 2022, 11, 1146.
- Paul, R.; Silkina, A.; Melville, L.; Suhartini, S.; Sulu, M. Optimization of ultrasound pretreatment of microalgal biomass for effective biogas production through anaerobic digestion process. Energies 2023, 16, 553.
- Schmid, B.; Navalho, S.; Schulze, P.S.C.; Van De Walle, S.; Van Royen, G.; Schüler, L.M.; Maia, I.B.; Bastos, C.R.V.; Baune, M.-C.; Januschewski, E.; et al. Drying microalgae using an industrial solar dryer: A biomass quality assessment. Foods 2022, 11, 1873.
- Workie, E.; Kumar, V.; Bhatnagar, A.; He, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wah Tong, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C. Advancing the bioconversion process of food waste into methane: A systematic review. Waste Manag. 2023, 156, 187–197.
- Abanades, S.; Abbaspour, H.; Ahmadi, A.; Das, B.; Ehyaei, M.A.; Esmaeilion, F.; El Haj Assad, M.; Hajilounezhad, T.; Jamali, D.H.; Hmida, A.; et al. A critical review of biogas production and usage with legislations framework across the globe. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 3377–3400.
- Richard, E.N.; Hilonga, A.; Machunda, R.L.; Njau, K.N. A review on strategies to optimize metabolic stages of anaerobic digestion of municipal solid wastes towards enhanced resources recovery. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 36.
- Lim, J.W.; Park, T.; Tong, Y.W.; Yu, Z. Chapter One: The microbiome driving anaerobic digestion and microbial analysis. In Advances in Bioenergy; Li, Y., Khanal, S.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 5, pp. 1–61.
- Zhang, L.; Yan, M.; Tsui, T.-H.; Lee, J.T.E.; Loh, K.-C.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y.W. Chapter 16-Functional microbial characteristics in acidogenic fermenters of organic wastes for production of volatile fatty acids. In Biomass, Biofuels, Biochemicals; Pandey, A., Tong, Y.W., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 367–394.
- Detman, A.; Bucha, M.; Treu, L.; Chojnacka, A.; Pleśniak, Ł.; Salamon, A.; Łupikasza, E.; Gromadka, R.; Gawor, J.; Gromadka, A.; et al. Evaluation of acidogenesis products’ effect on biogas production performed with metagenomics and isotopic approaches. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 125.
- Meegoda, J.N.; Li, B.; Patel, K.; Wang, L.B. A review of the processes, parameters, and optimization of anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2224.
- Nguyen, P.-D.; Tran, N.-S.T.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Dang, B.-T.; Le, M.-T.T.; Bui, X.-T.; Mukai, F.; Kobayashi, H.; Ngo, H.H. Long-term operation of the pilot scale two-stage anaerobic digestion of municipal biowaste in Ho Chi Minh City. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142562.
- Tiong, Y.W.; Sharma, P.; Tian, H.; Tsui, T.-H.; Lam, H.T.; Tong, Y.W. Startup performance and microbial communities of a decentralized anaerobic digestion of food waste. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137937.
- Paulo, L.M.; Castilla-Archilla, J.; Ramiro-Garcia, J.; Escamez-Picón, J.A.; Hughes, D.; Mahony, T.; Murray, M.; Wilmes, P.; O’Flaherty, V. Microbial community redundancy and resilience underpins high-rate anaerobic treatment of dairy-processing wastewater at ambient temperatures. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 192.
- Heitkamp, K.; Latorre-Pérez, A.; Nefigmann, S.; Gimeno-Valero, H.; Vilanova, C.; Jahmad, E.; Abendroth, C. Monitoring of seven industrial anaerobic digesters supplied with biochar. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 185.
- Golueke, C.G.; Oswald, W.J.; Gotaas, H.B. Anaerobic digestion of algae. Appl. Microbiol. 1957, 5, 47–55.
- Magdalena, J.A.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernandez, C. Efficient anaerobic digestion of microalgae biomass: Proteins as a key macromolecule. Molecules 2018, 23, 1098.
- Machado, L.; Carvalho, G.; Pereira, R.N. Effects of innovative processing methods on microalgae cell wall: Prospects towards digestibility of protein-rich biomass. Biomass 2022, 2, 80–102.
- Dunker, S.; Wilhelm, C. Cell wall structure of coccoid green algae as an important trade-off between biotic interference mechanisms and multidimensional cell growth. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 719.
- Mussgnug, J.H.; Klassen, V.; Schlüter, A.; Kruse, O. Microalgae as substrates for fermentative biogas production in a combined biorefinery concept. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 51–56.
- Ras, M.; Lardon, L.; Bruno, S.; Bernet, N.; Steyer, J.-P. Experimental study on a coupled process of production and anaerobic digestion of Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 200–206.
- Tg, I.; Haq, I.; Kalamdhad, A.S. 14-Factors affecting anaerobic digestion for biogas production: A review. In Advanced Organic Waste Management; Hussain, C., Hait, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 223–233.
- Shahbaz, M.; Ammar, M.; Korai, R.M.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, A.; Khalid, M.S.; Zou, D.; Li, X. Impact of C/N ratios and organic loading rates of paper, cardboard and tissue wastes in batch and CSTR anaerobic digestion with food waste on their biogas production and digester stability. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1436.
- Solé-Bundó, M.; Passos, F.; Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Ferrer, I.; Astals, S. Co-digestion strategies to enhance microalgae anaerobic digestion: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 471–482.
- Nagarajan, D.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Pretreatment of microalgal biomass for efficient biohydrogen production–Recent insights and future perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122871.
- Anwar, M.; Lou, S.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Hu, Z. Recent advancement and strategy on bio-hydrogen production from photosynthetic microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121972.
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q.; Chang, J.-S.; Ho, S.-H. Biohydrogen production from microalgae for environmental sustainability. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132717.
- Lakatos, G.E.; Ranglová, K.; Manoel, J.C.; Grivalský, T.; Kopecký, J.; Masojídek, J. Bioethanol production from microalgae polysaccharides. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 627–644.
- Hirano, A.; Ueda, R.; Hirayama, S.; Ogushi, Y. CO2 fixation and ethanol production with microalgal photosynthesis and intracellular anaerobic fermentation. Energy 1997, 22, 137–142.
- Hirayama, S.; Ueda, R.; Ogushi, Y.; Hirano, A.; Samejima, Y.; Hon-Nami, K.; Kunito, S. Ethanol production from carbon dioxide by fermentative microalgae. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Inui, T., Anpo, M., Izui, K., Yanagida, S., Yamaguchi, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 114, pp. 657–660.
- Ueno, Y.; Kurano, N.; Miyachi, S. Ethanol production by dark fermentation in the marine green alga, Chlorococcum littorale. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1998, 86, 38–43.
- de Farias Silva, C.E.; Bertucco, A. Bioethanol from microalgae and cyanobacteria: A review and technological outlook. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1833–1842.
- Gundolf, R.; Oberleitner, S.; Richter, J. Evaluation of new genetic toolkits and their role for ethanol production in cyanobacteria. Energies 2019, 12, 3515.
- Mund, N.K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Advances in metabolic engineering of cyanobacteria for production of biofuels. Fuel 2022, 322, 124117.
- Kopka, J.; Schmidt, S.; Dethloff, F.; Pade, N.; Berendt, S.; Schottkowski, M.; Martin, N.; Dühring, U.; Kuchmina, E.; Enke, H.; et al. Systems analysis of ethanol production in the genetically engineered cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 56.
- Chou, H.-H.; Su, H.-Y.; Chow, T.-J.; Lee, T.-M.; Cheng, W.-H.; Chang, J.-S.; Chen, H.-J. Engineering cyanobacteria with enhanced growth in simulated flue gases for high-yield bioethanol production. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 165, 107823.
- Deng, M.-D.; Coleman John, R. Ethanol synthesis by genetic engineering in cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 523–528.
- Dexter, J.; Fu, P. Metabolic engineering of cyanobacteria for ethanol production. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 857–864.
- Choi, Y.-N.; Park, J.M. Enhancing biomass and ethanol production by increasing NADPH production in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 213, 54–57.
- Lopes da Silva, T.; Passarinho, P.C.; Galriça, R.; Zenóglio, A.; Armshaw, P.; Pembroke, J.T.; Sheahan, C.; Reis, A.; Gírio, F. Evaluation of the ethanol tolerance for wild and mutant Synechocystis strains by flow cytometry. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 17, 137–147.
- Namakoshi, K.; Nakajima, T.; Yoshikawa, K.; Toya, Y.; Shimizu, H. Combinatorial deletions of glgC and phaCE enhance ethanol production in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 239, 13–19.
- Roussou, S.; Albergati, A.; Liang, F.; Lindblad, P. Engineered cyanobacteria with additional overexpression of selected Calvin-Benson-Bassham enzymes show further increased ethanol production. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2021, 12, e00161.
- Liang, F.; Englund, E.; Lindberg, P.; Lindblad, P. Engineered cyanobacteria with enhanced growth show increased ethanol production and higher biofuel to biomass ratio. Metab. Eng. 2018, 46, 51–59.
- Gao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Lu, X. Photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide in genetically engineered cyanobacteria. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9857–9865.
- Velmurugan, R.; Incharoensakdi, A. Metal oxide mediated extracellular NADPH regeneration improves ethanol production by engineered Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 148.
- Mohd Azhar, S.H.; Abdulla, R.; Jambo, S.A.; Marbawi, H.; Gansau, J.A.; Mohd Faik, A.A.; Rodrigues, K.F. Yeasts in sustainable bioethanol production: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 10, 52–61.
- Shokrkar, H.; Ebrahimi, S.; Zamani, M. Bioethanol production from acidic and enzymatic hydrolysates of mixed microalgae culture. Fuel 2017, 200, 380–386.
- de Farias Silva, C.E.; Meneghello, D.; Bertucco, A. A systematic study regarding hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation from microalgal biomass. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 172–182.
- Aikawa, S.; Inokuma, K.; Wakai, S.; Sasaki, K.; Ogino, C.; Chang, J.S.; Hasunuma, T.; Kondo, A. Direct and highly productive conversion of cyanobacteria Arthrospira platensis to ethanol with CaCl2 addition. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 50.
- Phwan, C.K.; Ong, H.C.; Chen, W.H.; Ling, T.C.; Ng, E.P.; Show, P.L. Overview: Comparison of pretreatment technologies and fermentation processes of bioethanol from microalgae. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 173, 81–94.
- Kim, H.M.; Oh, C.H.; Bae, H.J. Comparison of red microalgae (Porphyridium cruentum) culture conditions for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 44–50.
- Megawati, M.; Bahlawan, Z.A.S.; Damayanti, A.; Putri, R.D.A.; Triwibowo, B.; Prasetiawan, H. Comparative study on the various hydrolysis and fermentation methods of Chlorella vulgaris biomass for the production of bioethanol. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2022, 11, 515–522.
- Mirzaei, D.; Jazini, M.; Rahimi, M.; Mahdieh, M.; Karimi, K. Production of astaxanthin, ethanol and methane from Chromochloris zofingiensis microalga in an integrated biorefinery. Algal Res. 2022, 68, 102905.
- Hosseini, A.; Jazini, M.; Mahdieh, M.; Karimi, K. Efficient superantioxidant and biofuel production from microalga Haematococcus pluvialis via a biorefinery approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123100.
- Condor, B.E.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Leong, Y.K.; Chen, P.-T.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Bioethanol production from microalgae biomass at high-solids loadings. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 128002.
More
