You're using an outdated browser. Please upgrade to a modern browser for the best experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Jessie Wu and Version 1 by Luca Neri.
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most commonly utilized clinical tests for patient monitoring and assessment because it is easy to acquire and provides extensive information about patients’ cardiac health [1]. Instead, continuous, real-time, remote monitoring allows for a more rigorous oversight of patients’ conditions, even compared to in-hospital observation. Wearable devices to address monitoring are now a prominent focus of industry [1,2,3,4,5,6], which in turn provides strong motivation for applying artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to ECG signals for automated disease detection and prediction [7,8,9,10,11].
- ECG
- wearable technology
- machine learning
- deep learning
- m-health
1. Diseases
1.1. Arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmia is an abnormal rhythm of the heartbeat [19][1]. The electrical pathway of a normal cardiac contraction has a characteristic electrical pattern on an electrocardiogram (ECG) recording, comprised of a “P” wave (indicating atrial depolarization), followed by a “QRS” complex (indicating ventricular depolarization), and a “T” wave (indicating ventricular repolarization). A typical ECG is shown in Figure 1.
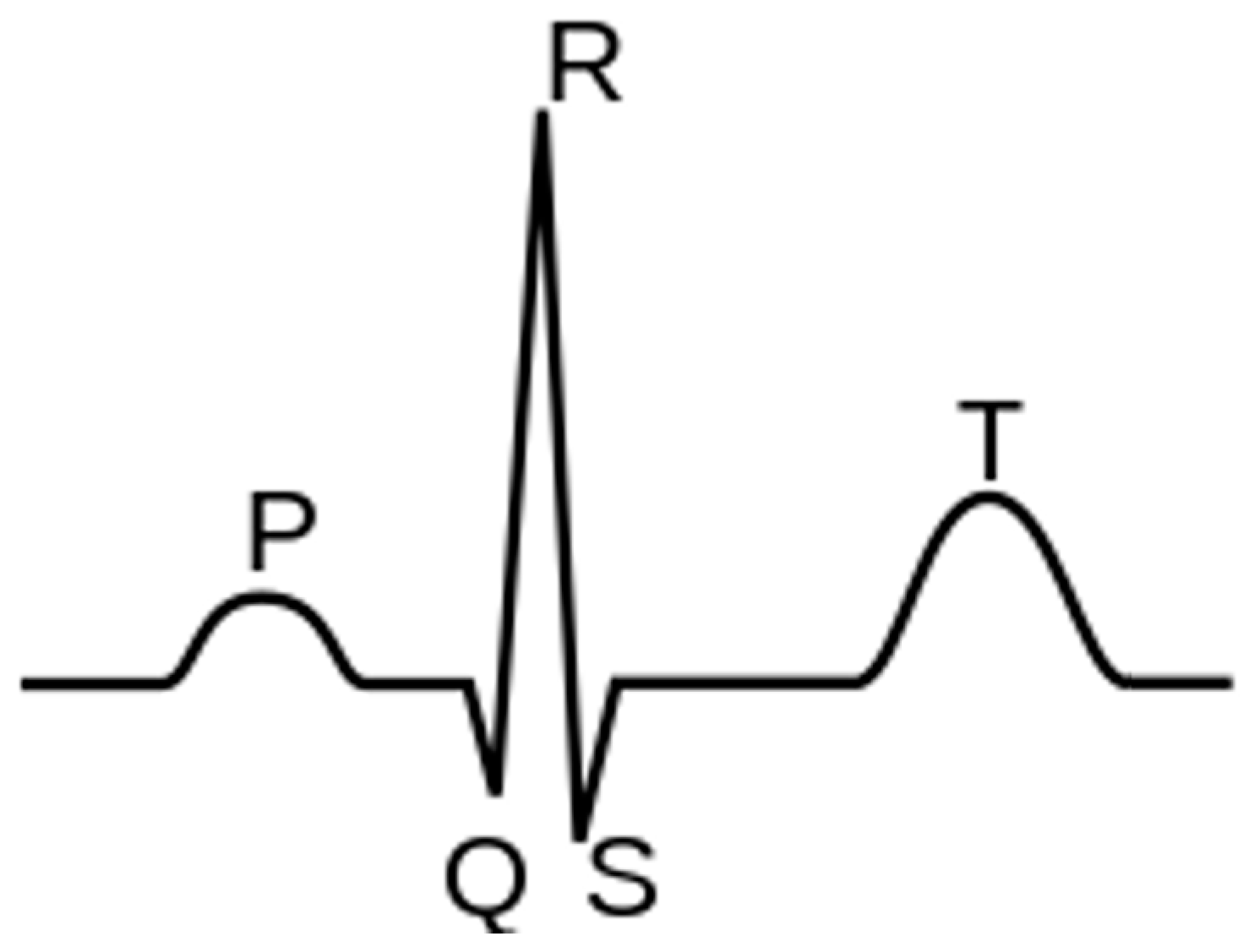
Figure 1.
Components of a normal electrocardiogram include P- and T-waves and the QRS complex.
Perturbations in the ECG may indicate underlying pathophysiologic changes. Common conditions that can be discerned from ECG changes include various arrhythmias. The most common type of irregular arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation (AF), which is characterized by disorganized electrical impulses of the atrium. AF increases the risk of stroke by up to 17% annually in high-risk individuals [20][2]. In addition, AF with sustained ventricular rates greater than 110 beats per minute can lead to cardiomyopathy, heart failure (HF), and sudden cardiac death if not adequately treated [21][3]. The worldwide prevalence of AF was estimated at approximately 46 million individuals in 2016 [22][4], with up to one-third of these individuals being asymptomatic and thus unaware they have AF while also being at increased risk of stroke.
In addition to AF, there are other arrhythmias for which wearable ECG devices are amenable including premature atrial contraction, premature ventricular contraction (PVC), atrial flutter, atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia, atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia, and first-, second-, or third-degree heart block. Several recent papers demonstrated the use of wearable technology capable of identifying premature atrial contractions or PVCs with over 97% accuracy [17,18,23,24][5][6][7][8]. A class of malignant arrhythmias has a high risk of progression to cardiac arrest or even death [25][9]. Examples of malignant rhythms include ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation.
1.2. Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is the insidious buildup of cholesterol plaques within the walls of the arteries of the heart, eventually leading to a narrowing of the blood vessels [26][10]. When the narrowing of blood vessels surpasses a critical threshold (often described as a narrowing of greater than 70% of the inner lumen of the artery), symptoms such as exertional chest pain (angina), exertional shortness of breath, and decreased exercise tolerance can occur. Coronary artery disease accounts for the vast majority of cardiac-related deaths [27][11]. A diagnosis of coronary heart disease generally requires a history and physical exam, a stress test, and an observation of ECG changes suggestive of cardiac ischemia.
Various ECG changes are associated with acute and chronic ischemia. For instance, the presence of Q waves in any lead other than the right-sided leads (i.e., aVR and V1, occasionally in III) is often pathognomonic for prior infarction and non-viable myocardium [28][12]. On the other hand, chronically inverted T-waves and ST depressions are generally described as non-specific ECG patterns and are difficult to interpret on their own, requiring additional context. However, in the correct clinical setting, these changes can be dynamic where they appear while the patient has active symptoms and normalize when they resolve. Such dynamic changes indicate significant coronary artery disease that needs to be aggressively investigated because the sudden development of ST-segment elevation associated with symptoms suggests an evolving coronary artery occlusion and subsequent myocardial impairment. Such patients need to be examined then treated immediately. Future work to develop ECG-AI wearables for real-time detection of acute ischemia will likely improve outcomes.
2. Wearables
ECG-AI has been combined with wearable devices to investigate various cardiac pathologies, including AF, stroke, cardiac arrest, and heart failure. In fact, arrhythmia monitoring is among the most popular applications of wearable devices in medicine. However, wearable devices are limited in their ability to detect arrhythmias other than AF [6[13][14],29], particularly ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation, which is why wearable technologies capable of accurately detecting either ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation were limited in the literature.
Overall, there are a limited number of studies involving wearables. Some studies use commercially available wearables to explore the implementation of ECG-AI. For example, devices such as the Amazfit Band 1S (PPG and single-lead ECG) [30][15], the HealthyPiV3 biosensors [31][16], or Polar H7 HR monitor [32][17] have been utilized. A few research groups have even built their own wearable ECG recording prototypes [33,34,35][18][19][20].
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved a single-lead ECG smartwatch proven to detect AF in the general population [36][21]. Another device developed for AF monitoring and detection includes a single-lead wireless ECG patch worn over the chest, which provides real-time ECG monitoring using cloud-based data analysis and data sharing with medical providers [13][22]. Similarly, a custom wrist-based wearable ECG recorder was compared to the standard 12-lead configuration via a prospective, registration-only, single-center study for the detection of AF [37][23]. Although a small dataset based on a relatively low number of patients was used, a sensitivity and specificity of 99.4% and 99.8%, respectively, were reported. The wrist-based device’s convenience and ease of use was highlighted as an attractive modality for arrhythmia detection in the general population. Lastly, a single-lead ECG chest belt that transmits data to a cloud service for analysis was described, and a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 95.4%, respectively, were reported [38][24]. The study included a user experience questionnaire, showing that 77% of participants preferred the chest belt to a standard 3-lead Holter monitor. Additional studies detecting AF have been performed using commercially available heart rate monitors and ECG systems [30,31,32,39,40,41][15][16][17][25][26][27].
3. Algorithms
3.1. Arrhythmia
Due to their ubiquitous availability, most ECG-AI research has been performed using public databases such as the PhysioNet [42][28] MIT-BIH Arrhythmia database [43,44][29][30] while only a few research groups have independently acquired data from patients. Curated and publicly available datasets include physician annotations that provide a reference for ECG-AI algorithm training (Table 1).
Machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) have both been extensively applied to ECG data to detect arrhythmias. Despite being relatively poorer performing, ML is utilized for arrhythmia detection due to some of the limitations of DL, including resource-intensive hyper-parameters to find the optimal network configuration and the challenges in understanding the rules underlying trained prediction models [45][31]. However, DL has shown modest improvements over ML for arrhythmia detection. The varying sample resolutions could pose a challenge for these techniques, but it was shown that it is possible to accurately detect arrythmias using down sampled ECG data [46][32].
ML approaches often include the use of decision tree ensembles such as Random Forest [13,47][22][33] or support vector machines (SVMs) [40,48][26][34] for arrhythmia classification. Multi-stage and multi-level classification systems derive local features of atrial and ventricular activity through a combination of SVMs and decision trees and global features from the raw ECG recording, ultimately leading to classification through linear SVMs. Furthermore, a rotated linear-kernel SVM has been proposed in which two SVM classifiers are trained, one on the global dataset and the other on a patient-dependent dataset obtaining two different discriminant hyperplanes. The final hyperplane, obtained by rotating the first hyperplane by a specific amount towards the second hyperplane, resulted in an improved sensitivity [49][35]. Similarly, this ML method has been used with a classifier of de-correlated Lorenz plots of inter-beat intervals [32][17], and with another classifier built on features extracted through pre-processing methods from density Poincaré plots that represented the ECG segments [23][7]. Alternatively, the use of SVMs through a semi-supervised learning method was demonstrated [50][36], while the hybrid framework effectively combined the advantages of ensemble learning and evolutionary computation to maximize arrhythmia classification accuracy [51][37].
With regard to DL approaches, convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture was applied to arrhythmia [52,53,54][38][39][40] and AF classifications [24,55][8][41]. Other architectures of interest for AF classification include a deep densely connected neural network based on 12-lead ECG [15][42], a feedforward neural network based on features encompassing R-R intervals [56][43] and another based on the Lightweight Fusing Transformer [17][5]. Hybrid constructions have also been presented, frequently involving an architecture based on a CNN and long short-term memory (LSTM) [57,58,59[44][45][46][47],60], as well as an extension to SVM with predictions from a CNN [41][27]. With a similar premise to the rotated linear-kernel SVM [49][35], a study has proposed a Generic CNN suitable for all individuals, and a tuned dedicated CNN as obtained by finetuning the previous model with respect to a specific individual [61][48]. Another approach of interest is the use of multi-scale (MS) CNNs to improve feature extraction and classification from ECG data [62][49]. Additionally, a global hybrid multi-scale convolutional neural network (Acc 99.84%) was proposed as an advanced alternative to other MS-based approaches through their hybrid multi-scale convolution module [63][50].
Previous research has also designed lightweight DL models using cloud-based applications to efficiently classify ECG data. These approaches utilize fused recurrent neural network (RNN) layers instead of standard RNN layers [39][25]. The application of compression [44,64][30][51] and conversion techniques (Acc 99.60%) [65][52], and model-hardware co-optimization [66][53] to reduce the model’s size in terms of computational parameters, resulted in lower memory consumption and inference time. Other techniques to accelerate arrhythmia detection include real-time data compression, signal processing, and data transmission [67,68,69][54][55][56]. Alternatively, ECG data may be compressed to enable real-time AF classification [70,71][57][58].
In addition to directly processing ECG data, some studies focused on its two-dimensional representation, which can be used for feature extraction and/or classification. Examples of these representations include spectrograms [31][16] and iris spectrograms [72][59]. Alternatively, the ECG signal may be transformed into an electrocardiomatrix, which is a two-dimensional representation that includes the rhythm and shape of the QRS complex [73][60]. A beat-interval-texture CNN was then used to process the electrocardiomatrix. In this architecture, there are four different layers: the first two layers perform low-level feature extraction, and the two subsequent layers perform high-level feature extraction using three types of convolution filters (beat, interval, and texture). Next, a feature attention layer weighs the identified features concerning the arrhythmia classes and uses such weighted features for classification.
Deep metric learning for PVC detection has also been demonstrated [18][6]. Such learning methods combine the mechanisms of metric learning for effective feature extraction in which the features are processed with k-nearest neighbors for binary classification. In comparing ML and DL, the former may use the ECG to define summary features that provide physiologic insight, whereas the latter automatically extracts discriminating information from complete waveforms [74][61]. ML and DL may complement one another, as demonstrated by the multiview fusion classification model in which both summary and deep features from ECG signals were fused [57][44]. However, DL may independently offer some physiologic information via gradient-weighted class activation mapping, which can highlight the relative contributions of the temporal regions of the ECG signal that most contribute to the AI-obtained classification [73][60].
68] and LSTM [80][69] algorithms. More complex DL models include a deep belief network for unsupervised heart rate variability (HRV) feature extraction and selection with LSTM for classification [76][63], a multi-channel lightweight model for the simultaneous analysis and classification of four ECG leads [81][70], and a two-dimensional CNN for the classification of ECG waveform snapshots [34][19]. It is important to notice that the ECG-AI determination of myocardial infarction commonly involves 12-lead data because the different leads represent different projections of the heart’s electrical activity, which is necessary to capture region-specific ischemia [12,16,78,79,80,81][65][66][67][68][69][70]. However, some algorithms were assessed based on data recorded from wearable single-lead devices [34,35][19][20].
Table 2.
Summary of ECG-based AI algorithms applied to other cardiovascular diseases.
| Authors (Year) | Specific Application | ECG System (Sampling Frequency) |
AI Algorithm/Method | Database/Dataset | Performance (%) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | Sen | Spe | AUC | F1 | ||||||||||||||
| Gibson et al. (2022) [12 | General arrhythmias | ][682-lead ECG patch [Samsung S-Patch 2] (256 Hz) |
Recurrent Neural Networks | ]MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Wearable device: S-Patch 2 |
Myocardial Infarction99.80 | -- | - | CNN | Latin America Telemedicine Infarct Network (LATIN) | 90.50 | 86.00 | 94.50- | -- | |||||
| - | Plawiak et al. (2020) [51][37] | General arrhythmias | - | |||||||||||||||
| Baloglu et al. (2019) [16][65] | Myocardial Infarction | - | Deep Genetic Ensemble of Classifiers | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 99.37 | 94.62 | 99.66 | CNN | PTB ECG: MI on standard 12-lead ECG data | 99.78 | 99.80- | -- | ||||||
| - | - | Panganiban et al. (2021) [31][16] | ||||||||||||||||
| Cho et al. (2021) [82] | General arrhythmias | [2-lead ECG [HealthyPiV3 biosensors] (n.s.) |
CNN | MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation, PAF Prediction Challenge, PTB Diagnostic ECG, Challenge 2015 Training Set, Fantasia, and PAF Prediction Challenge. ECG signals collected for this study | 7198.73 | 96.83 | 99.21 | - | ] | Heart Failure96.83 | ||||||||
| 12-lead ECG [Page Writer Cardiograph—Philips] | (500 Hz) | Short-time Fourier transform–CNN combination | ECG from multicenter study | 82.50 | 92.10 | 82.10 | 92.90 | - | Alqudah et al. (2021) [72][59] | General arrhythmias | ||||||||
| Wasimuddin et al. (2021) [34][19 | - | CNN | IEEE DataPort | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia |
99.13 | 99.31 | 99.81 | - | - | |||||||||
| ] | Myocardial Infarction | Custom 1-lead ECG (n.s.) |
CNN | European ST-T Custom wearable device |
99.26 | 99.27 | 99.27 | - | - | Yildirim et al. (2018) [52][38] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 95.20 | 93.52 | ||
| Chowdhury et al. (2019) [35][20 | 99.61 | - | 92.45 | |||||||||||||||
| ] | Myocardial Infarction-Cardiac Arrest | Custom 1-lead ECG (500 Hz) |
Support Vector Machine | MIT-BIH ST Change Normal subjects and an ECG simulator to simulate abnormal ST-elevated MI situations to test the functionality of the complete system in real-time |
97.40 | 99.10 | - | - | 98.70 | Bazi et al. (2020) [40][26] | ||||||||
| Shahnawaz et al. (2021) [79 | General arrhythmias | ]Wireless 3-lead ECG sensor [Shimmer Sensing (100, 200 Hz) |
SVM | [12-lead Tech-Patient CARDIO ECG simulator Wearable device: Shimmer Sensing MIT-BIH Arrhythmia |
95.10 | 95.80 | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 67] | Myocardial Infarction | - | Artificial Neural Network | PTB (PhysioNet) | 99.10 | 100.00 | 98.10 | - | 99.00 | Lee et al. (2022) [44][30] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN | ECG from patients at the Korea University Anam Hospital in Seoul, Korea | 97.90 | 98.30 | 97.60 | 99.70 |
| Sopic, et al. (2018) [78][66 | 97.70 | |||||||||||||||||
| ] | Myocardial Infarction | - | Random Forest | PTB (PhysioNet) | 80.30 | 87.95 | 79.63 | - | - | Itzhak et al. (2022) [46][32] | General arrhythmias | - | Random Forest | |||||
| Martin et al. (2021) [80][ | Annotated Holter ECG database acquired at the University of Virginia Heart Station | 69] | Myocardial Infarction | - | Deep Long Short-Term Memory93.30 | 91.30 | 81.30 | 95.30 | PTB-XL and PTB (PhysioNet) | 79.69 | 76.59 | 85.89 | -90.60 | |||||
| 83.42 | Li et al. (2018) [61][48] | General arrhythmias | - | Generic CNN and Tuned Dedicated CNN | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 96.89 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| AF | ||||||||||||||||||
| 12-lead ECG | ||||||||||||||||||
| (500 Hz) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Deep Densely connected Neural Network | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cao et al. (2021) [81][70] | Myocardial Infarction | - | Multi-Channel Lightweight model | PTB (PhysioNet) | 96.65 | Ran et al. (2022) [66][53] | General arrhythmias | 12-lead ECG prototype (500Hz) |
Deep CNN | 12-lead ECG recordings from three centers of Tongji Hospital | - | 89.10 | 99.70 | 94.40 | 91.30 | |||
| 94.30 | 97.72 | 96.71 | - | Ribeiro et al. (2022) [65][52] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 99.60 | 98.50 | 99.80 | - | 98.80 | |||||
| Hua et al. (2018) [50][36] | General arrhythmias | - | SVM | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 98.58 | 97.70 | 99.62 | - | - | |||||||||
| Karthiga et al. (2021) [53][39] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 91.92 | 90.21 | 95.19 | - | 90.11 | |||||||||
| Zhang et al. (2022) [54][40] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 98.74 | 98.11 | 99.05 | - | - | |||||||||
| Lee et al. (2021) [73][60] | General arrhythmias | - | Beat-Interval-Texture CNN | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge | - | 80.73 | - | - | 81.75 | |||||||||
| Smisek et al. (2018) [48][34] | General arrhythmias | - | SVMs Decision Tree | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge |
- | - | - | - | 81.00 | |||||||||
| Shin et al. (2022) [58][45] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN-Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 91.70 | 92.00 | 91.00 | 99.40 | 92.00 | |||||||||
| Alqudah et al. (2021) [75][62] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 93.80 | 95.20 | 97.40 | - | 93.60 | |||||||||
| Huang, et al. (2021) [57][44] | General arrhythmias | - | CNN-LSTM | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 98.93 | 96.46 | 99.33 | - | - | |||||||||
| Tang et al. (2019) [49][35] | General arrhythmias | - | SVM | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 98.90 | 92.80 | 99.40 | - | 92.00 | |||||||||
| Sakib et al. (2021) [64][51] | General arrhythmias | - | Deep-Learning-based Lightweight Arrhythmia Classification (CNN) | MIT-BIH Supraventricular Arrhythmia MIT-BIH Arrhythmia St Petersburg INCART 12-lead Arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death Holter |
96.67 | - | - | 97.96 | - | |||||||||
| Shao et al. (2020) [13][22] | AF | Custom 1-lead ECG patch (250 Hz) |
Decision Tree Ensemble | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation Simulated ECG signals from generator FLUKE MPS450 |
99.62 | 99.61 | 99.64 | - | 92.00 | |||||||||
| Chen et al. (2020) [30][15] | AF | PPG & 1-lead ECG [Amazfit Health Band 1S] (250 Hz) |
CNN | PPG and single-channel ECG data | 94.76 | 87.33 | 99.20 | - | - | |||||||||
| Cai et al. (2020) [15][42] | 12-lead ECG 10s recordings collected from multiple hospitals and wearable ECG devices (3 different data sources) | 99.35 | 99.19 | 99.44 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Cheng et al. (2020) [70][57] | AF | - | Deep Learning Neural Networks | MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation | 97.52 | 97.59 | 97.40 | - | 98.02 | |||||||||
| Fan et al. (2018) [62][49] | AF | - | Multi-Scale CNN | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge | 98.13 | 93.77 | 98.77 | - | - | |||||||||
| Ramesh et al. (2021) [55][41] | AF | - | CNN | Train: MIT-BIH Normal Sinus Rhythm, MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation, MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Test: UMass PPG, acquired from wrist-worn wearable devices |
95.50 | 94.50 | 96.00 | 95.30 | 93.40 | |||||||||
| Ma et al. (2020) [41][27] | AF | SmartVest system (400 Hz) |
SVM extended with CNN predictions | Train: MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation Test: PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge 2017, China Physiological Signal Challenge (CPSC) 2018, 24-h ECG recording (12 h before and 12 h after the radio frequency ablation surgery) collected from an AF patient with the wearable device |
99.08 | 98.67 | 99.50 | - | - | |||||||||
| Lown et al. (2020) [32][17] | AF | 1. 12-lead ECG (n.s.) 2. HR monitor [Polar H7 (PH7) HR] (n.s.) |
SVM | MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation MIT-BIH Arrhythmia |
- | 100.0 | 97.60 | - | - | |||||||||
| Zhang et al. (2021) [63][50] | AF | - | Global Hybrid Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network | China Physiological Signal Challenge 2018 (12-lead ECG) 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge (single-lead ECG) |
99.84 | 99.65 | 99.98 | - | 99.54 | |||||||||
| Zhang et al. (2020) [71][58] | AF | - | CNN | MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation | 96.23 | 95.92 | 96.55 | - | 96.25 | |||||||||
| Chen et al. (2022) [56][43] | AF | - | Feedforward Neural Network | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge MIT-BIH Arrhythmia |
84.00 | 84.26 | 93.23 | 89.40 | - | |||||||||
| Mei et al. (2018) [47][33] | AF | - | Baggin Trees | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge |
96.60 | 83.20 | 98.60 | - | - | |||||||||
| Wu et al. (2020) [45][31] | AF | - | Extreme Gradient Boosting | 2017 PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge MIT-BIH Atrial Fibrillation MIT-BIH Normal Sinus Rhythm MIT-BIH Arrhythmia |
95.47 | 94.59 | 96.40 | - | 95.56 | |||||||||
| Bashar et al. (2021) [23][7] | AF, PAC and PVC | - | SVM | Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC) III | 97.45 | 98.99 | 95.18 | - | - | |||||||||
| Yu et al. (2021) [18][6] | PVCs | - | Deep Metric Learning K-Nearest Neighbors | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 99.70 | 97.45 | 99.87 | - | - | |||||||||
| Wang (2021) [24][8] | PVCs | - | CNN with improved Gated Recurrent Unit network | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia China Physiological Signal Challenge 2018 |
98.30 | 98.40 | 98.20 | - | - | |||||||||
| Meng et al. (2022) [17][5] | PVC, SPB | - | Lightweight Fussing Transformer with LightConv Attention | The 3rd China Physiological Signal Challenge 2020 | 99.32 | 92.44 | - | - | 93.63 | |||||||||
| Khan et al. (2020) [33][18] | CVDs | - | SVM | Cleveland Heart Disease dataset from the UCI repository | 93.33 | 94.29 | 92.73 | - | - | |||||||||
| Dami et al. (2021) [76][63] | CVDs | - | LSTM Deep Belief Network | Four databases: DB1—KAGGLE heart disease dataset|DB2—Shahid Beheshti Hospital Research Center|DB3—Physionet site—Hypertensive patients|DB4—UCI Heart Disease dataset |
88.42 | 85.13 | 85.54 | - | - | |||||||||
| Khan et al. (2020) [77][64] | CVDs | Custom 1-lead ECG (n.s.) |
Deep Convolutional Neural Network | UCI machine learning repository, Framingham, and Public Health Dataset | 98.20 | 97.80 | 92.80 | - | 95.00 | |||||||||
| Tan et al. (2021) [60][47] | CVDs and COVID-19 | - | CNN-LSTM | MIT-BIH Arrhythmia | 99.29 | 97.77 | 99.53 | - | - | |||||||||
| Mazumder et al. (2021) [59][46] | VT and VF | - | CNN-LSTM | MIT-BIH Malignant Ventricular Arrhythmia (VFDB) Creighton University Ventricular Tachycardia (CUDB) |
- | 99.21 | 99.68 | - | - | |||||||||
Notes: Bold type highlights the wearable device when present and used to collect data. The best AI model/algorithm and results, when different models/algorithms, datasets, signals, and events are considered, were reported. Abbreviations: AF = atrial fibrillation; CVD = cardiovascular disease; PAC = premature atrio ventricular contractions; PVC = premature ventricular contraction; VF = ventricular tachycardia; VF = ventricular fibrillation; SPB = supraventricular premature beat; ECG = electrocardiogram; PPG = photoplethysmography; n.s. = not specified; HR = heart rate; CCN = convolutional neural network; LSTM = long short-term memory; SVM = support vector machine; Acc = accuracy; Sen = sensitivity; Spe = specificity; AUC = area under the curve of receiver-operating characteristic curves.
3.2. Other Cardiovascular Diseases
Other cardiovascular conditions amenable to ECG-AI include myocardial infarction and heart failure (Table 2). Particularly with myocardial infarction detection, there has been a shift from ML techniques towards DL techniques [16,35,78][20][65][66] due to their higher performances and the fact that no handcrafted feature extraction is required. DL techniques for myocardial infarction detection include the application of both simple and complex models. Examples of simple DL models include an artificial neural network with only three layers (Acc 99.10%) [79][67] and CNN [12,16][65][
Notes: Bold type highlights the wearable device when present and used to collect data. The best AI model/algorithm and results, when different models/algorithms, datasets, signals, and events are considered, were reported. Abbreviations: n.s. = not specified; CNN = convolutional neural network; Acc = accuracy; Sen = sensitivity; Spe = specificity; AUC = area under the curve of receiver-operating characteristic curves.
The analysis of 12-lead data also enabled the screening of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (Acc 82.50%) [82][71]. Following a short-time Fourier transform in combination with a CNN, an interpretable model highlighted the essential regions in the various ECG leads associated with the final classification. In particular, the lateral (aVL, I, −aVR, V5, V6) and anterior leads (V3, V4) greatly impacted heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction detection. In contrast, the performance of the inferior leads (II, aVF, III) was relatively poor. The findings also confirmed that a rightward T-wave axis, prolonged QT duration, and prolonged QTc are associated with heart failure and that the T-wave axis is an independent and strong risk factor for cardiac events in the elderly.
References
- Ellenbogen, K.A. Josephson’s Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 957–958.
- Lip, G.Y.; Nieuwlaat, R.; Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Crijns, H.J. Refining Clinical Risk Stratification for Predicting Stroke and Thromboembolism in Atrial Fibrillation Using a Novel Risk Factor-Based Approach. Chest 2010, 137, 263–272.
- Gopinathannair, R.; Sullivan, R.M.; Olshansky, B. Tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy: Recognition and management. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2009, 6, 257–264.
- Kornej, J.; Börschel, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Schnabel, R.B. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation in the 21st Century. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 4–20.
- Meng, L.; Tan, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, R.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Y. Enhancing dynamic ECG heartbeat classification with lightweight transformer model. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 124, 102236.
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, J. Automatic Premature Ventricular Contraction Detection Using Deep Metric Learning and KNN. Biosensors 2021, 11, 69.
- Bashar, S.K.; Han, D.; Zieneddin, F.; Ding, E.; Fitzgibbons, T.P.; Walkey, A.J.; McManus, D.D.; Javidi, B.; Chon, K.H. Novel Density Poincaré Plot Based Machine Learning Method to Detect Atrial Fibrillation from Premature Atrial/Ventricular Contractions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 448–460.
- Wang, J. Automated detection of premature ventricular contraction based on the improved gated recurrent unit network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106284.
- Zipes, D.P.; Wellens, H.J.J. Sudden Cardiac Death. Circulation 1998, 98, 2334–2351.
- Malakar, A.K.; Choudhury, D.; Halder, B.; Paul, P.; Uddin, A.; Chakraborty, S. A review on coronary artery disease, its risk factors, and therapeutics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 16812–16823.
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639.
- Zipes, M. Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 2019. Available online: https://evolve.elsevier.com/cs/product/9780323611886?role=student (accessed on 28 November 2022).
- Witvliet, M.P.; Karregat, E.P.M.; Himmelreich, J.C.L.; de Jong, J.S.S.G.; Lucassen, W.A.M.; Harskamp, R.E. Usefulness, pitfalls and interpretation of handheld single-lead electrocardiograms. J. Electrocardiol. 2021, 66, 33–37.
- Mannhart, D.; Lischer, M.; Knecht, S.; Lavallaz, J.D.F.D.; Strebel, I.; Serban, T.; Vögeli, D.; Schaer, B.; Osswald, S.; Mueller, C.; et al. Clinical Validation of 5 Direct-to-Consumer Wearable Smart Devices to Detect Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2023, 9, 232–242.
- Chen, E.; Jiang, J.; Su, R.; Gao, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Huo, Y. A new smart wristband equipped with an artificial intelligence algorithm to detect atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2020, 17, 847–853.
- Panganiban, E.B.; Paglinawan, A.C.; Chung, W.Y.; Paa, G.L.S. ECG diagnostic support system (EDSS): A deep learning neural network based classification system for detecting ECG abnormal rhythms from a low-powered wearable biosensors. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 31, 100398.
- Lown, M.; Brown, M.; Brown, C.; Yue, A.M.; Shah, B.N.; Corbett, S.J.; Lewith, G.; Stuart, B.; Moore, M.; Little, P. Machine learning detection of Atrial Fibrillation using wearable technology. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227401.
- Khan, M.A.; Abbas, S.; Atta, A.; Ditta, A.; Alquhayz, H.; Rahman, A.U.; Naqvi, R.A. Intelligent Cloud Based Heart Disease Prediction System Empowered with Supervised Machine Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 65, 139–151.
- Wasimuddin, M.; Elleithy, K.; Abuzneid, A.; Faezipour, M.; Abuzaghleh, O. Multiclass ECG Signal Analysis Using Global Average-Based 2-D Convolutional Neural Network Modeling. Electronics 2021, 10, 170.
- Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Alzoubi, K.; Khandakar, A.; Khallifa, R.; Abouhasera, R.; Koubaa, S.; Ahmed, R.; Hasan, A. Wearable Real-Time Heart Attack Detection and Warning System to Reduce Road Accidents. Sensors 2019, 19, 2780.
- Perez, M.V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Hedlin, H.; Rumsfeld, J.S.; Garcia, A.; Ferris, T.; Balasubramanian, V.; Russo, A.M.; Rajmane, A.; Cheung, L.; et al. Large-Scale Assessment of a Smartwatch to Identify Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1909–1917.
- Shao, M.; Zhou, Z.; Bin, G.; Bai, Y.; Wu, S. A Wearable Electrocardiogram Telemonitoring System for Atrial Fibrillation Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 606.
- Fu, W.; Li, R. Diagnostic performance of a wearing dynamic ECG recorder for atrial fibrillation screening: The HUAMI heart study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 558.
- Santala, O.E.; Halonen, J.; Martikainen, S.; Jäntti, H.; Rissanen, T.T.; Tarvainen, M.P.; Laitinen, T.P.; Laitinen, T.M.; Väliaho, E.-S.; Hartikainen, J.E.K.; et al. Automatic Mobile Health Arrhythmia Monitoring for the Detection of Atrial Fibrillation: Prospective Feasibility, Accuracy, and User Experience Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2021, 9, e29933.
- Jeon, E.; Oh, K.; Kwon, S.; Son, H.; Yun, Y.; Jung, E.-S.; Kim, M.S. A Lightweight Deep Learning Model for Fast Electrocardiographic Beats Classification with a Wearable Cardiac Monitor: Development and Validation Study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2020, 8, e17037.
- Bazi, Y.; Al Rahhal, M.M.; AlHichri, H.; Ammour, N.; Alajlan, N.; Zuair, M. Real-Time Mobile-Based Electrocardiogram System for Remote Monitoring of Patients with Cardiac Arrhythmias. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2058013.
- Ma, C.; Wei, S.; Chen, T.; Zhong, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C. Integration of Results from Convolutional Neural Network in a Support Vector Machine for the Detection of Atrial Fibrillation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, E215–E220.
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.N.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.-K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 2000, 101, E215–E220.
- Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G. The impact of the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 45–50.
- Lee, K.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.J.; Chon, S.; Kim, S.; Jang, J.; Kim, J.-K.; Jang, S.; Gil, Y.; et al. Compressed Deep Learning to Classify Arrhythmia in an Embedded Wearable Device. Sensors 2022, 22, 1776.
- Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, C.-H.; He, Z. Extracting deep features from short ECG signals for early atrial fibrillation detection. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 109, 101896.
- Ben Itzhak, S.; Ricon, S.S.; Biton, S.; Behar, J.A.; Sobel, J.A. Effect of temporal resolution on the detection of cardiac arrhythmias using HRV features and machine learning. Physiol. Meas. 2022, 43, 045002.
- Mei, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Automatic Atrial Fibrillation Detection Based on Heart Rate Variability and Spectral Features. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 53566–53575.
- Smisek, R.; Hejc, J.; Ronzhina, M.; Nemcova, A.; Marsanova, L.; Kolarova, J.; Smital, L.; Vitek, M. Multi-stage SVM approach for cardiac arrhythmias detection in short single-lead ECG recorded by a wearable device. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 094003.
- Tang, X.; Ma, Z.; Hu, Q.; Tang, W. A Real-Time Arrhythmia Heartbeats Classification Algorithm Using Parallel Delta Modulations and Rotated Linear-Kernel Support Vector Machines. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 978–986.
- Hua, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Guo, F. Direct Arrhythmia Classification from Compressive ECG Signals in Wearable Health Monitoring System. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2018, 27, 1850088.
- Pławiak, P.; Acharya, U.R. Novel deep genetic ensemble of classifiers for arrhythmia detection using ECG signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 11137–11161.
- Yıldırım, Ö.; Pławiak, P.; Tan, R.-S.; Acharya, U.R. Arrhythmia detection using deep convolutional neural network with long duration ECG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 102, 411–420.
- Karthiga, S.; Abirami, A.M. Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Network for ECG Signal Classification Aggregated Using IoT. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 42, 851–866.
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; He, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. A CNN Model for Cardiac Arrhythmias Classification Based on Individual ECG Signals. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2022, 13, 548–557.
- Ramesh, J.; Solatidehkordi, Z.; Aburukba, R.; Sagahyroon, A. Atrial Fibrillation Classification with Smart Wearables Using Short-Term Heart Rate Variability and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 7233.
- Cai, W.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Han, B.; Shi, Y.; Ji, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Luo, J. Accurate detection of atrial fibrillation from 12-lead ECG using deep neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 116, 103378.
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wan, X. Atrial Fibrillation Detection Using a Feedforward Neural Network. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2022, 42, 63–73.
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, X. A multiview feature fusion model for heartbeat classification. Physiol. Meas. 2021, 42, 065003.
- Shin, S.; Kang, M.; Zhang, G.; Jung, J.; Kim, Y.T. Lightweight Ensemble Network for Detecting Heart Disease Using ECG Signals. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3291.
- Mazumder, O.; Banerjee, R.; Roy, D.; Mukherjee, A.; Ghose, A.; Khandelwal, S.; Sinha, A. Computational Model for Therapy Optimization of Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator: Shockable Rhythm Detection and Optimal Electrotherapy. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 787180.
- Tan, L.; Yu, K.; Bashir, A.K.; Cheng, X.; Ming, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X. Toward real-time and efficient cardiovascular monitoring for COVID-19 patients by 5G-enabled wearable medical devices: A deep learning approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 1–14.
- Li, Y.; Pang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Patient-specific ECG classification by deeper CNN from generic to dedicated. Neurocomputing 2018, 314, 336–346.
- Fan, X.; Yao, Q.; Cai, Y.; Miao, F.; Sun, F.; Li, Y. Multiscaled Fusion of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Screening Atrial Fibrillation from Single Lead Short ECG Recordings. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1744–1753.
- Zhang, P.; Ma, C.; Sun, Y.; Fan, G.; Song, F.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, G. Global hybrid multi-scale convolutional network for accurate and robust detection of atrial fibrillation using single-lead ECG recordings. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 139, 104880.
- Sakib, S.; Fouda, M.M.; Fadlullah, Z.M.; Nasser, N.; Alasmary, W. A Proof-of-Concept of Ultra-Edge Smart IoT Sensor: A Continuous and Lightweight Arrhythmia Monitoring Approach. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26093–26106.
- Ribeiro, H.D.M.; Arnold, A.; Howard, J.P.; Shun-Shin, M.J.; Zhang, Y.; Francis, D.P.; Lim, P.B.; Whinnett, Z.; Zolgharni, M. ECG-based real-time arrhythmia monitoring using quantized deep neural networks: A feasibility study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 26093–26106.
- Ran, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, Y. Homecare-Oriented ECG Diagnosis with Large-Scale Deep Neural Network for Continuous Monitoring on Embedded Devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2503113.
- Qaisar, S.M.; Hussain, S.F. Arrhythmia Diagnosis by Using Level-Crossing ECG Sampling and Sub-Bands Features Extraction for Mobile Healthcare. Sensors 2020, 20, 2252.
- Qaisar, S.M.; Subasi, A. Cloud-based ECG monitoring using event-driven ECG acquisition and machine learning techniques. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 623–634.
- Qaisar, S.M.; Mihoub, A.; Krichen, M.; Nisar, H. Multirate Processing with Selective Subbands and Machine Learning for Efficient Arrhythmia Classification. Sensors 2021, 21, 1511.
- Cheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hou, M.; Pan, T.; He, W.; Ye, Y. Atrial Fibrillation Detection Directly from Compressed ECG with the Prior of Measurement Matrix. Information 2020, 11, 436.
- Zhang, H.; Dong, Z.; Gao, J.; Lu, P.; Wang, Z. Automatic screening method for atrial fibrillation based on lossy compression of the electrocardiogram signal. Physiol. Meas. 2020, 41, 075005.
- Alqudah, A.M.; Alqudah, A. Deep learning for single-lead ECG beat arrhythmia-type detection using novel iris spectrogram representation. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 1123–1139.
- Lee, H.; Shin, M. Learning Explainable Time-Morphology Patterns for Automatic Arrhythmia Classification from Short Single-Lead ECGs. Sensors 2021, 21, 4331.
- Seo, W.; Kim, N.; Kim, S.; Lee, C.; Park, S.-M. Deep ECG-Respiration Network (DeepER Net) for Recognizing Mental Stress. Sensors 2019, 19, 3021.
- Alqudah, A.M.; Qazan, S.; Al-Ebbini, L.; Alquran, H.; Abu Qasmieh, I. ECG heartbeat arrhythmias classification: A comparison study between different types of spectrum representation and convolutional neural networks architectures. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 4877–4907.
- Dami, S.; Yahaghizadeh, M. Predicting cardiovascular events with deep learning approach in the context of the internet of things. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 7979–7996.
- Khan, M.A. An IoT Framework for Heart Disease Prediction Based on MDCNN Classifier. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 34717–34727.
- Baloglu, U.B.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, O.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Classification of myocardial infarction with multi-lead ECG signals and deep CNN. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 122, 23–30.
- Sopic, D.; Aminifar, A.; Atienza, D. Real-Time Event-Driven Classification Technique for Early Detection and Prevention of Myocardial Infarction on Wearable Systems. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 982–992.
- Shahnawaz, M.B.; Dawood, H. An Effective Deep Learning Model for Automated Detection of Myocardial Infarction Based on Ultrashort-Term Heart Rate Variability Analysis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, e6455053.
- Gibson, C.M.; Mehta, S.; Ceschim, M.R.; Frauenfelder, A.; Vieira, D.; Botelho, R.; Fernandez, F.; Villagran, C.; Niklitschek, S.; Matheus, C.I.; et al. Evolution of single-lead ECG for STEMI detection using a deep learning approach. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 346, 47–52.
- Martin, H.; Morar, U.; Izquierdo, W.; Cabrerizo, M.; Cabrera, A.; Adjouadi, M. Real-time frequency-independent single-Lead and single-beat myocardial infarction detection. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 121, 102179.
- Cao, Y.; Wei, T.; Zhang, B.; Lin, N.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Li, J.; Zhang, D. ML-Net: Multi-Channel Lightweight Network for Detecting Myocardial Infarction. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 3721–3731.
- Cho, J.; Lee, B.; Kwon, J.-M.; Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Oh, B.-H.; Jeon, K.-H.; Park, J.; Kim, K.-H. Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Screening Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction Using Electrocardiography. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 314–321.
More
