Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Lindsay Dong and Version 1 by Bartłomiej Zieniuk.
Dihydrocaffeic acid (DHCA) is a phenolic acid bearing a catechol ring and three-carbon side chain. Despite its being found in minor amounts in numerous plants and fungi of different origins, it has attracted the interest of various research groups in many fields of science, from food to biomedical applications.
- dihydrocaffeic acid
- phenolic acids
- antioxidants
- biological properties
- enzymatic synthesis
1. Introduction
Dihydrocaffeic acid (3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid, DHCA 1; Figure 1a) is a phenolic acid belonging to the group of phenylpropanoic acids, which can be differentiated by a six-carbon aromatic ring and a three-carbon side chain with the carboxyl group at the end of the carbon chain. The molecule of DHCA itself comprises catechol moiety and the aforementioned propanoic tail. In some ways, it also resembles the structure of dopamine (2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethylamine, Figure 1b) [1], one of the significant neuromodulatory molecules. From the physical-chemical point of view, dihydrocaffeic acid is a white to beige to orange powder. It has a molecular weight of 182.17 g/mol and a melting point of 136 °C. It is soluble in water and ethanol and has very limited solubility in nonpolar organic solvents [2]. DHCA is a phytochemical that occurs naturally in a number of plants, but it is definitely present less frequently and in lesser amounts in comparison with its unsaturated derivative, i.e., caffeic acid (Figure 1c).
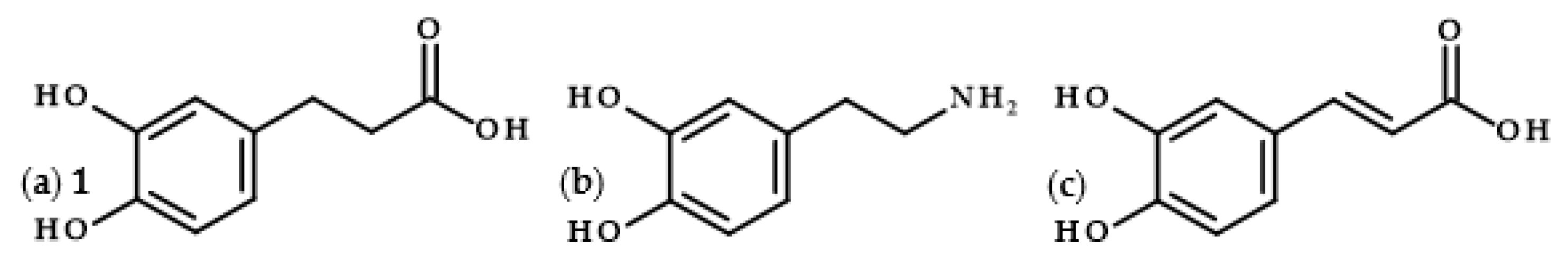
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of dihydrocaffeic acid
1
(
a
), dopamine (
b
), and caffeic acid (
c).
2. The Occurrence of Dihydrocaffeic Acid and Its Derivatives
The presence of dihydrocaffeic acid has been confirmed in various plant species, including fruits, lycophytes, and ornamental and medicinal plants [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. DHCA with a concentration of 0.03 mg/kg dry weight was a minor constituent determined to be in the methanolic extract of dyer’s woad leaves (
).
2. The Occurrence of Dihydrocaffeic Acid and Its Derivatives
The presence of dihydrocaffeic acid has been confirmed in various plant species, including fruits, lycophytes, and ornamental and medicinal plants [3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18]. DHCA with a concentration of 0.03 mg/kg dry weight was a minor constituent determined to be in the methanolic extract of dyer’s woad leaves (
Isatis tinctoria
), a plant belonging to the Brassicaceae family and with a long history of use both in folk medicine and for the extraction of indigo dye from the leaves [3]. Phenolic acid, of interest, has also been confirmed as an ingredient of extracts of two Asteraceae plants, namely in the white ray florets of
Matricaria recutita
Gynura bicolor
[5]. It is one of the most numerous families of vascular plants; therefore, the statement that DHCA is present in plants of the Asteraceae family is an extremely exaggerated statement. Moreover, dihydrocaffeic acid was one of the 35 constituents of transformed root cultures of
Nepeta teydea
, a plant from the Lamiaceae family. The freeze-dried hairy roots of
N. teydea
were extracted with methanol, and individual fractions were then purified to give 2 mg of DHCA (10.53 mg/kg freeze-dried roots) [6]. Other natural sources of dihydrocaffeic acid are: the aerial part of
Lindera glauca
Selaginella stautoniana
Polyscias murrayi
—with the highest observed concentration in the literature of 352.32 mg/kg fresh weight [9], the concentrated juice of
Rosa roxburghii
Furthermore, the presence of this acid was claimed in four different varieties of dates, namely Tantbouchte, Tafizaouine, Tazerzait, and Tazizaout [12]. Going further, olives, especially, but not only, black ones, as well as olive oils, are a known source of phenolic compounds, and, therefore, DHCA [13,14,15]. Black olives pericarp was an abundant source of phenolic compounds and dihydrocaffeic acid, with a determined content of 1.790 ± 0.030 g/kg dry weight, was the fourth most significant compound after hydroxytyrosol, acetoside-1, and acetoside-2. In olive processing, brining is a method for removing bitterness and increasing the taste of olive drupes, but, simultaneously, may be a process of partially decreasing phenolic content. Therefore, the authors also evaluated the brine in terms of these compounds. The brine consisted mainly of hydroxytyrosol (0.600 ± 0.010 g/L) and dihydrocaffeic acid (0.183 ± 0.001 g/L). On the contrary, green olives and their brine were only a source of hydroxytyrosol, and only traces of other phenolics were detected [13].
It is a well-known fact that alcoholic beverages, e.g., wines, beers, and ciders, are also precious sources of phenolic compounds. The presence of dihydrocaffeic acid was observed in the red wine Lacrima di Morro d’Alba, produced in the region of Marche in Italy [16]. The phenolic profiles of a large group of Asturian (Spain) ciders were analyzed by Madrera et al. [17] and Suarez et al. [18]. For both papers, DHCA was the most abundant and accounted for 12–35% of all phenolic compounds. In the former, 92 natural ciders available in the market from the years 1999 and 2000 were compared, and the content of this acid was in the range from roughly 26 to almost 150 mg/L. The second had a similar concentration range (55.8–110.5 mg/L).
Furthermore, the presence of this acid was claimed in four different varieties of dates, namely Tantbouchte, Tafizaouine, Tazerzait, and Tazizaout [12]. Going further, olives, especially, but not only, black ones, as well as olive oils, are a known source of phenolic compounds, and, therefore, DHCA [13][14][15]. Black olives pericarp was an abundant source of phenolic compounds and dihydrocaffeic acid, with a determined content of 1.790 ± 0.030 g/kg dry weight, was the fourth most significant compound after hydroxytyrosol, acetoside-1, and acetoside-2. In olive processing, brining is a method for removing bitterness and increasing the taste of olive drupes, but, simultaneously, may be a process of partially decreasing phenolic content. Therefore, the scholars also evaluated the brine in terms of these compounds. The brine consisted mainly of hydroxytyrosol (0.600 ± 0.010 g/L) and dihydrocaffeic acid (0.183 ± 0.001 g/L). On the contrary, green olives and their brine were only a source of hydroxytyrosol, and only traces of other phenolics were detected [13].
It is a well-known fact that alcoholic beverages, e.g., wines, beers, and ciders, are also precious sources of phenolic compounds. The presence of dihydrocaffeic acid was observed in the red wine Lacrima di Morro d’Alba, produced in the region of Marche in Italy [16]. The phenolic profiles of a large group of Asturian (Spain) ciders were analyzed by Madrera et al. [17] and Suarez et al. [18]. For both papers, DHCA was the most abundant and accounted for 12–35% of all phenolic compounds. In the former, 92 natural ciders available in the market from the years 1999 and 2000 were compared, and the content of this acid was in the range from roughly 26 to almost 150 mg/L. The second had a similar concentration range (55.8–110.5 mg/L).
3. Biosynthesis of Dihydrocaffeic Acid
The biosynthesis of dihydrocaffeic acid is a complex process. Unfortunately, the detailed metabolic route for DHCA formation has not been described so far. Referring to [34,35,36,37,38,39], the simplified pathway of dihydrocaffeic acid biosynthesis is presented inThe biosynthesis of dihydrocaffeic acid is a complex process. Unfortunately, the detailed metabolic route for DHCA formation has not been described so far. Referring to [19][20][21][22][23][24], the simplified pathway of dihydrocaffeic acid biosynthesis is presented in
Figure 3.
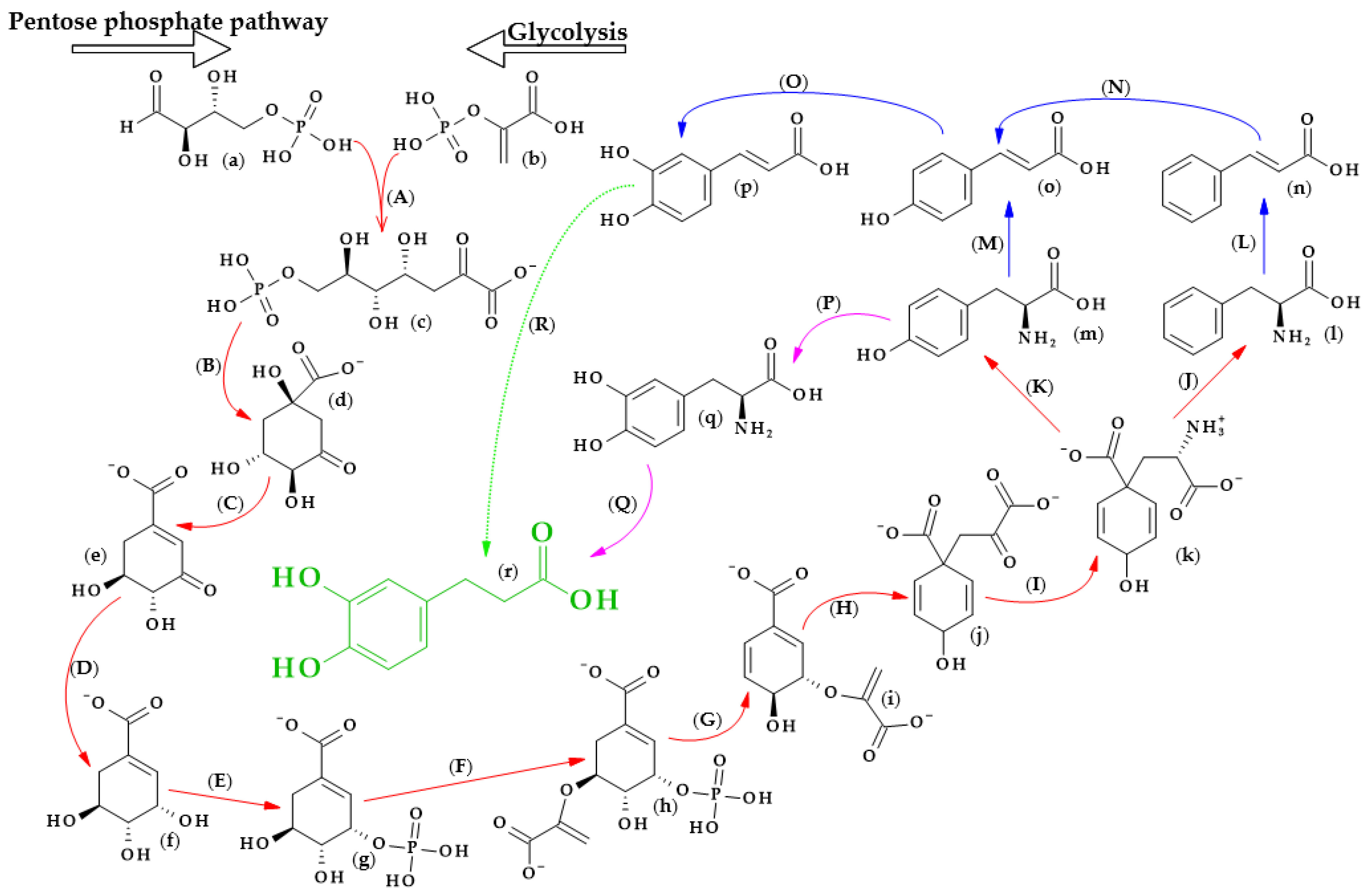
Figure 3. Dihydrocaffeic acid biosynthesis—proposed simplified pathway (adapted and modified from [34,35,36,37,38,39]). Explanations: (
Dihydrocaffeic acid biosynthesis—proposed simplified pathway (adapted and modified from [19][20][21][22][23][24]). Explanations: (
a
)–(
r
)—compounds, A–R—enzymes, i.e., (
a
)—D-Erythrose 4-phosphate, (
b
)—Phosphoenolpyruvate, (
c
)—7-phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate, (
d
)—3-Dehydroquinate, (
e
)—3-Dehydroshikimate, (
f
)—Shikimate, (
g
)—Shikimate-3-phosphate, (
h
)—5-
O
-(1-carboxyvinyl)-3-phosphoshikimate, (
i
)—Chorismate, (
j
)—Prephenate, (
k
)—L-Arogenate, (
l
)—Phenylalanine, (
m
)—Tyrosine, (
n
)—
trans
-Cinnamic acid, (
o
)—
p
-Coumaric acid, (
p
)—Caffeic acid, (
q
)—3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (L-Dopa), (
r
)—Dihydrocaffeic acid, (
A
)—3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.54), (
B
)—3-dehydroquinate synthase (EC 4.2.3.4), (
C
)—3-dehydroquinate dehydratase I (EC 4.2.1.10), (
D
)—shikimate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.25), (
E
)—shikimate kinase (EC 2.7.1.71), (
F
)—3-phosphoshikimate 1-carboxyvinyltransferase (EC 2.5.1.19), (
G
)—chorismate synthase (EC 4.2.3.5), (
H
)—chorismate mutase (EC 5.4.99.5), (
I
)—bifunctional aspartate aminotransferase and glutamate/aspartate-prephenate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.1, EC 2.6.1.78, EC 2.6.1.79), (
J
)—arogenate/prephenate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.91, EC 4.2.1.51), (
K
)—arogenate dehydrogenase (NADP
+
) (EC 1.3.1.78), (
L
)—phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.24), (
M
)—phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.25), (
N
)—
trans
-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.91), (
O
)—
p
-coumarate 3-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.-), (
P
)—tyrosine 3-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.16.2), (
Q
)—3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.22), and (
R
)—double bond reductase (EC 1.3.1.-).
As with other phenolic acids, several common elements of these pathways can be distinguished. It all starts with the formation of 7-phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate from D-erythrose 4-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate, products of the pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis, respectively. The part of the process in
Figure 3 that is marked with red lines is the so-called Shikimate pathway, and in plants it is responsible for the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine). Eight subsequent reactions lead to obtaining L-arogenate, the last compound in the formation of phenylalanine and its hydroxylated derivative, i.e., tyrosine, and two crucial amino acids in phenylpropanoids biosynthesis [35].
that is marked with red lines is the so-called Shikimate pathway, and in plants it is responsible for the biosynthesis of the aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tryptophan, and tyrosine). Eight subsequent reactions lead to obtaining L-arogenate, the last compound in the formation of phenylalanine and its hydroxylated derivative, i.e., tyrosine, and two crucial amino acids in phenylpropanoids biosynthesis [20].
4. Metabolism of Dihydrocaffeic Acid by Intestinal and Lactic Acid Bacteria
Phenolic compounds are undoubtedly one of the most valuable substances that we intake with food. Bioavailability, metabolism, and digestion, as well as the pharmacokinetics of food products that are abundant in phenolics, are issues that are gaining the interest of the scientific community, especially due to the progress in analytical chemistry and chromatographic and spectroscopic methods. Dihydrocaffeic acid is a compound that is observed in samples of plasma, urine, or faeces after the consumption of products with a high content of chlorogenic and caffeic acids, which indicates, e.g., the activity of intestinal microbiota on the metabolic fate of these compounds. In recent years, scientists have examined what happens to the phenolic compounds that are ingested along with the following food products: coffee, yerba mate, cocoa, and artichoke, as well as berry, grape, and apple products [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50].Phenolic compounds are undoubtedly one of the most valuable substances that we intake with food. Bioavailability, metabolism, and digestion, as well as the pharmacokinetics of food products that are abundant in phenolics, are issues that are gaining the interest of the scientific community, especially due to the progress in analytical chemistry and chromatographic and spectroscopic methods. Dihydrocaffeic acid is a compound that is observed in samples of plasma, urine, or faeces after the consumption of products with a high content of chlorogenic and caffeic acids, which indicates, e.g., the activity of intestinal microbiota on the metabolic fate of these compounds. In recent years, scientists have examined what happens to the phenolic compounds that are ingested along with the following food products: coffee, yerba mate, cocoa, and artichoke, as well as berry, grape, and apple products [25][26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35].
As one of the most consumed beverages worldwide, coffee is the main source of chlorogenic acid in the human diet. Redeuil et al. [40] conducted research on the coffee metabolites in the plasma of nine people after the ingestion of 400 mL of instant coffee. The authors identified 34 compounds, and they were mainly reduced (dihydrocaffeic acid), methylated (dihydroferulic acid, dimethoxycinnamic acid), and sulfated (dihydroferulic acid 4′-As one of the most consumed beverages worldwide, coffee is the main source of chlorogenic acid in the human diet. Redeuil et al. [25] conducted research on the coffee metabolites in the plasma of nine people after the ingestion of 400 mL of instant coffee. The scholars identified 34 compounds, and they were mainly reduced (dihydrocaffeic acid), methylated (dihydroferulic acid, dimethoxycinnamic acid), and sulfated (dihydroferulic acid 4′-
O-sulfate and caffeic acid 3′-
O-sulfate) forms of caffeic acid. Moreover, it was found that the highest concentration of DHCA in plasma was observed 10 h after ingestion and that DHCA 4′-
O-sulfate was also present in the samples.
A complete and detailed metabolic fate of dihydrocaffeic acid was investigated by Poquet et al. [51]. The authors carried out metabolism experiments with the use of cell cultures, and elaborated in vitro and ex vivo models for transport studies and liver metabolism, as well as in vivo metabolism studies of 100 µmol DHCA/kg orally administrated to Sprague–Dawley rats. According to the authors’ findings, dihydrocaffeic acid in its free form was absorbed by the stomach, by duodenal or jejunal cells, or more often, when it occurred in an esterified or more complicated form, by the ileum or the colon as a result of intestinal microflora activity. Right after the ingestion, dihydrocaffeic acid was metabolized to its glucuronide, sulphate, or methylated derivatives. The authors identified the following compounds in the plasma samples: 3′- and 4′-A complete and detailed metabolic fate of dihydrocaffeic acid was investigated by Poquet et al. [36]. The scholars carried out metabolism experiments with the use of cell cultures, and elaborated in vitro and ex vivo models for transport studies and liver metabolism, as well as in vivo metabolism studies of 100 µmol DHCA/kg orally administrated to Sprague–Dawley rats. According to the scholars’ findings, dihydrocaffeic acid in its free form was absorbed by the stomach, by duodenal or jejunal cells, or more often, when it occurred in an esterified or more complicated form, by the ileum or the colon as a result of intestinal microflora activity. Right after the ingestion, dihydrocaffeic acid was metabolized to its glucuronide, sulphate, or methylated derivatives. The scholars identified the following compounds in the plasma samples: 3′- and 4′-
O-glucuronides and 3′- and 4′-
O-sulfates of dihydrocaffeic acid, and also dihydroferulic, ferulic, and isoferulic acids. Moreover, the authors claimed that the 3-OH position in the catechol ring was favoured for conjugations or methylation, and, in the intestinal epithelium glucuronidation of DHCA, occurred more often and, oppositely, in the rat liver, sulfation was preferred. Eventually, part of this compound in a free, bound, or metabolized form remained excreted in urine [51].-sulfates of dihydrocaffeic acid, and also dihydroferulic, ferulic, and isoferulic acids. Moreover, the scholars claimed that the 3-OH position in the catechol ring was favoured for conjugations or methylation, and, in the intestinal epithelium glucuronidation of DHCA, occurred more often and, oppositely, in the rat liver, sulfation was preferred. Eventually, part of this compound in a free, bound, or metabolized form remained excreted in urine [36].
A different study, or rather, a different fermented product, was presented by Oh et al. [61]. The authors applied four different strains of A different study, or rather, a different fermented product, was presented by Oh et al. [37]. The scholars applied four different strains of
L. gasseri, a probiotic isolate of human origin, for the fermentation of milk that was enriched with the leaf extract of
Cudrania tricuspidata. This herb is used in Asian folk medicine and is abundant in chlorogenic, neochlorogenic, and caffeic acids, as well as in flavonoids such as rutin and glycosides of quercetin and kaempferol. Phenolic acids were predominantly metabolized by the used LAB strains, with the simultaneous formation of DHCA as a major derivative formed during fermentation. Caffeic acid was the compound whose concentrations decreased the most, and in the case of dihydrocaffeic acid, after 48 h, its concentration ranged from 82 to 108 μg/g dry matter depending on the
L. gasseri strain [61].
References
- Zieniuk, B.; Ononamadu, C.J.; Jasińska, K.; Wierzchowska, K.; Fabiszewska, A. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis, Antioxidant Activity, Antimicrobial Properties and Molecular Docking Studies of Butyl Dihydrocaffeate. Molecules 2022, 27, 5024.
- Compound Summary 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)Propionic Acid. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3-_3_4-Dihydroxyphenyl_propionic-acid (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Hartleb, I.; Seifert, K. Acid Constituents from Isatis tinctoria. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 95–96.
- Nakurte, I.; Berga, M.; Pastare, L.; Kienkas, L.; Senkovs, M.; Boroduskis, M.; Ramata-Stunda, A. Valorization of Bioactive Compounds from By-Products of Matricaria recutita White Ray Florets. Plants 2023, 12, 396.
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Gu, J.; Luo, G. Isolation and Identification of Antioxidant Compounds from Gynura bicolor Stems and Leaves. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 233–241.
- Fraga, B.M.; Gonzalez-Coloma, A.; Alegre-Gomez, S.; Lopez-Rodriguez, M.; Amador, L.J.; Diaz, C.E. Bioactive constituents from transformed root cultures of Nepeta teydea. Phytochemistry 2017, 133, 59–68.
- Chang, Y.C.; Chang, F.R.; Wu, Y.W. The Constituents of Lindera glauca. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2000, 47, 373–380.
- Feng, W.S.; Zhu, B.; Zheng, X.K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yang, L.G.; Li, Y.J. Chemical Constituents of Selaginella stautoniana. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 9, 108–111.
- Buchanan, M.S.; Carroll, A.R.; Edser, A.; Parisot, J.; Addepalli, R.; Quinn, R.J. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors from the rainforest tree Polyscias murrayi. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 481–485.
- van Rensburg, C.J.; Erasmus, E.; Loots, D.T.; Oosthuizen, W.; Jerling, J.C.; Kruger, H.S.; Louw, R.; Brits, M.; van der Westhuizen, F.H. Rosa roxburghii supplementation in a controlled feeding study increases plasma antioxidant capacity and glutathione redox state. Eur. J. Nutr. 2005, 44, 452–457.
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Brenciani, A.; Mazzoni, L.; Gasparrini, M.; Gonzalez-Paramas, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Morroni, G.; Simoni, S.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; et al. Apis mellifera vs. Melipona beecheii Cuban polifloral honeys: A comparison based on their physicochemical parameters, chemical composition and biological properties. LWT 2018, 87, 272–279.
- Mansouri, A.; Embarek, G.; Kokkalou, E.; Kefalas, P. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of the Algerian ripe date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 411–420.
- Owen, R.W.; Haubner, R.; Mier, W.; Giacosa, A.; Hull, W.E.; Spiegelhalder, B.; Bartsch, H. Isolation, structure elucidation and antioxidant potential of the major phenolic and flavonoid compounds in brined olive drupes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 703–717.
- Bianco, A.; Uccella, N. Biophenolic components of olives. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 475–485.
- Senizza, B.; Ganugi, P.; Trevisan, M.; Lucini, L. Combining untargeted profiling of phenolics and sterols, supervised multivariate class modelling and artificial neural networks for the origin and authenticity of extra-virgin olive oil: A case study on Taggiasca Ligure. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134543.
- Boselli, E.; Giomo, A.; Minardi, M.; Frega, N.G. Characterization of phenolics in Lacrima di Morro d’Alba wine and role on its sensory attributes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 709–720.
- Madrera, R.R.; Lobo, A.P.; Valles, B.S. Phenolic Profile of Asturian (Spain) Natural Cider. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2006, 54, 120–124.
- Suarez, B.; Palacios, N.; Fraga, N.; Rodriguez, R. Liquid chromatographic method for quantifying polyphenols in ciders by direct injection. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1066, 105–110.
- Białecka-Florjańczyk, E.; Fabiszewska, A.; Zieniuk, B. Phenolic Acids Derivatives-Biotechnological Methods of Synthesis and Bioactivity. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 1098–1113.
- KEGG Phenylalanine, Tyrosine and Tryptophan Biosynthesis—Reference Pathway. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map00400 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- KEGG Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis—Reference Pathway. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map00940 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- KEGG Tyrosine Metabolism—Reference Pathway. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/map00350 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Soares, A.R.; Marchiosi, R.; de Cassia Siqueira-Soares, R.; de Lima, R.B.; dos Santos, W.D.; Ferrarese-Filho, O. The role of L-DOPA in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e28275.
- Ibdah, M.; Berim, A.; Martens, S.; Valderrama, A.L.H.; Palmieri, L.; Lewinsohn, E.; Gang, D.R. Identification and cloning of an NADPH-dependent hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA double bond reductase involved in dihydrochalcone formation in Malus×domestica Borkh. Phytochemistry 2014, 107, 24–31.
- Redeuil, K.; Smarrito-Menozzi, C.; Guy, P.; Rezzi, S.; Dionisi, F.; Williamson, G.; Nagy, K.; Renouf, M. Identification of novel circulating coffee metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4678–4688.
- Lang, R.; Dieminger, N.; Beusch, A.; Lee, Y.M.; Dunkel, A.; Suess, B.; Skurk, T.; Wahl, A.; Hauner, H.; Hofmann, T. Bioappearance and pharmacokinetics of bioactives upon coffee consumption. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 8487–8503.
- Scherbl, D.; Renouf, M.; Marmet, C.; Poquet, L.; Cristiani, I.; Dahbane, S.; Emady-Azar, S.; Sauser, J.; Galan, J.; Dionisi, F.; et al. Breakfast consumption induces retarded release of chlorogenic acid metabolites in humans. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 791–806.
- de Oliveira, D.M.; Sampaio, G.R.; Pinto, C.B.; Catharino, R.R.; Markowicz Bastos, D.H. Bioavailability of chlorogenic acids in rats after acute ingestion of maté tea (Ilex paraguariensis) or 5-caffeoylquinic acid. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2541–2556.
- Urpi-Sarda, M.; Monagas, M.; Khan, N.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Sacanella, E.; Castell, M.; Permanyer, J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Epicatechin, procyanidins, and phenolic microbial metabolites after cocoa intake in humans and rats. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1545–1556.
- Wittemer, S.M.; Ploch, M.; Windeck, T.; Muller, S.C.; Drewelow, B.; Derendorf, H.; Veit, M. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids after oral administration of Artichoke leaf extracts in humans. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 28–38.
- Azzini, E.; Bugianesi, R.; Romano, F.; Di Venere, D.; Miccadei, S.; Durazzo, A.; Foddai, M.S.; Catasta, G.; Linsalata, V.; Maiani, G. Absorption and metabolism of bioactive molecules after oral consumption of cooked edible heads of Cynara scolymus L. (cultivar Violetto di Provenza) in human subjects: A pilot study. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 963–969.
- Ancillotti, C.; Ulaszewska, M.; Mattivi, F.; Del Bubba, M. Untargeted Metabolomics Analytical Strategy Based on Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Linear Ion Trap Quadrupole/Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for Discovering New Polyphenol Metabolites in Human Biofluids after Acute Ingestion of Vaccinium myrtillus Berry Supplement. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 381–402.
- Bøhn, S.K.; Myhrstad, M.C.W.; Thoresen, M.; Erlund, I.; Vasstrand, A.K.; Marciuch, A.; Carlsen, M.H.; Bastani, N.E.; Engedal, K.; Flekkøy, K.M.; et al. Bilberry/red grape juice decreases plasma biomarkers of inflammation and tissue damage in aged men with subjective memory impairment—A randomized clinical trial. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 75.
- Bazzocco, S.; Mattila, I.; Guyot, S.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Aura, A.M. Factors affecting the conversion of apple polyphenols to phenolic acids and fruit matrix to short-chain fatty acids by human faecal microbiota In Vitro. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 442–452.
- Kahle, K.; Kempf, M.; Schreier, P.; Scheppach, W.; Schrenk, D.; Kautenburger, T.; Hecker, D.; Huemmer, W.; Ackermann, M.; Richling, E. Intestinal transit and systemic metabolism of apple polyphenols. Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 50, 507–522.
- Poquet, L.; Clifford, M.N.; Williamson, G. Investigation of the metabolic fate of dihydrocaffeic acid. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1218–1229.
- Oh, N.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.; Joung, J.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y. Improved functionality of fermented milk is mediated by the synbiotic interaction between Cudrania tricuspidata leaf extract and Lactobacillus gasseri strains. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5919–5932.
More
