Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Khushboo-E Fatima and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is seen as an emerging technology that can accelerate business processes through the automation of repetitive, strenuous, and rule-based tasks in supply chain systems. RPA is often referred to as software robotics or “bots”, and follows instructions defined by the end-users to automate repetitive processes or activities in business organisations.
- robotic process automation
- beef supply chains
- sustainability
- simulation
1. Introduction
The supply chain system plays a vital role in the effective functioning of business processes. The term “supply chain”, defined as a network of information, goods, resources, and business activities, emerged and developed from logistics, marketing, production, and distribution [1]. The coordination of materials, resources, information, and financial flows is an important aspect of a supply chain system. In a broader sense, a supply chain is also known as an inter-organisational flow of services with important units to consider, such as production, marketing, procurement, and finances. Businesses aim to govern and monitor supply chain processes with enhanced efficiency and accuracy in order to perform effectively. Gayialis et al. [2] highlighted that high production levels, lower operational costs, fast-paced production systems, and enhanced sustainability strategies are currently some of the main objectives of organisations. As businesses have become more competitive than before, as a result of technological advancements and innovative implementations and adoptions, it is crucial to manage supply chain processes with more attentiveness and diligence [2].
According to Popkova et al. [3], technological innovations have improved process delivery and enabled organisations to meet sustainability criteria by streamlining business operations and increasing profit margins. Emerging technological solutions such as robotic process automation (RPA) have greatly improved and enhanced food processing and manufacturing and have helped supply chains achieve sustainability and a competitive advantage, as well as create value in business processes. Sustainable food production, which is safer, healthier, and more secure for human consumption, is currently one of the prominent and growing concerns for food supply chains. RPA helps food manufacturers to improve and speed up their business procedures to ensure the production of high-quality, healthy, and safe food with reduced operational and functional costs. In food production, it is extremely important to consider the economic growth and financial health of businesses as organisations are expected to cater to wider masses and a growing food demand, which is quite challenging, especially in a competitive business world [4].
RPA is seen as an emerging technology that can accelerate business processes through the automation of repetitive, strenuous, and rule-based tasks in supply chain systems. RPA is often referred to as software robotics or “bots”, and follows instructions defined by the end-users to automate repetitive processes or activities in business organisations. RPA technology uses software bots in place of the human workforce to perform tedious tasks. The implementation of RPA technology not only facilities business processes by making them less complex, but also reduces human error to make supply chains more well synchronized, integrated, and systematic. Digital transformation, such as RPA, has attracted corporate attention as a result of several supply chain complexities, uncertainties, risks, and barriers due to increased globalization and wide-spread supply chains. Technological advancements such as RPA have gained popularity as they accelerate supply chain processes, and reduce the time, cost, and energy required to enhance supply chain operations. RPA’s promising benefits include value addition and a competitive advantage for supply chains, thus creating sustainability. Achieving sustainable value is the main concern of supply chains; RPA automates tasks and makes businesses less reliant on the human workforce, thus enhancing production levels, improving supply chain processes, and reducing operational costs, which create sustainability in supply chain processes [5][6][7][5,6,7].
The beef supply chain is highly fragmented, which makes its management system complex and challenging. Sustainable beef manufacturing and processing has attracted attention globally and is a cause of concern for beef manufacturers. The beef sector involves various stages that include complex procedures in beef production and involve system uncertainties and disruptions. The beef manufacturing supply chains constantly face supply chain risks and challenges related to high operational costs, beef productivity, quality, safety, and shelf life. The beef sector, a representative of the food industry, has social, environmental, and economic challenges. Growing awareness towards beef quality and safety raises concerns for beef manufacturers, who constantly strive to achieve sustainable value and produce nutritious, healthy beef at low operational costs. Process automation within beef supply chains facilitates work-flow management systems, eases complex and tedious tasks through process excellence, and reduces human error to speed up processes. Moreover, automation in the beef sector serves as a process facilitator that enhances supply chain performance and boosts task delivery, resulting in a higher output to satisfy the growing demand for beef. Sustainability-oriented innovations and solutions such as RPA could reduce supply chain risks through process acceleration and support the beef sector to reduce operational costs and meet sustainability goals. RPA further enhances employee-level efficiency as bots are able to work 24/7, unlike humans, on processing lines to manufacture high-quality, sustainable beef at a low cost. Technological breakthroughs such as RPA have the potential to enhance supply chain operations and satisfy customers by maintaining quality standards. Automation acts as a sustainability driver in beef supply chains to add value in business processes. Innovative approaches such as automation within the beef sector improve production levels, increase supply chain resilience, and make businesses more competitive [8][9][10][8,9,10].
Sustainability in beef supply chains is a constant concern and challenge for the beef industry [11]. Beef supply chains are complex and large in order to cater to their dynamic structure and business system. Beef supply chains struggle to produce high-quality, nutritious beef due to the high financial costs and overhead expenses of production systems that companies install and implement for efficient beef production. The beef sector strives to achieve sustainable beef production to add value to their supply chains and satisfy the high customer demand due to growing consumer needs and requirements. Beef supply chains are fragmented and very complex across the world as well as in the UK with respect to their functioning, monitoring, and management. High production costs including labour work, machinery usage, technological adoptions, and organizational set-up are some of the financial aspects that are concerning for beef manufacturers. Manufacturing supply chains are seeking sustainable procedures and methods to ensure reduced financial burden and lower operational costs while aiming for higher production levels [12]. This promising RPA technology allows beef supply chains to achieve sustainable production systems.
This research aims to investigate the financials aspects that are important to consider in the RPA adoption process. The study further analyses the financial barriers or risks that may potentially exist in the adoption process of RPA within the beef supply chain system. This researchtudy adopts the process model developed in previous research to conduct a ‘what-if’ scenario analysis based on financial parameters for the identification of financial barriers or risks in the adoption process of RPA that could potentially impact supply chain production levels, costs, and efficiency. Beef supply chain characteristics and features are critically analysed to understand the implementation process of RPA in the beef sector in an enhanced manner, considering the financial aspects. By simulating the business process model and considering the cost-related parameters, this researchstudy allows for the assessment and evaluation of the socio-economic benefits of RPA adoption, as well as how RPA can be adopted in a successful manner by eliminating financial barriers to create sustainability within beef supply chains.
 The beef manufacturers constantly face sustainability challenges, as the supply chain system is typically complex and difficult to manage. The beef supply chain is sensitive to manage as it involves environment, financial, and food-related concerns and challenges, which increase its complexity [16][28]. Considerations regarding beef shelf life, quality, human consumption, and financial aspects makes the beef supply chain challenging. Because of the constant social and financial pressure faced by beef manufacturers, they are constantly seeking sustainable strategies that could be implemented to address these concerns. According to Cox et al. [17][29], the supply and demand of beef is highly uncertain due to the nature and distinctive features of the beef supply chain. Beef manufacturers are seeking sustainable approaches and autonomous production systems in order to meet the growing demand for beef, achieve customer satisfaction, and maintain a high level of production. Some central problems related to beef production are quality concerns, shelf life, environmental challenges, and high costs. Globalization and technological advancements have the potential to enhance production systems, cut-down labour costs, and increase operational and employee-level efficiency to achieve sustainability and a competitive advantage [18][30].
The demand for beef is growing as a result of the increasing population, which has introduced challenges within the beef sector. The dynamics of the beef supply chain are unique and complex due to the presence of various actors in the stages of the supply chain. These actors involve breeders, butchers, slaughterhouses, producers, manufacturers, retailers, end consumers, etc., which increase its managerial and processing complexities in task delivery. The beef industry is competitive and faces issues such as cultural and managerial challenges, economic difficulties, supply chain disruptions, and unprecedented events, which make the processes in the supply chain complicated and risky to handle. To address these issues and prevent any discrepancies that could cause supply chain disruptions, it is crucial to assess the risks in advance and to develop an efficient management system by adopting systematic, innovative tools and techniques [19][31].
The beef supply chain is also considered to be risky as it consists of its complex production and manufacturing stages involving strenuous processes that could be harmful to the environment and employees working on the processing lines. Widespread stages and procedures in the supply chain result in coordination, synchronization, and managerial issues. The beef industry faces unprecedented events that raise concerns about its manual-centric processes; the adoption of innovative and sustainable strategies that could create supply chain resilience is thus encouraged. Resilience in beef supply chains is important as the consumption of beef is directly related to human health concerns that impact both society and the environment. Sustainable solutions and innovative procedures in the supply chain could help these procedures, thus making the supply chain resilient to any risks or disruptive events such as COVID-19. Other than disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, other risks such as animal diseases and agricultural disturbances also impact the production and manufacture of beef. The beef industry is focussed on addressing labour shortages, supply and demand uncertainties, high operational costs, and environmental issues; to achieve resilience in these issues, sustainable and long-term strategies should be adopted to avoid any losses or failures in the respective supply chains. As a result of these prevailing sustainability challenges, the beef sector should endeavour to adopt efficient techniques and systems to deal with environmental and social concerns, such as labour scarcity and the transmission of diseases, in order to create financial and operational resilience and enhance management practices [20][21][32,33].
The beef manufacturers constantly face sustainability challenges, as the supply chain system is typically complex and difficult to manage. The beef supply chain is sensitive to manage as it involves environment, financial, and food-related concerns and challenges, which increase its complexity [16][28]. Considerations regarding beef shelf life, quality, human consumption, and financial aspects makes the beef supply chain challenging. Because of the constant social and financial pressure faced by beef manufacturers, they are constantly seeking sustainable strategies that could be implemented to address these concerns. According to Cox et al. [17][29], the supply and demand of beef is highly uncertain due to the nature and distinctive features of the beef supply chain. Beef manufacturers are seeking sustainable approaches and autonomous production systems in order to meet the growing demand for beef, achieve customer satisfaction, and maintain a high level of production. Some central problems related to beef production are quality concerns, shelf life, environmental challenges, and high costs. Globalization and technological advancements have the potential to enhance production systems, cut-down labour costs, and increase operational and employee-level efficiency to achieve sustainability and a competitive advantage [18][30].
The demand for beef is growing as a result of the increasing population, which has introduced challenges within the beef sector. The dynamics of the beef supply chain are unique and complex due to the presence of various actors in the stages of the supply chain. These actors involve breeders, butchers, slaughterhouses, producers, manufacturers, retailers, end consumers, etc., which increase its managerial and processing complexities in task delivery. The beef industry is competitive and faces issues such as cultural and managerial challenges, economic difficulties, supply chain disruptions, and unprecedented events, which make the processes in the supply chain complicated and risky to handle. To address these issues and prevent any discrepancies that could cause supply chain disruptions, it is crucial to assess the risks in advance and to develop an efficient management system by adopting systematic, innovative tools and techniques [19][31].
The beef supply chain is also considered to be risky as it consists of its complex production and manufacturing stages involving strenuous processes that could be harmful to the environment and employees working on the processing lines. Widespread stages and procedures in the supply chain result in coordination, synchronization, and managerial issues. The beef industry faces unprecedented events that raise concerns about its manual-centric processes; the adoption of innovative and sustainable strategies that could create supply chain resilience is thus encouraged. Resilience in beef supply chains is important as the consumption of beef is directly related to human health concerns that impact both society and the environment. Sustainable solutions and innovative procedures in the supply chain could help these procedures, thus making the supply chain resilient to any risks or disruptive events such as COVID-19. Other than disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, other risks such as animal diseases and agricultural disturbances also impact the production and manufacture of beef. The beef industry is focussed on addressing labour shortages, supply and demand uncertainties, high operational costs, and environmental issues; to achieve resilience in these issues, sustainable and long-term strategies should be adopted to avoid any losses or failures in the respective supply chains. As a result of these prevailing sustainability challenges, the beef sector should endeavour to adopt efficient techniques and systems to deal with environmental and social concerns, such as labour scarcity and the transmission of diseases, in order to create financial and operational resilience and enhance management practices [20][21][32,33].
Sustainability has gained a lot of attention and has become a primary goal of beef supply chains to add value and achieve corporate social responsibility [35][47]. Sustainable beef processing and manufacturing brings considerable benefits to organisations as they could achieve long-term viability, profit, and cost reduction. Sustainable business strategies and procedures such as the use of technology could prevent risks and hazards and achieve a positive social, economic, and environmental impact. The use of RPA tools can maximize profits and enhance task efficiency in processes such as beef cutting, deboning, and packaging. The implementation of RPA can also reduce environmental or social hazards such as accidents on the processing line or the transmission of diseases by replacing humans with software bots to complete tasks. The bots are also able to work 24/7 and do not require any breaks, which increases beef production levels; this also ensures the quality of beef produced as the chances of meat contamination are reduced. RPA not only provides technological support to beef supply chains, but also enables decision-makers and managers to achieve sustainability criteria in the fast-paced market. RPA is a valuable addition to beef supply chains as it assists and improves system processes and allows firms to achieve sustainable value and achieve a competitive advantage [36][48].
Modern technological advancements in simulation and process automation have been widely adapted for use within businesses and industry. Incorporating sustainable technologies in organisations has gained value as automation can relieve employees who perform strenuous, repetitive tasks, as well as provide sustainable solutions to complex and disruptive business environments. RPA is a leading and widely adopted technology that has the potential to improve business process management through task automation and it is considered a sustainable practice to enhance supply chain operations. RPA technology facilitates, improves, and optimizes business processes considering the addition of value and sustainability criteria. For instance, RPA acts as a helpful sustainability tool to enhance workforce efficiency by replacing tough and repetitive tasks with automation, allowing humans to use their potential and expertise in judgement-based tasks or managerial areas. Moreover, RPA also simulates different process systems and analyses the data to develop a more cost-effective and sustainable method of organising. It is crucial for business users to decide which processes would be most suitable for automation in order for successful adoption of the process. Digital transformation, such as RPA, continuously improves supply chain operations and process efficiency, and helps organisations meet their sustainability agendas and goals [37][49].
RPA serves as a process efficiency tool to create sustainable value in beef supply chains. Automation solutions such as RPA accelerate production processes by speeding up the processing line and reducing errors by replacing the human workforce with software bots. New sustainability demands are linked to beef quality, safety, and cost and are associated with supply chain processes in the beef industry. The integration and adoption of RPA assists by adding value to supply chain processes and producing high quality beef that is sae for human consumption. RPA also allows for an eco-friendly beef production environment as tasks are automated, resulting is less human error; reduced chances of accidents on the processing line; lower transmission of diseases; and less time, cost, and energy consumed when conducting strenuous tasks. It also improves supply chain synchronization and coordination through the removal or reduction of human error and through efficient process delivery at different stages of the beef supply chain [38][50]. RPA is now perceived as an asset as it eases employee-level pressure by improving processes, thus allowing the human workforce to concentrate on meaningful and skilled-based activities. RPA provides business organizations with various advantages for achieving effectiveness and competitiveness. RPA increases productivity levels, improves the quality of production, and ensures enhanced consumer satisfaction. The value provided by RPA technology improves accuracy levels, increases profitability margins, and boosts the financial conditions of the business organization [39][51].
2. The Dynamics and Challenges of the Beef Supply Chain
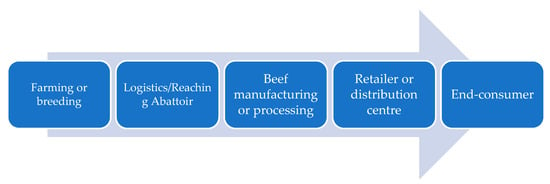
Singh et al. [13][25] described beef supply chains as a challenging business system involving complex processes and stages. It is imperative to consider the dynamics and features of the beef supply chain system in order to understand its unique characteristics and procedures that are different from other food supply chains. The beef supply chain has various stages and phases that demand high vigilance, monitoring, and handling due to the complexity of the execution process and beef production. In previous years, the beef sector has mainly been manual-centric because of procedures requiring human handling and intervention. However, as a result of the growing demand for beef, technological advancements, fast-paced competitive markets, and unprecedented events such as the pandemic, the industry has started to consider adopting innovative technology. Technological innovations such as RPA have simplified beef processing tasks and relieved employees from performing strenuous and repetitive tasks. The beef industry involves complicated procedures as the animal must be disassembled into different products for human consumption or sale in the market. The products are marketed to different industries, such as retailers, export, and food service. The beef industry was also impacted by COVID-19 as the business processes were mostly manual-centric in the past. The beef sector was impacted economically as a result of the pandemic, and producers, manufacturers, and consumers were significantly impacted [14][26]. The beef supply chain involves different stages in which the carcass is processed for the produced and manufactured into beef products that ultimately reach the consumer for the purpose of consumption. The first stage of the beef supply chain is the farming or breeding stage, after which the cattle progress to the next stage of logistics or reaching the abattoir, as depicted in Figure 1. The third stage is the beef manufacturing or processing stage, where the carcass is processed further for boning, fat trimming, cutting, etc. Then, the processed beef reaches the retailer or distribution centre, after which it reaches its last stage of the supply chain—the customer. The Figure 1 depicts all the significant beef supply chain stages that are crucial to highlight for firmer understanding.
3. RPA Technology—An Essential Sustainability Tool in the Beef Sector
The beef industry has been a late adopter of technology due to the unique structure of the supply chain system and its individual characteristics and features; hence, most of its procedures are manual-centric. Producing nutritious beef is challenging for manufacturers as a result of variables in the weight, height, and colour of the carcass; intensive beef cutting procedures; maintaining standards of quality; and health concerns. RPA allows for process excellence by using software bots to perform rule-based, repetitive tasks that were manually conducted in the past. The adoption of RPA enhances the operational and financial efficiency of the beef supply chain and ensures that high-quality, healthy beef that is safe for human consumption can be manufactured. The promising benefits of RPA also include a high level of productivity and faster manufacturing lines, as well as being time saving, energy efficient, and cost effective; these are currently concerns of the beef industry and supply chains due to the increasing demand for beef. RPA provides autonomous solutions to complex systems and its implementation could reduce the costs and energy use of organisations, thus achieving maximized output levels and satisfying consumers [22][34]. Lynch et al. [23][35] shed lights on sustainability-focused innovation, which has been a topic of debate within the beef sector due to the complex management and attributes of its supply chains. Recently, the beef supply chain has faced many challenges related to human health, animal welfare, biodiversity, greenhouse gas emissions, quality, and shelf life. The beef industry seeks to implement sustainable approaches and solutions to cater to all of these problems and to gain sustainable beef production for human consumption. Achieving sustainability remains a multi-dimensional issue within the beef supply chain and it requires attention and focus. This is because the structure of the beef supply chain is broad and wide-spread, and its procedures are not fully automated due to their individual complexities. Therefore, the supply chain still requires human involvement and handling. The use of RPA in the beef sector will allow tasks to be automated, less complex, and improve beef quality and safety. RPA also enables organisations to enjoy long-term financial and social gains by reducing operational costs, minimizing beef wastage during processing, and preventing any accidents or environmental hazards. Innovative efforts such as RPA could bring socio-economic gains and help business owners gain a sustainable competitive advantage in beef production and processing. Sustainability-oriented innovations such as RPA will pave the way for green production, as automated tasks produce less waste along the processing line with lower chances of disease and viral transmissions. Developing sustainable beef production systems through by implementing and adopting technological innovations such as RPA enables the production of low-cost, high-quality beef with social, economic, and environmental benefits. Food safety and quality in beef has encouraged decision-makers to pursue and implement sustainable technological solutions in order to enhance the performance, maximize financial benefits by lowering the associated operational costs, and meet health and safety requirements [24][25][36,37]. Achieving sustainability has created awareness within business setups, encouraging the adoption of sustainable business approaches so that long-term advantages can be achieved. The awareness and recognition of sustainable supply chains incorporating modern technology such as RPA has attracted many businesses [26][38]. The different approaches and perspectives of sustainable supply chains are explained in Table 1.Table 1.
Definitions of sustainable supply chains.
| Definition of Sustainable Supply Chains | Reference |
|---|---|
| A sustainable supply chain is described as the management of business processes including social, environmental, and financial aspects. | [27][39] |
| The term sustainable supply chain is focussed on considering and implementing sustainable business ideas, innovations, and approaches for long-term benefits. | [28][40] |
| Sustainable supply chains employ and incorporate methods of green production and operations management to ensure social, environmental, and economic gains. | [29][41] |
| Sustainable supply chains strive to achieve adding value and competitive advantage by engaging in sustainable business activities. | [30][42] |
| A sustainable supply chain is a business system concentrating on competitive opportunity, public interests, and green production systems. | [31][43] |
| Sustainable supply chains possess an enhanced understanding of digitally enabled processes and innovative business approaches to minimize supply chain complexities and risks. | [32][44] |
| Sustainable supply chains concern the identification of potential barriers and implement technology to enhance operational and employee-level efficiency. | [33][45] |
| Sustainable supply chains aim towards process excellence, innovative solutions, and greater business efficiency while reducing any negative impacts on the environment and society. | [34][46] |
