Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Vinit K Chugh and Version 3 by Conner Chen.
Since its first report in 2006, magnetic particle spectroscopy (MPS)-based biosensors have flourished over the past decade. Currently, MPS is used for a wide range of applications, such as disease diagnosis, foodborne pathogen detection, etc.
- magnetic particle spectroscopy
- biosensor
- volumetric assay
- magnetic particle imaging
- magnetic nanoparticles
1. Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are regarded as highly promising materials with widespread applications in various fields, including magnetic separation, diagnostics, and therapeutics [1][2][3][4][5][2,7,19,20,21]. MNPs with proportional sizes to biomolecules have demonstrated outstanding properties, including a high reactivity, significant surface-to-volume ratio, and unique magnetic characteristics, compared to their primary bulk materials. In order to produce MNPs, magnetic materials such as pure metals (e.g., Co, Ni, Fe), alloys (e.g., FeCo, alnico, permalloy), and oxides (e.g., Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, CoFe2O4) with high saturation magnetizations are preferred. Although pure metals can produce higher saturation magnetizations, they are not suitable for biomedical applications due to their cytotoxicity or susceptibility to oxidation [1][2]. Iron oxides are currently the most commonly used MNPs due to their high chemical and colloidal stability, amazing biocompatibility, and affordability.
Over the last 30 years, there has been a fascinating era of MNPs synthesis with remarkable physical characteristics for biological and biomedical purposes, and several of these synthesis approaches have been commercially produced [1][3][6][7][8][2,19,22,23,24]. For example, various techniques, including ball milling, gas phase condensation (GPC), thermal decomposition, sol–gel and others, have successfully been used to prepare monodispersed magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) [9][10][11][12][25,26,27,28]. These synthesis methods offer different kinds of MNPs for a wide variety of applications. Iron oxide MNPs are very popular as they are inexpensive and extremely stable at ambient temperature. Meanwhile, MNPs made from Fe, Co, Ni, and their alloys are also of interest due to the raw materials’ high saturation magnetizations. In addition, high-magnetic-moment MNPs (a high magnetic moment per particle) with highly biocompatible, organic or non-organic shells (i.e., the core–shell structure) play a crucial role in the field of nanomedicine [1][11][2,27]. For imparting biological recognition and interaction skills, the surface functionalization of MNPs with biomolecules, polymers, and ligands is essential.
The magnetic properties of MNPs, such as magnetic anisotropy and saturation magnetization, are primarily dependent on their crystalline structures, sizes, and shapes. The magnetic moment (m) is the product of the magnetic core volume (Vm) and spontaneous saturation magnetization (Ms), which is the most significant property of MNPs for nanomedicine-oriented applications [1][13][2,29]. For having a higher magnetic signal (in applications such as magnetic biosensing, imaging, etc.) and a stronger magnetic force (in applications such as magnetic manipulation and drug/gene delivery), a higher magnetic moment per MNP is desired. It should be mentioned that the insufficiency of translational crystal symmetry in the surface layer of MNP will inevitably lead to the dissimilarity of the surface layer’s magnetic properties compared to the inner core. As an outcome, lower saturation magnetizations (Ms) and higher anisotropy constants are observed in MNPs in comparison to their corresponding bulk materials [13][14][15][29,30,31].
2. Superparamagnetism
Superparamagnetism is a type of unique magnetic property that emerges in small ferro- or ferrimagnetic nanoparticles. When the energy barrier Eb is comparable to or lower than the thermal fluctuation energy KbT under a finite temperature T, the magnetic moment in an MNP flips direction frequently during a measurement time window τm, resulting in a zero averaged net magnetization, namely the superparamagnetic state. At a specific measurement time and temperature, there is a critical size Dsp that determines the transition from a single-domain nanoparticle to a superparamagnetic nanoparticle, which varies for different magnetic materials and typically ranges from a few nanometers to several tens of nanometers [16][32]. Due to the fast flipping of their magnetic moments, superparamagnetic nanoparticles exhibit magnetic moments even in the absence of an external magnetic field. However, when subjected to an external field, their magnetic moments align along the field direction, producing detectable magnetic signals. The magnetic moment of superparamagnetic nanoparticles versus the applied magnetic field is typically a reversible S-shape. In the superparamagnetic state, an external magnetic field can magnetize the nanoparticles similarly to a paramagnet, but with a much larger magnetic susceptibility under small fields [1][17][2,33]. For most biomedical applications, the MNPs are generally superparamagnetic in order to avoid the aggregation and potential clotting for in vivo applications.
3. Higher Harmonics of MNPs Subjected to Sinusoidal Magnetic Fields
Due to the nonlinear magnetization response of MNPs subjected to external excitation magnetic field H(t), the induced magnetization responses, M(t), contain not only the ‘modulation field’ frequency f but also a series of higher odd harmonics occurring at 3f, 5f, 7f, and 9f, etc. (in a mono-frequency driving field scenario). Appropriate filtering can be used to extract these higher harmonics for analysis. In MPI, a magnetic gradient field that is equal to zero in the FFP (field free point) and increases toward the edges is applied on top of the ‘modulation field’ in order to suppress these harmonics for spatial encoding purposes. The magnetization response in the form of harmonics from the MNPs outside the FFP is fully saturated by this non-zero gradient field, and those harmonics are largely suppressed. In comparison to the odd harmonics generated by MNPs within the FFP, the amplitudes of these harmonics from outside the FFP are insignificant. Therefore, MNPs within the FFP are the only magnetic signal sources responsible for 3D tomographic imaging in MPI [18][19][47,48]. MPI emerges as a new 3D imaging technique for real-time in vivo scanning, and it is expected to reach the clinical stage soon [20][49]. Meanwhile, various MPS platforms, which originated from MPI, have been described for use in bioassays and have subsequently become a novel research focus in the field of magnetic bioassays [19][21][22][48,50,51]. Nikiet et al. [21][50] and Krause et al. [22][51] independently reported the first-generation MPS platforms. In 2006, a magnetic bioassay platform was developed that utilized a magnetic drive field with two frequency components (fH and fL) to drive MNPs into the saturation region. Subsequently, another version of the MPS platform for bioassay applications was introduced that only used a magnetic drive field with a single-frequency component f [23][24][9,42]. It should be noted that the modulation field in MPI and the magnetic drive field in MPS are both sinusoidal fields that are utilized to repeatedly saturate MNPs. However, in order to differentiate between these two techniques, the term “magnetic drive field” is used only in MPS. In MPS, the magnetic drive field is responsible for triggering the nonlinear magnetization responses of MNPs and higher harmonics that serve as indicators for bioassay applications. Additionally, since MPS does not require tomographic scanning, the gradient field can be removed.4. Volumetric and Surface MPS Bioassays Mechanisms
Currently, two types of MPS bioassay strategies are investigated frequently: surface- and volumetric-based methods. The innate main differences between these two methods are that the volumetric-based bioassays monitor the degree of clustering (or, the rotational freedom) of MNPs in the presence of target analytes whereas the surface-based bioassay methods monitor the number of MNPs captured onto a nonmagnetic reaction substrate in the presence of target analytes. In the volumetric-based MPS bioassay methods, MNPs are functionalized with capture probes that can specifically bind to target analytes (for example, via antibody–antigen recognition) in liquid. As shown in Figure 14A, MNPs are surface-functionalized with polyclonal detection antibodies. In the presence of target antigens, these polyclonal antibodies will bind to different epitopes from each protein molecule, thus causing the cross-linking of MNPs. As a result, the hydrodynamic sizes of MNPs increase, as well as the Brownian relaxation time. Thus, lower harmonic amplitudes and a larger phase lag are observed as schematically drawn in Figure 14(A3) [19][25][26][48,62,63]. In another example of the volumetric-based method as shown in Figure 14(A2), non-magnetic beads are introduced as the reaction surface to further reduce the rotational freedom of the MNPs. As a result of these binding and clustering events, the MPS spectrum in Figure 14(A3) becomes weaker and weaker as Brownian relaxation is hindered. The volumetric-based MPS bioassay method is a homogeneous bioassay platform that spots the target analytes straight from the liquid sample without wash steps, making it suitable for future point-of-care (POC) applications. Currently, the volumetric-based MPS bioassays demonstrate a high bioassay sensitivity and specificity, as well as the ability to multiplex different analytes in a single sample [27][28][29][64,65,66].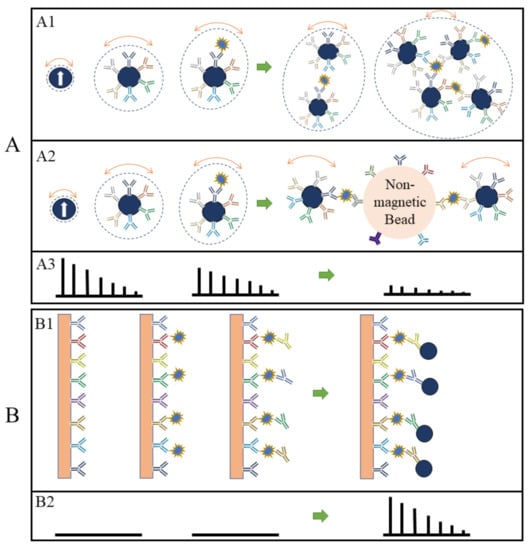
Figure 14. (A, B) depict the volumetric- and surface-based MPS bioassay mechanisms, respectively. (A1,A2,B1) schematically show the different bioassay steps. (A3,B2) show the corresponding MPS spectra observed at each bioassay stage.
