Front Cover: Monomer feed rate regulates the chemical structure of smart plasma copolymer coating and its surface wettability in various pH environment. The combined effect of surface chemical compositions and surface roughness causes tunable wettability from superhydrophobicity to superhydrophilicity of smart plasma copolymer coatings. Further on, the presence of the carboxylic acid functional group in plasma copolymer coatings made this surface wettability switchable for different pH environment.
Further details can be found in the article by I. Muzammil et al. from the Dalian University of Technology.
- surface wettability
- plasma copolymer coatings
- carboxylic acid
- superhydrophilicity
- superhydrophobicity
- tunable wettability
- surface roughness
- SUrface Science
- surface chemistry
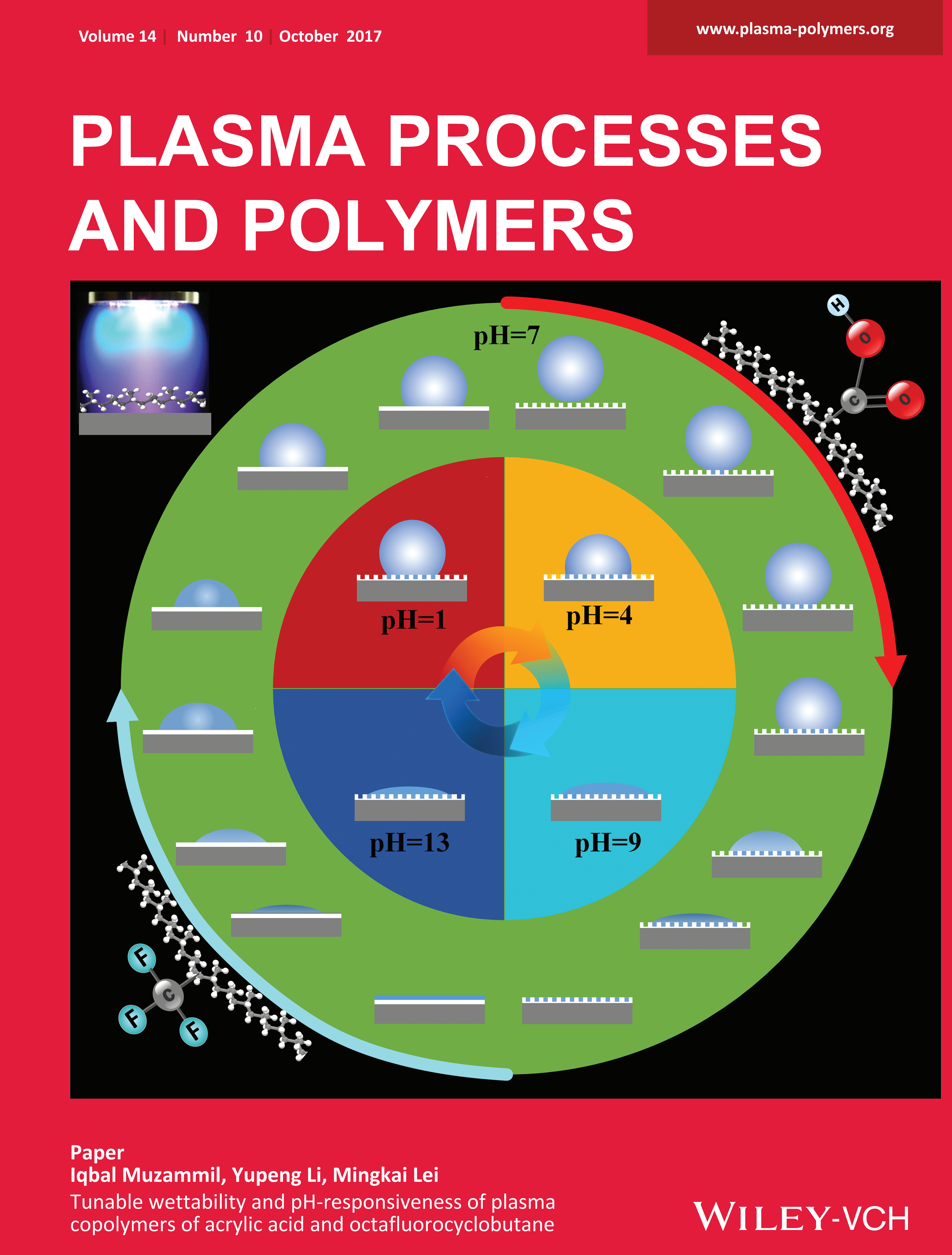
Monomer feed rate regulates the chemical structure of smart plasma copolymer coating and its surface wettability in various pH environment. The combined effect of surface chemical compositions and surface roughness causes tunable wettability from superhydrophobicity to superhydrophilicity of smart plasma copolymer coatings. Further on, the presence of the carboxylic acid functional group in plasma copolymer coatings made this surface wettability switchable for different pH environment.
Further details can be found in the article by I. Muzammil et al. on 1700053. [1][2]
References
- Muzammil Iqbal; Yupeng Li; Mingkai Lei; Cover Picture: Plasma Process. Polym. 10∕2017. Plasma Processes and Polymers 2017, 14, 1770019, 10.1002/ppap.201770019.
- Muzammil Iqbal; Yupeng Li; Mingkai Lei; Tunable wettability and pH-responsiveness of plasma copolymers of acrylic acid and octafluorocyclobutane. Plasma Processes and Polymers 2017, 14, 1700053, 10.1002/ppap.201700053.
 Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia



